J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2015 Jun;56(6):875-884. 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.6.875.
Comparison of Clinical Outcomes between Diffractive and Refractive Multifocal Intraocular Lens with Same Near Added
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cheil Eye Hospital, Daegu, Korea. eyepark9@naver.com
- KMID: 2339152
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2015.56.6.875
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the clinical outcomes between refractive-type multifocal intraocular lenses (IOL) (Lentis Mplus(R) LS 313, Oculentis GmbH., Berlin, Germany) and diffractive-type multifocal IOL (Acrysof Restor(R); SN6AD1, Alcon Lab., Fort Worth, TX, USA) with same near added.
METHODS
We evaluated 30 eyes implanted with Lentis Mplus(R) IOL and 33 eyes implanted with Acrysof Restor(R) IOL after phacoemulsification. The distant, intermediate, and near uncorrected visual acuities of the 2 groups were evaluated at 2 weeks and 1, 3, and 6 months postoperatively. Optical quality obtained using the Optical Quality Analysis System II (OQAS II(R), Visiometrics, Castelldefels, Barcelona, Spain), higher-order aberrations (HOAs), and patient satisfaction questionnaire of the 2 groups were evaluated at 3 months postoperatively.
RESULTS
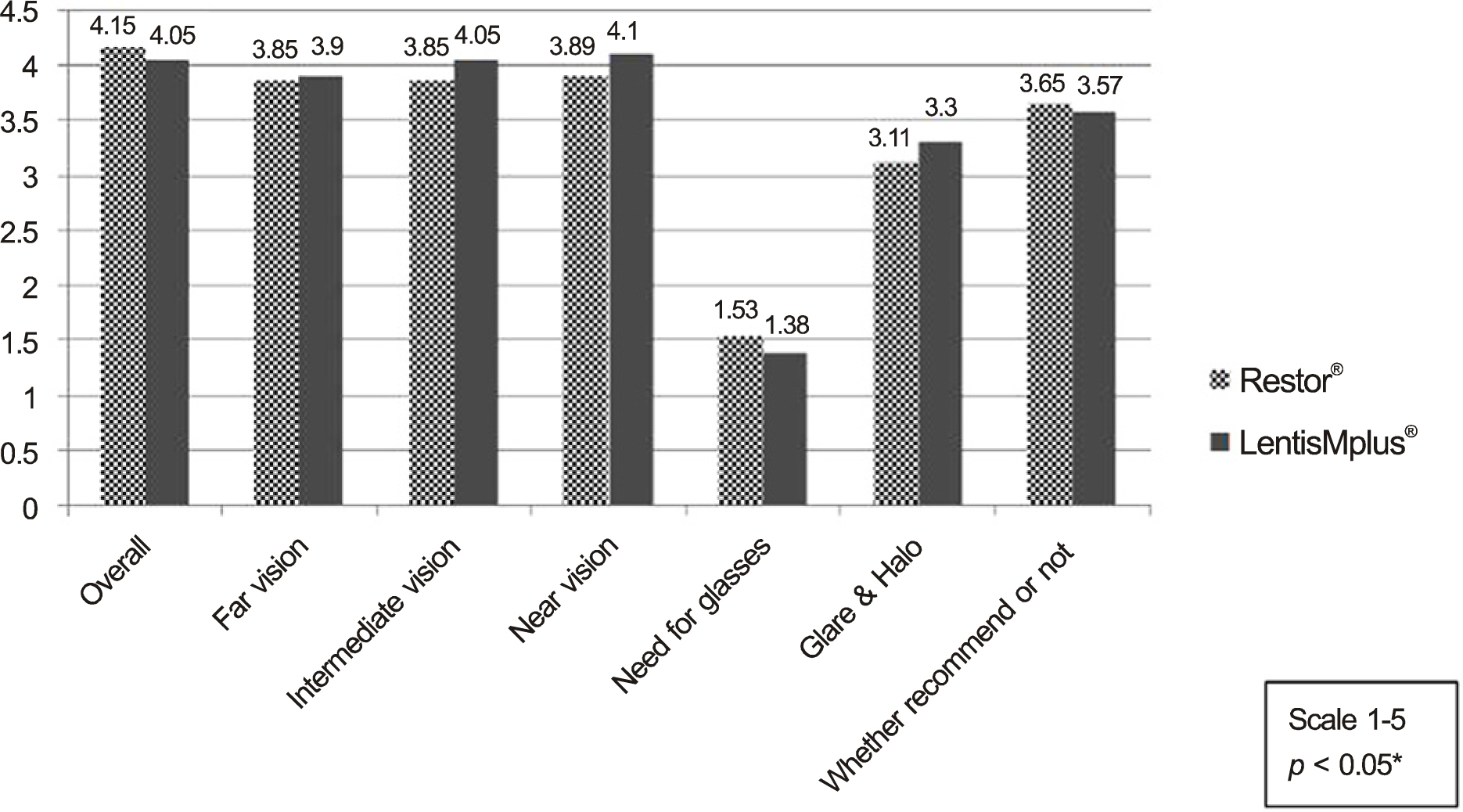
The visual acuity of intermediate 100 cm was statistically better in the Lentis Mplus(R) group (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences between the 2 groups with distant, intermediate 63 cm, and near vision. At the 3-month postoperative follow-up, objective scatter index, modulation transfer function (MTF) cutoff value, and pseudo-accommodation range measured by OQAS II(R) showed no differences between the 2 groups, but Strhel ratio was higher in the Acrysof Restor(R) group. HOAs of 5 mm and 6 mm increased significantly in the Lentis Mplus(R) group. No significant differences were found in the patient satisfaction questionnaire.
CONCLUSIONS
Both refractive and diffractive-type multifocal IOL implantation in patients with cataracts and presbyopia offered good and comparable visual acuity at distance and near. However, the Lentis Mplus(R) IOL provided better intermediate vision than the Acrysof Restor(R) IOL.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison of the Visual Outcomes after Cataract Surgery with Implantation of a Bifocal and Trifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lens
Sung Yu, Yong Il Kim, Sang Won Ha, Gwang Ja Lee, Kyoo Won Lee, Young Jeung Park
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016;57(3):405-412. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.3.405.
Reference
-
References
1. Alfonso JF, Fernández-Vega L, Baamonde MB, Montés-Micó R. Prospective visual evaluation of apodized diffractive intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1235–43.
Article2. Lee HS, Park SH, Kim MS. Clinical results and some problems of multifocal apodized diffractive intraocular lens implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1235–41.
Article3. de Vries NE, Webers CA, Montés-Micó R, et al. Long-term fol-low-up of a multifocal apodized diffractive intraocular lens after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1476–82.
Article4. Woodward MA, Randleman JB, Stulting RD. Dissatisfaction after multifocal intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:992–7.
Article5. Cheon MH, Lee JE, Kim JH, et al. One-year outcome of monocular implant of aspheric multifocal IOL. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:822–8.
Article6. Kim SM, Kim CH, Chung ES, Chung TY. Visual outcome and patient satisfaction after implantation of multifocal IOLs: three- month follow-up results. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:230–7.7. de Vries NE, Nuijts RM. Multifocal intraocular lenses in cataract surgery: literature review of benefits and side effects. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:268–78.
Article8. Alfonso JF, Puchades C, Fernández-Vega L, et al. Contrast sensitivity comparison between AcrySof ReSTOR and Acri.LISA aspheric intraocular lenses. J Refract Surg. 2010; 26:471–7.
Article9. Castillo-Gómez A, Carmona-González D, Martínez-de-la-Casa JM, et al. Evaluation of image quality after implantation of 2 diffractive multifocal intraocular lens models. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1244–50.
Article10. Alfonso JF, Fernández-Vega L, Blázquez JI, Montés-Micó R. Visual function comparison of 2 aspheric multifocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:242–8.
Article11. Blaylock JF, Si Z, Vickers C. Visual and refractive status at different focal distances after implantation of the ReSTOR multifocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1464–73.
Article12. Kohnen T, Allen D, Boureau C, et al. European multicenter study of the AcrySof ReSTOR apodized diffractive intraocular lens. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:578–84.e1.
Article13. Nochez Y, Majzoub S, Pisella PJ. Effect of interaction of macro-aberrations and scattered light on objective quality of vision in pseudophakic eyes with aspheric monofocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:633–40.
Article14. McAlinden C, Moore JE. Multifocal intraocular lens with a sur-face-embedded near section: short-term clinical outcomes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:441–5.
Article15. Alió JL, Plaza-Puche AB, Piñero DP, et al. Comparative analysis of the clinical outcomes with 2 multifocal intraocular lens models with rotational asymmetry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:1605–14.
Article16. Muñoz G, Albarrán-Diego C, Ferrer-Blasco T, et al. Visual function after bilateral implantation of a new zonal refractive aspheric multifocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:2043–52.
Article17. Alió JL, Plaza-Puche AB, Montalban R, Javaloy J. Visual outcomes with a single-optic accommodating intraocular lens and a low-addition-power rotational asymmetric multifocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:978–85.
Article18. Alio JL, Plaza-Puche AB, Javaloy J, et al. Comparison of a new refractive multifocal intraocular lens with an inferior segmental near add and a diffractive multifocal intraocular lens. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:555–63.
Article19. Chung YK, Park CW, Hwang JH, Joo CK. Clinical outcomes of M-plus intraocular lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:519–26.
Article20. Hayashi K, Manabe S, Yoshida M, Hayashi H. Effect of astigmatism on visual acuity in eyes with a diffractive multifocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1323–9.
Article21. Nanavaty MA, Spalton DJ, Marshall J. Effect of intraocular lens asphericity on vertical coma aberration. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:215–21.
Article22. Nishi T, Nawa Y, Ueda T, et al. Effect of total higher-order aberrations on accommodation in pseudophakic eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1643–9.
Article23. Nochez Y, Majzoub S, Pisella PJ. Effect of interaction of macro-aberrations and scattered light on objective quality of vision in pseudophakic eyes with aspheric monofocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:633–40.
Article24. Diaz-Valle D, Arriola-Villalobos P, García-Vidal SE, et al. Effect of lubricating eyedrops on ocular light scattering as a measure of vision quality in patients with dry eye. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:1192–7.
Article25. Cabot F, Saad A, McAlinden C, et al. Objective assessment of crystalline lens opacity level by measuring ocular light scattering with a double-pass system. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 155:629–35. 635.e1-2.
Article26. Lee K, Ahn JM, Kim EK, Kim TI. Comparison of optical quality parameters and ocular aberrations after wavefront-guided laser in-situ keratomileusis versus wavefront-guided laser epithelial keratomileusis for myopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013; 251:2163–9.
Article27. Saad A, Saab M, Gatinel D. Repeatability of measurements with a double-pass system. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:28–33.
Article28. Castillo-Gómez A, Carmona-González D, Martínez-de-la-Casa JM, et al. Evaluation of image quality after implantation of 2 diffractive multifocal intraocular lens models. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1244–50.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pseudoaccomodation in Pseudophakic Eyes with 3M Multifocal Intraocular Lens
- Clinical Results of 3M Multifocal Intraocular Lens
- Clinical Outcomes of Diffractive Multifocal Toric Intraocular Lens Implantation
- Clinical Outcomes of M-Plus Intraocular Lenses
- Clinical outcomes of currently available multifocal intraocular lenses