Korean Circ J.
2016 Jul;46(4):542-549. 10.4070/kcj.2016.46.4.542.
Non-Responders to Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Coronary Artery Dilatation in Kawasaki Disease: Predictive Parameters in Korean Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. nakim2016.5@gmail.com
- KMID: 2344430
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2016.46.4.542
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
In Kawasaki disease (KD), high dose intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) significantly lowers the coronary complications. However, some patients either do not respond to initial therapy or develop coronary complications. We aimed to identify the predictive factors for unresponsiveness to initial IVIG therapy and coronary artery dilatation (CAD; defined by Z-score≥2.5) in the acute phase and convalescent phase.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
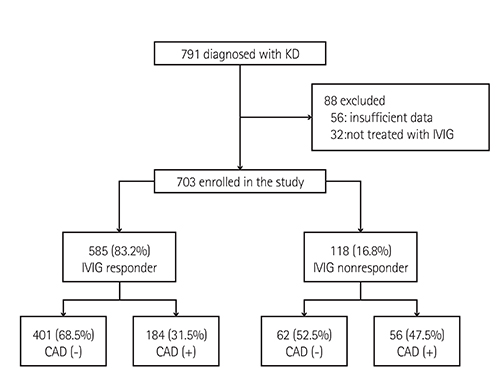
A retrospective review was conducted of 703 patients with KD, admitted to Gachon University Gil Medical Center between January 2005 and June 2013. The patients were divided into two groups-IVIG responders vs. non-responders-based on the IVIG treatments, and presence of fever after treatment. Further, these groups were divided into two subgroups based on their CAD.
RESULTS
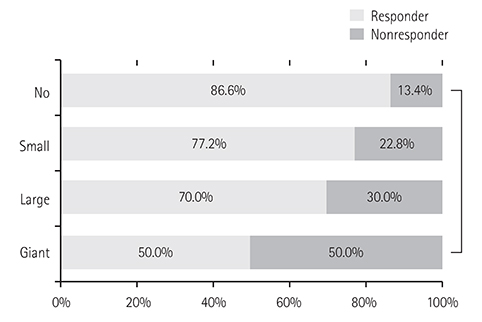
Among the 703 patients with KD, the rate of non-responders to initial IVIG was 16.8%. Serum total bilirubin, platelet count, and neutrophil proportion were independent predictive parameters of unresponsiveness (p<0.05). CAD was found in 234 patients (33.3%) in the acute phase, and in 32 patients (4.6%) in the convalescent phase. Male gender, fever duration, serum C-reactive protein, and white blood cell count were related to CAD (p<0.05). CAD was detected more frequently in non-responders than in the responders (47.5% vs. 31.5%, p=0.001). Kobayashi, Egami, and Sano scoring systems applied to our study population reflected low sensitivities (28.0-33.9%).
CONCLUSION
Several independent parameters were related to unresponsiveness to the initial IVIG or CAD. These parameters might be helpful in establishing more focused and careful monitoring of high-risk KD patients in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Factors Predicting Resistance to Intravenous Immunoglobulin Treatment and Coronary Artery Lesion in Patients with Kawasaki Disease: Analysis of the Korean Nationwide Multicenter Survey from 2012 to 2014
Min Kyu Kim, Min Seob Song, Gi Beom Kim
Korean Circ J. 2018;48(1):71-79. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2017.0136.
Reference
-
1. Kawasaki T. Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes in children. Arerugi. 1967; 16:178–222.2. Burns JC, Capparelli EV, Brown JA, Newburger JW, Glode MP. Intravenous gamma-globulin treatment and retreatment in Kawasaki disease US/Canadian Kawasaki Syndrome study group. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998; 17:1144–1148.3. Wallace CA, French JW, Kahn SJ, Sherry DD. Initial intravenous gammaglobulin treatment failure in Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics. 2000; 105:E78.4. Koren G, Lavi S, Rose V, Rowe R. Kawasaki disease: review of risk factors for coronary aneurysms. J Pediatr. 1986; 108:388–392.5. Kobayashi T, Inoue Y, Takeuchi K, et al. Prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin unresponsiveness in patients with Kawasaki disease. Circulation. 2006; 113:2606–2612.6. Egami K, Muta H, Ishii M, et al. Prediction of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2006; 149:237–240.7. Sano T, Kurotobi S, Matsuzaki K, et al. Prediction of non-responsiveness to standard high-dose gamma-globulin therapy in patients with acute Kawasaki disease before starting initial treatment. Eur J Pediatr. 2007; 166:131–137.8. Dallaire F, Dahdah N. New equations and a critical appraisal of coronary artery Z scores in healthy children. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011; 24:60–74.9. Manlhiot C, Millar K, Golding F, McCrindle BW. Improved classification of coronary artery abnormalities based only on coronary artery z-scores after Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 2010; 31:242–249.10. Kim GB, Han JW, Park YW, et al. Epidemiologic features of Kawasaki disease in South Korea: data from nationwide survey, 2009-2011. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014; 33:24–27.11. Matsubara T, Ichiyama T, Furukawa S. Immunological profile of peripheral blood lymphocytes and monocytes/macrophages in Kawasaki disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005; 141:381–387.12. Tremoulet AH, Best BM, Song S, et al. Resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin in children with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2008; 153:117–121.13. Ashouri N, Takahashi M, Dorey F, Mason W. Risk factors for nonresponse to therapy in Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2008; 153:365–368.14. Fu PP, Du ZD, Pan YS. Novel predictors of intravenous immunoglobulin resistance in Chinese children with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2013; 32:e319–e323.15. Cha S, Yoon M, Ahn Y, Han M, Yoon KL. Risk factors for failure of initial intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in Kawasaki disease. J Korean Med Sci. 2008; 23:718–722.16. Do YS, Kim KW, Chun JK, Cha BH, Namgoong MK, Lee HY. Predicting factors for refractory Kawasaki disease. Korean Circ J. 2010; 40:239–242.17. Park HM, Lee DW, Hyun MC, Lee SB. Predictors of nonresponse to intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in Kawasaki disease. Korean J Pediatr. 2013; 56:75–79.18. Sleeper LA, Minich LL, McCrindle BM, et al. Evaluation of Kawasaki disease risk-scoring systems for intravenous immunoglobulin resistance. J Pediatr. 2011; 269:831–835.e3.19. Choi MH, Park CS, Kim DS, Kim KH. Prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin nonresponse Kawasaki disease in Korea. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2014; 21:29–36.20. Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics. 2004; 114:1708–1733.21. Cho KH, Kang SJ. Clinically useful predictors of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin and prognosis of coronary artery lesions in patients with incomplete Kawasaki disease. Korean Circ J. 2014; 44:328–335.22. Hashino K, Ishii M, Iemura M, Akagi T, Kato H. Re-treatment for immune globulin-resistant Kawasaki disease: a comparative study of additional immune globulin and steroid pulse therapy. Pediatr Int. 2001; 43:211–217.23. Beiser AS, Takahashi M, Baker AL, Sundel RP, Newburger JW. A predictive instrument for coronary artery aneurysms in Kawasaki disease. US Multicenter Kawasaki Disease Study Group. Am J Cardiol. 1998; 81:1116–1120.24. Honkanen VE, McCrindle BW, Laxer RM, Feldman BM, Schneider R, Silverman ED. Clinical relevance of the risk factors for coronary artery inflammation in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 2003; 24:122–126.25. Gersony WM. Predicting coronary aneurysms in Kawasaki disease. Am J Cardiol. 1998; 81:1162–1164.26. Park MJ, Jeon IS, Tchah H, Cho KH, Jung MJ, Choi DY. Predictive indicators of coronary artery complications in Kawasaki disease. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:1161–1166.27. Singh S, Aulakh R, Kawasaki T. Kawasaki disease and the emerging coronary artery disease epidemic in India: is there a correlation? Indian J Pediatr. 2014; 81:328–332.28. Kawai H, Takakuwa Y, Naruse H, et al. Two cases with past Kawasaki disease developing acute myocardial infarction in their thirties, despite being regarded as at low risk for coronary events. Heart Vessels. 2015; 30:549–553.29. Ogata S, Ogihara Y, Honda T, Kon S, Akiyama K, Ishii M. Corticosteroid pulse combination therapy for refractory Kawasaki disease: a randomized trial. Pediatrics. 2012; 129:e17–e23.30. Chen S, Dong Y, Yin Y, Krucoff MW. Intravenous immunoglobulin plus corticosteroid to prevent coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease: a meta-analysis. Heart. 2013; 99:76–82.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Laboratory Values in Patients with Kawasaki Disease after Intravenous Immunoglobulin: Comparison of Patients with Coronary Artery Lesions to those without Coronary Artery Lesions
- Predictors and management of intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease
- The characteristic laboratory findings of non-responsiveness to intravenous immunoglobulin in children with Kawasaki disease
- A Clinical Study of Atypical Kawasaki Disease: A Rate of Coronary Artery Involvement
- Limitation of Prediction on Intravenous Immunoglobulin Responsiveness in Kawasaki Disease