Anesth Pain Med.
2016 Jul;11(3):236-248. 10.17085/apm.2016.11.3.236.
Mechanisms of postoperative pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesia, University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa, USA. sinyoung-kang@uiowa.edu
- KMID: 2344925
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.3.236
Abstract
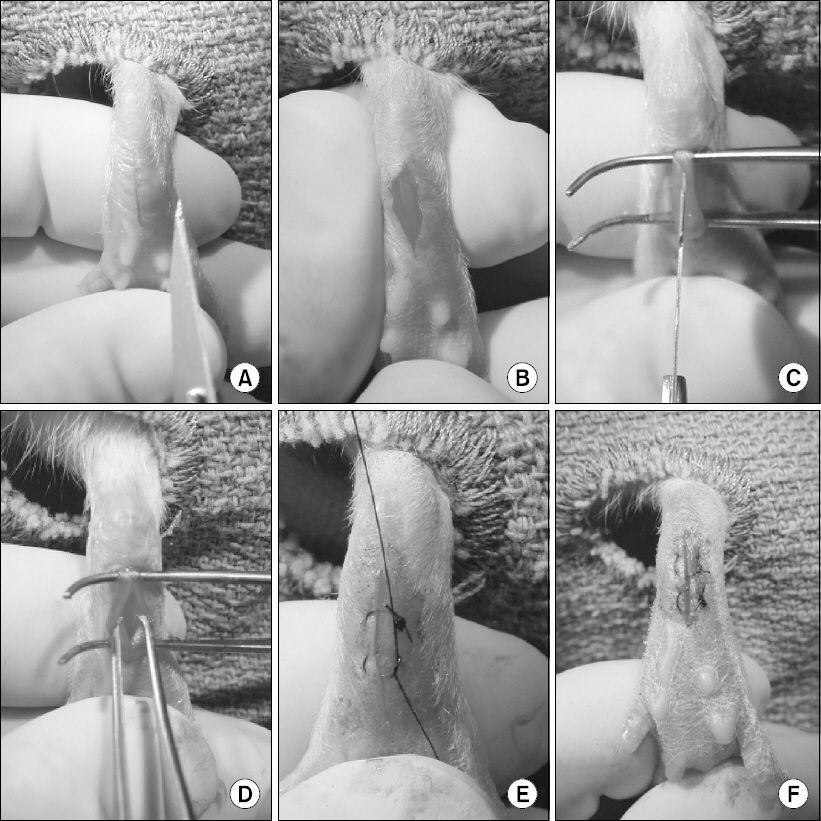
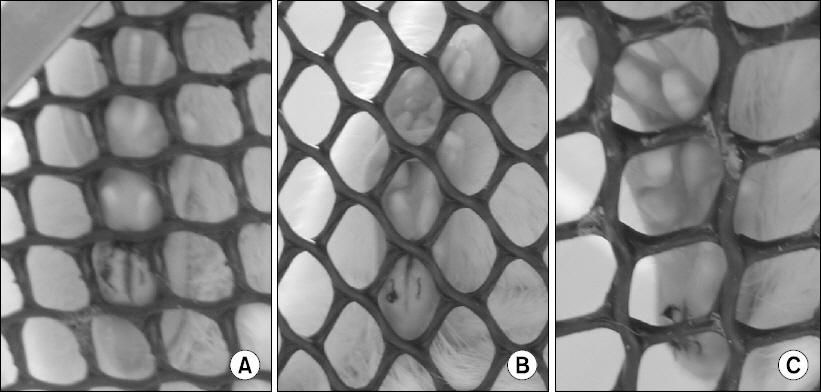
- Good pain control after surgery is important to facilitate overall recovery, improve patient satisfaction, decrease morbidity, and reduce health care cost. However, despite heightened awareness and development of new guidelines in recent decades, we have failed to make major improvements in postoperative pain control. Currently available analgesic therapies have limited efficacy, and pain after surgery continues to be a significant clinical problem. Our goal is to develop more effective and safer clinical strategies that will eliminate or greatly reduce postoperative pain, and a better understanding of the mechanisms of pain induced by surgery would be essential to achieve this goal. Evidence suggests that the pathophysiological mechanisms and optimal treatment of postoperative pain are different from many other painful conditions. Recognizing the necessity and importance of relevant pre-clinical models, we have developed and characterized rodent incision models that have close similarities to postoperative pain in patients. Previous studies have demonstrated the clinical relevance and translatability of these pre-clinical models of postoperative pain. In this review, we describe the rodent incision pain models, and summarized our current understanding of the mechanisms of postoperative pain, highlighting key findings from our previous studies using these models.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of sec-O-glucosylhamaudol on mechanical allodynia in a rat model of postoperative pain
Gi-Ho Koh, Hyun Song, Sang Hun Kim, Myung Ha Yoon, Kyung Joon Lim, Seon-Hee Oh, Ki Tae Jung
Korean J Pain. 2019;32(2):87-96. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2019.32.2.87.
Reference
-
1. Gan TJ, Habib AS, Miller TE, White W, Apfelbaum JL. Incidence, patient satisfaction, and perceptions of post-surgical pain: results from a US national survey. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014; 30:149–60. DOI: 10.1185/03007995.2013.860019. PMID: 24237004.
Article2. Gerbershagen HJ, Aduckathil S, van Wijck AJ, Peelen LM, Kalkman CJ, Meissner W. Pain intensity on the first day after surgery: a prospective cohort study comparing 179 surgical procedures. Anesthesiology. 2013; 118:934–44. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31828866b3. PMID: 23392233.3. Sommer M, de Rijke JM, van Kleef M, Kessels AG, Peters ML, Geurts JW, et al. The prevalence of postoperative pain in a sample of 1490 surgical inpatients. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2008; 25:267–74. DOI: 10.1017/S0265021507003031. PMID: 18053314.
Article4. Chou R, Gordon DB, de Leon-Casasola OA, Rosenberg JM, Bickler S, Brennan T, et al. Management of Postoperative Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American Pain Society, the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, and the American Society of Anesthesiologists’ Committee on Regional Anesthesia, Executive Committee, and Administrative Council. J Pain. 2016; 17:131–57. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2015.12.008. PMID: 26827847.
Article5. American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Acute Pain Management. Practice guidelines for acute pain management in the perioperative setting: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Acute Pain Management. Anesthesiology. 2012; 116:248–73. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31823c1030. PMID: 22227789.6. Banik RK, Woo YC, Park SS, Brennan TJ. Strain and sex influence on pain sensitivity after plantar incision in the mouse. Anesthesiology. 2006; 105:1246–53. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200612000-00025. PMID: 17122588.
Article7. Pogatzki EM, Niemeier JS, Brennan TJ. Persistent secondary hyperalgesia after gastrocnemius incision in the rat. Eur J Pain. 2002; 6:295–305. DOI: 10.1053/eujp.2002.0339. PMID: 12161095.
Article8. Brennan TJ, Vandermeulen EP, Gebhart GF. Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain. Pain. 1996; 64:493–501. DOI: 10.1016/0304-3959(95)01441-1.
Article9. Pogatzki EM, Raja SN. A mouse model of incisional pain. Anesthesiology. 2003; 99:1023–7. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200310000-00041.
Article10. Zahn PK, Gysbers D, Brennan TJ. Effect of systemic and intrathecal morphine in a rat model of postoperative pain. Anesthesiology. 1997; 86:1066–77. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199705000-00010. PMID: 9158356.
Article11. Navratilova E, Xie JY, Okun A, Qu C, Eyde N, Ci S, et al. Pain relief produces negative reinforcement through activation of mesolimbic reward-valuation circuitry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109:20709–13. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1214605109. PMID: 23184995. PMCID: PMC3528534.
Article12. Dalm BD, Reddy CG, Howard MA, Kang S, Brennan TJ. Conditioned place preference and spontaneous dorsal horn neuron activity in chronic constriction injury model in rats. Pain. 2015; 156:2562–71. DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000365. PMID: 26584420.
Article13. Zahn PK, Umali E, Brennan TJ. Intrathecal non-NMDA excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists inhibit pain behaviors in a rat model of postoperative pain. Pain. 1998; 74:213–23. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3959(97)00181-4.
Article14. Spofford CM, Ashmawi H, Subieta A, Buevich F, Moses A, Baker M, et al. Ketoprofen produces modality-specific inhibition of pain behaviors in rats after plantar incision. Anesth Analg. 2009; 109:1992–9. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181bbd9a3. PMID: 19923531. PMCID: PMC2869594.
Article15. Zahn PK, Brennan TJ. Primary and secondary hyperalgesia in a rat model for human postoperative pain. Anesthesiology. 1999; 90:863–72. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199903000-00030.
Article16. Jang JH, Liang D, Kido K, Sun Y, Clark DJ, Brennan TJ. Increased local concentration of complement C5a contributes to incisional pain in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2011; 8:80. DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-80. PMID: 21736743. PMCID: PMC3141504.
Article17. Banik RK, Subieta AR, Wu C, Brennan TJ. Increased nerve growth factor after rat plantar incision contributes to guarding behavior and heat hyperalgesia. Pain. 2005; 117:68–76. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2005.05.017. PMID: 16061324.
Article18. Wu C, Boustany L, Liang H, Brennan TJ. Nerve growth factor expression after plantar incision in the rat. Anesthesiology. 2007; 107:128–35. DOI: 10.1097/01.anes.0000267512.08619.bd. PMID: 17585224.
Article19. Wu C, Erickson MA, Xu J, Wild KD, Brennan TJ. Expression profile of nerve growth factor after muscle incision in the rat. Anesthesiology. 2009; 110:140–9. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318190bc84. PMID: 19104181. PMCID: PMC2727137.
Article20. Spofford CM, Brennan TJ. Gene expression in skin, muscle, and dorsal root ganglion after plantar incision in the rat. Anesthesiology. 2012; 117:161–72. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31825a2a2b. PMID: 22617252. PMCID: PMC3389501.
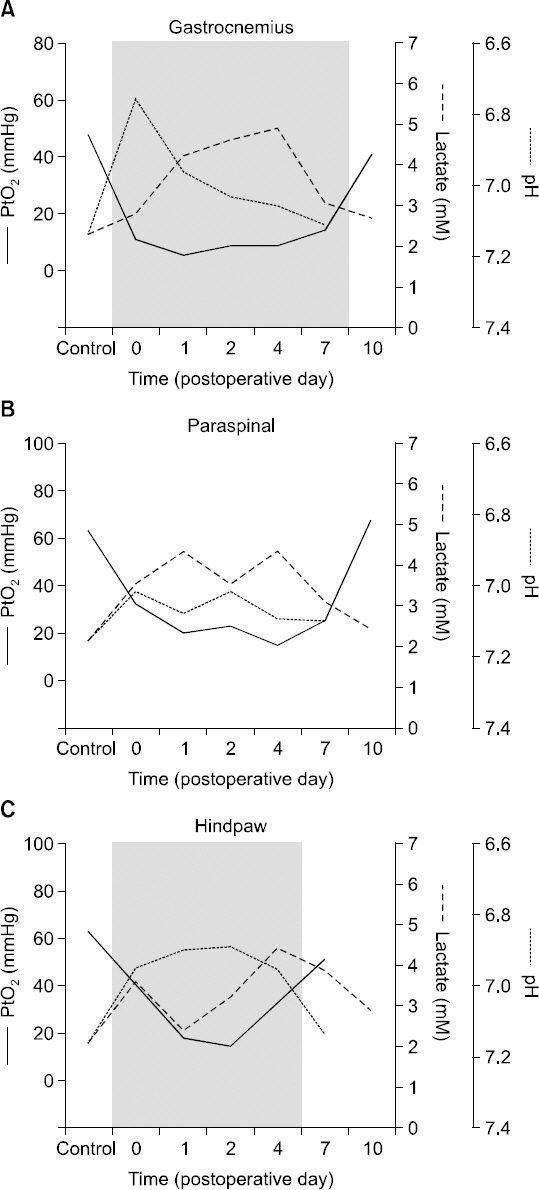
Article21. Kang S, Lee D, Theusch BE, Arpey CJ, Brennan TJ. Wound hypoxia in deep tissue after incision in rats. Wound Repair Regen. 2013; 21:730–9. DOI: 10.1111/wrr.12081. PMID: 23926943. PMCID: PMC3776009.
Article22. Kim TJ, Freml L, Park SS, Brennan TJ. Lactate concentrations in incisions indicate ischemic-like conditions may contribute to postoperative pain. J Pain. 2007; 8:59–66. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2006.06.003. PMID: 16949881.
Article23. Woo YC, Park SS, Subieta AR, Brennan TJ. Changes in tissue pH and temperature after incision indicate acidosis may contribute to postoperative pain. Anesthesiology. 2004; 101:468–75. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200408000-00029. PMID: 15277931.
Article24. Xu J, Richebe P, Brennan TJ. Separate groups of dorsal horn neurons transmit spontaneous activity and mechanosensitivity one day after plantar incision. Eur J Pain. 2009; 13:820–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2008.10.005. PMID: 19081275.
Article25. Pogatzki EM, Vandermeulen EP, Brennan TJ. Effect of plantar local anesthetic injection on dorsal horn neuron activity and pain behaviors caused by incision. Pain. 2002; 97:151–61. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3959(02)00014-3.
Article26. Xu J, Brennan TJ. Comparison of skin incision vs. skin plus deep tissue incision on ongoing pain and spontaneous activity in dorsal horn neurons. Pain. 2009; 144:329–39. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.05.019. PMID: 19527922. PMCID: PMC2759309.
Article27. Pogatzki EM, Gebhart GF, Brennan TJ. Characterization of Adelta- and C-fibers innervating the plantar rat hindpaw one day after an incision. J Neurophysiol. 2002; 87:721–31. PMID: 11826041.28. Xu J, Gu H, Brennan TJ. Increased sensitivity of group III and group IV afferents from incised muscle in vitro. Pain. 2010; 151:744–55. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.09.003. PMID: 20888124. PMCID: PMC2972383.
Article29. Banik RK, Brennan TJ. Spontaneous discharge and increased heat sensitivity of rat C-fiber nociceptors are present in vitro after plantar incision. Pain. 2004; 112:204–13. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2004.08.026. PMID: 15494202.
Article30. Kang S, Brennan TJ. Chemosensitivity and mechanosensitivity of nociceptors from incised rat hindpaw skin. Anesthesiology. 2009; 111:155–64. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181a16443. PMID: 19512876. PMCID: PMC2737702.
Article31. Hämäläinen MM, Gebhart GF, Brennan TJ. Acute effect of an incision on mechanosensitive afferents in the plantar rat hindpaw. J Neurophysiol. 2002; 87:712–20. PMID: 11826040.32. Xu J, Brennan TJ. Guarding pain and spontaneous activity of nociceptors after skin versus skin plus deep tissue incision. Anesthesiology. 2010; 112:153–64. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181c2952e. PMID: 19996955. PMCID: PMC2907154.
Article33. Banik RK, Brennan TJ. Sensitization of primary afferents to mechanical and heat stimuli after incision in a novel in vitro mouse glabrous skin-nerve preparation. Pain. 2008; 138:380–91. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2008.01.017. PMID: 18316159. PMCID: PMC3787122.34. Kang S, Wu C, Banik RK, Brennan TJ. Effect of capsaicin treatment on nociceptors in rat glabrous skin one day after plantar incision. Pain. 2010; 148:128–40. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.10.031. PMID: 19948377. PMCID: PMC2815239.
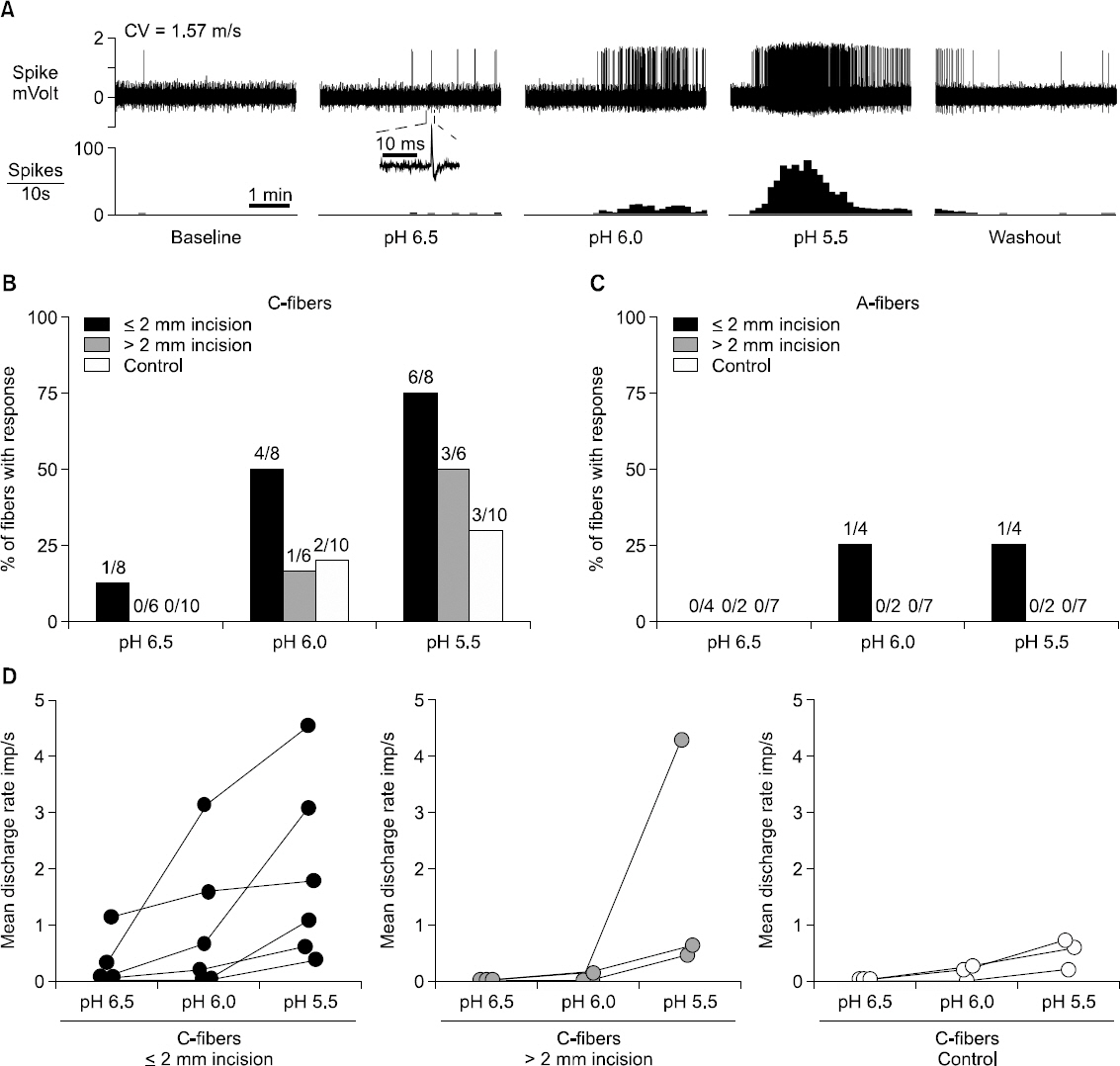
Article35. Kido K, Gautam M, Benson CJ, Gu H, Brennan TJ. Effect of deep tissue incision on pH responses of afferent fibers and dorsal root ganglia innervating muscle. Anesthesiology. 2013; 119:1186–97. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31829bd791. PMID: 23732174. PMCID: PMC4028173.
Article36. Immke DC, McCleskey EW. Lactate enhances the acid-sensing Na+channel on ischemia-sensing neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2001; 4:869–70. DOI: 10.1038/nn0901-869. PMID: 11528414.37. Naves LA, McCleskey EW. An acid-sensing ion channel that detects ischemic pain. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2005; 38:1561–9. DOI: 10.1590/S0100-879X2005001100001. PMID: 16258623.
Article38. Deval E, Noël J, Gasull X, Delaunay A, Alloui A, Friend V, et al. Acid-sensing ion channels in postoperative pain. J Neurosci. 2011; 31:6059–66. DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5266-10.2011. PMID: 21508231.
Article39. Zahn PK, Subieta A, Park SS, Brennan TJ. Effect of blockade of nerve growth factor and tumor necrosis factor on pain behaviors after plantar incision. J Pain. 2004; 5:157–63. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2004.02.538. PMID: 15106128.
Article40. Wolf G, Livshits D, Beilin B, Yirmiya R, Shavit Y. Interleukin-1 signaling is required for induction and maintenance of postoperative incisional pain: genetic and pharmacological studies in mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2008; 22:1072–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2008.03.005. PMID: 18442892.
Article41. Tillu DV, Melemedjian OK, Asiedu MN, Qu N, De Felice M, Dussor G, et al. Resveratrol engages AMPK to attenuate ERK and mTOR signaling in sensory neurons and inhibits incision-induced acute and chronic pain. Mol Pain. 2012; 8:5. DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-8-5. PMID: 22269797. PMCID: PMC3284441.
Article42. Wu C, Gavva NR, Brennan TJ. Effect of AMG0347, a transient receptor potential type V1 receptor antagonist, and morphine on pain behavior after plantar incision. Anesthesiology. 2008; 108:1100–8. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31817302b3. PMID: 18497612.
Article43. Banik RK, Brennan TJ. Trpv1 mediates spontaneous firing and heat sensitization of cutaneous primary afferents after plantar incision. Pain. 2009; 141:41–51. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2008.10.004. PMID: 19010598. PMCID: PMC2654272.
Article44. Hamalainen MM, Subieta A, Arpey C, Brennan TJ. Differential effect of capsaicin treatment on pain-related behaviors after plantar incision. J Pain. 2009; 10:637–45. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2009.01.003. PMID: 19386553. PMCID: PMC2730882.
Article45. Kawamata M, Watanabe H, Nishikawa K, Takahashi T, Kozuka Y, Kawamata T, et al. Different mechanisms of development and maintenance of experimental incision-induced hyperalgesia in human skin. Anesthesiology. 2002; 97:550–9. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200209000-00006. PMID: 12218519.
Article46. Pogatzki EM, Niemeier JS, Sorkin LS, Brennan TJ. Spinal glutamate receptor antagonists differentiate primary and secondary mechanical hyperalgesia caused by incision. Pain. 2003; 105:97–107. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3959(03)00169-6.
Article47. Zahn PK, Brennan TJ. Incision-induced changes in receptive field properties of rat dorsal horn neurons. Anesthesiology. 1999; 91:772–85. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199909000-00030.
Article48. Zahn PK, Brennan TJ. Lack of effect of intrathecally administered N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists in a rat model for postoperative pain. Anesthesiology. 1998; 88:143–56. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199801000-00022.
Article49. Pogatzki EM, Zahn PK, Brennan TJ. Effect of pretreatment with intrathecal excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists on the development of pain behavior caused by plantar incision. Anesthesiology. 2000; 93:489–96. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200008000-00029. PMID: 10910500.
Article50. Zahn PK, Brennan TJ. Intrathecal metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists do not decrease mechanical hyperalgesia in a rat model of postoperative pain. Anesth Analg. 1998; 87:1354–9. DOI: 10.1097/00000539-199812000-00026.
Article51. Jin HC, Keller AJ, Jung JK, Subieta A, Brennan TJ. Epidural tezampanel, an AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist, produces postoperative analgesia in rats. Anesth Analg. 2007; 105:1152–9. DOI: 10.1213/01.ane.0000281435.58012.e3. PMID: 17898404.
Article52. Zahn PK, Pogatzki-Zahn EM, Brennan TJ. Spinal administration of MK-801 and NBQX demonstrates NMDA-independent dorsal horn sensitization in incisional pain. Pain. 2005; 114:499–510. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2005.01.018. PMID: 15777875.
Article53. Zahn PK, Sluka KA, Brennan TJ. Excitatory amino acid release in the spinal cord caused by plantar incision in the rat. Pain. 2002; 100:65–76. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3959(02)00241-5.
Article54. Brennan TJ, Umali EF, Zahn PK. Comparison of pre- versus post-incision administration of intrathecal bupivacaine and intrathecal morphine in a rat model of postoperative pain. Anesthesiology. 1997; 87:1517–28. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199712000-00031. PMID: 9416737.
Article55. Ogonda L, Wilson R, Archbold P, Lawlor M, Humphreys P, O’Brien S, et al. A minimal-incision technique in total hip arthroplasty does not improve early postoperative outcomes. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:701–10. DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.D.02645. PMID: 15805196.56. Dorr LD, Maheshwari AV, Long WT, Wan Z, Sirianni LE. Early pain relief and function after posterior minimally invasive and conventional total hip arthroplasty. A prospective, randomized, blinded study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:1153–60. DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.F.00940. PMID: 17545416.57. Kawamata M, Takahashi T, Kozuka Y, Nawa Y, Nishikawa K, Narimatsu E, et al. Experimental incision-induced pain in human skin: effects of systemic lidocaine on flare formation and hyperalgesia. Pain. 2002; 100:77–89. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3959(02)00233-6.
Article58. Aasvang EK, Hansen JB, Malmstrøm J, Asmussen T, Gennevois D, Struys MM, et al. The effect of wound instillation of a novel purified capsaicin formulation on postherniotomy pain: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Anesth Analg. 2008; 107:282–91. DOI: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31816b94c9. PMID: 18635499.
Article59. Hartrick CT, Pestano C, Carlson N, Hartrick S. Capsaicin instillation for postoperative pain following total knee arthroplasty: a preliminary report of a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Clin Drug Investig. 2011; 31:877–82. DOI: 10.1007/BF03256925. PMID: 21971213.60. Field MJ, Holloman EF, McCleary S, Hughes J, Singh L. Evaluation of gabapentin and S-(+)-3-isobutylgaba in a rat model of postoperative pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997; 282:1242–6. PMID: 9316831.61. Ho KY, Gan TJ, Habib AS. Gabapentin and postoperative pain--a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Pain. 2006; 126:91–101. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2006.06.018. PMID: 16846695.
Article62. Tiippana EM, Hamunen K, Kontinen VK, Kalso E. Do surgical patients benefit from perioperative gabapentin/pregabalin? A systematic review of efficacy and safety. Anesth Analg. 2007; 104:1545–56. DOI: 10.1213/01.ane.0000261517.27532.80. PMID: 17513656.
Article