J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Aug;55(8):1233-1237.
A Case of Syphilitic Scleritis Initially Misdiagnosed as Noninfectious Nodular or Fungal Scleritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Myung-Gok Eye Research Institute, Department of Ophthalmology, Kim's Eye Hospital, Konyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jaelim.chung@gmail.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report a case of syphilitic scleritis initially misdiagnosed as noninfectious nodular or fungal scleritis.
CASE SUMMARY
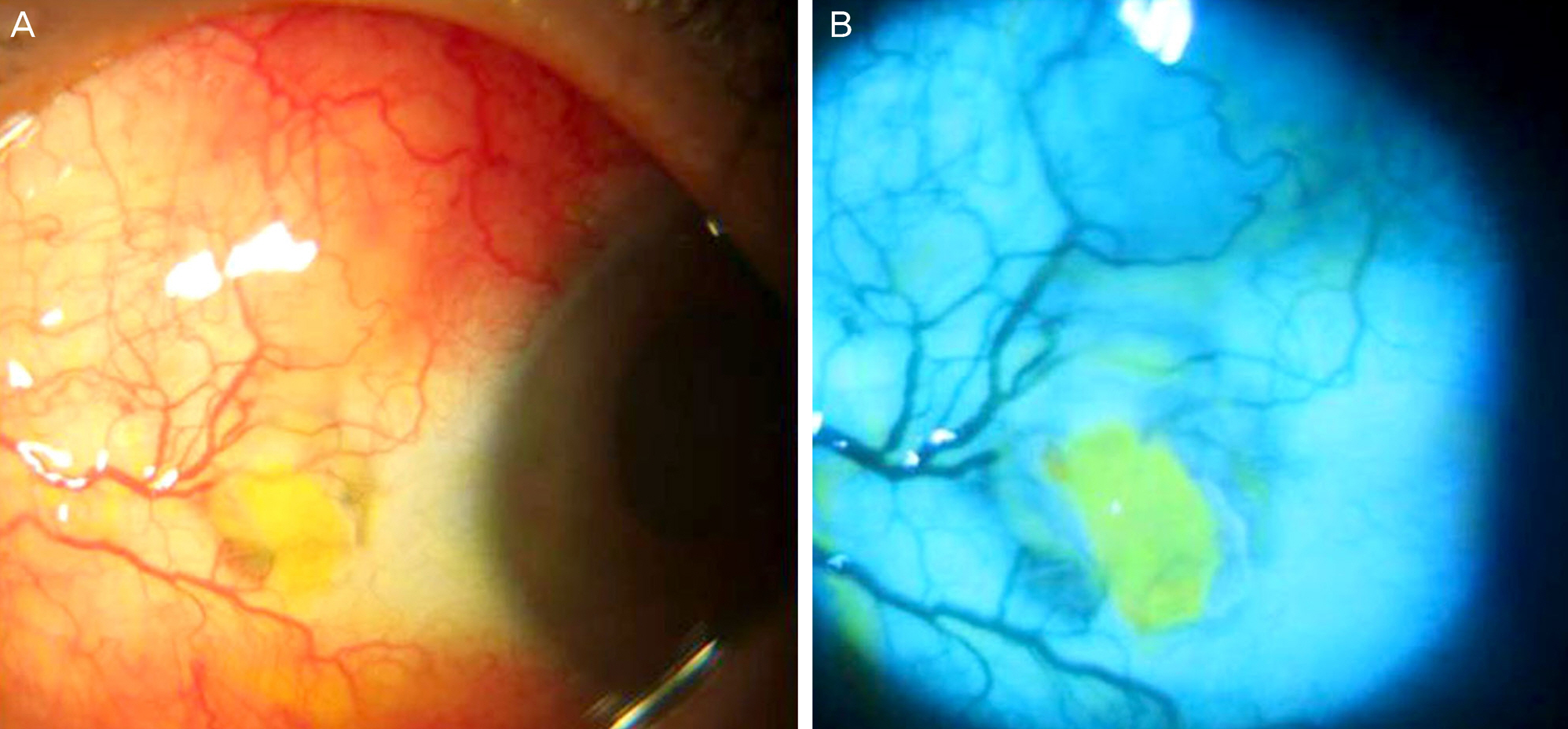
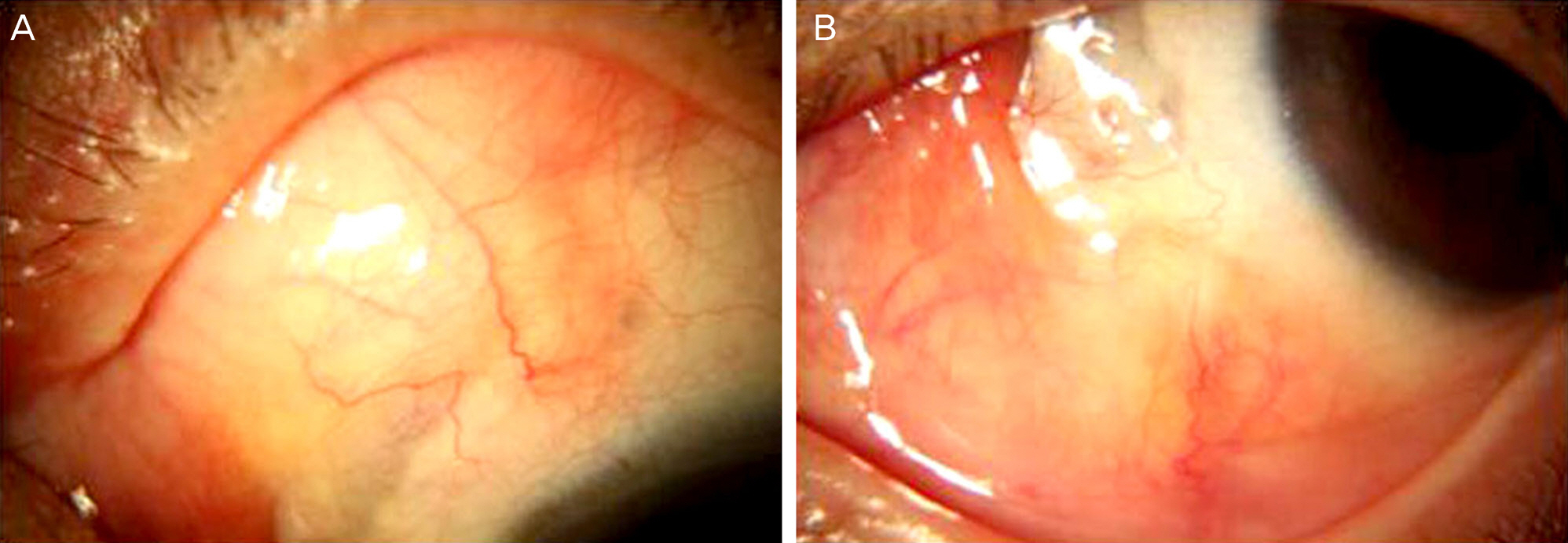
A 63-year-old female, who had severe headaches and ocular pain in her left eye despite treatment with topical and oral NSAIDs for the past 4 months, was transferred from a local clinic. The patient had a history of pterygium excision in the same eye 4 years prior. Upon presentation, she had a scleromalacia with calcified plaque at the nasal conjunctiva. An erythematous nodular elevated lesion was observed in the superonasal sclera. Microbiological smear and cultures were performed to exclude infectious scleritis. Under the suspicion of noninfectious nodular scleritis, the patient was prescribed topical oral steroid and oral NSAIDs. Candida parapsilosis was identified by the microbiological culture. Under the suspicion of fungal scleritis, oral fluconazole and topical amphotericin B were administered, but the lesions did not improve. On the 23rd day of treatment, we discovered the patient had a history of syphilis. The serology test was negative for RPR and FTA-ABS IgM but positive for FTA-ABS IgG. Under the suspicion of syphilitic scleritis, oral doxycycline (200 mg bid) was administered and benzathine penicillin M (2.4 million units) was injected intramuscularly 3 times at 1-week intervals. After the doxycycline and benzathine penicillin therapy, the pain and nodular erythematous lesions were completely resolved.
CONCLUSIONS
As shown in this case, syphilitic scleritis should be considered when the patient is resistant to other conventional treatments and shows positive serological tests for syphilis. This is important because syphilitic scleritis is usually aggravated by steroid treatment but can be cured by proper anti-syphilitic chemotherapy.
MeSH Terms
-
Amphotericin B
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Candida
Conjunctiva
Doxycycline
Drug Therapy
Female
Fluconazole
Headache
Humans
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulin M
Middle Aged
Penicillin G Benzathine
Pterygium
Sclera
Scleritis*
Serologic Tests
Syphilis
Treponema pallidum
Amphotericin B
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Doxycycline
Fluconazole
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulin M
Penicillin G Benzathine
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Reynolds MG, Alfonso E. Treatment of infectious scleritis and keratoscleritis. Am J ophthalmol. 1991; 112:543–7.
Article2. O'Donoghue E, Lightman S, Tuft S, Watson P. Surgically induced necrotising sclerokeratitis (SINS)–precipitating factors and response to treatment. Br J Ophthalmol. 1992; 76:17–21.3. Diaz-valle D, Benitez del Castillo JM, Castillo A, et al. Immunologic and clinical evaluation of postsurgical necrotizing sclerocorneal ulceration. Cornea. 1998; 17:371–5.
Article4. Kim YK, Kim TY. 4 case of Pseudomonas scleritis after pterygium excision. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2304–12.5. Watson PG, Hayreh SS. Scleritis and episcleritis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1976; 60:163–91.
Article6. Rao Na, Marak GE, Hydayat AA. Necrotizing scleritis. A clinico-pathologic study of 41 cases. Ophthalmology. 1985; 92:1542–9.7. Su CY, Tsai JJ, Chang YC, Lin CP. Immunologic and clinical manifestations of infectious scleritis after pterygium excision. Cornea. 2006; 25:663–6.
Article8. Okhravi N, Odufuwa B, McCluskey P, Lightman S. Scleritis. Surv Ophthalmol. 2005; 50:351–63.
Article9. Cunningham MA, Alexander JK, Matoba AY, et al. Management and outcome of microbial anterior scleritis. Cornea. 2011; 30:1020–3.
Article10. Tamesis RR, Foster CS. Ocular syphilis. Ophthalmology. 1990; 97:1281–7.
Article11. Foster CS, Tamesis RR. Ocular syphilis. In : Albert DM, Jakobiec FA, editors. Principles and Practice of Ophthalmology. 1st ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co;1994. p. 968–72.12. Yoon KC, Im SK, Seo MS, Park YG. Neurosyphilitic episcleritis. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005; 83:265–6.
Article13. Aldave AJ, King JA, Cunningham ET Jr. Ocular syphilis. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2001; 12:433–41.
Article14. Centers for Disease control and prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines 2002. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2002; 51:1–78.15. Casey R, Flowers CW Jr, Jones DD, Scott L. Anterior nodular scleritis secondary to syphilis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996; 114:1015–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Nodular Scleritis in Association With Behcet's Disease
- Effect of Intravitreal Dexamethasone Implant Injection in a Patient with Recurrent Nodular Anterior Scleritis
- Retinal Pigment Epithelial Detachment in Posterior Scleritis
- Efficacy of Autologous Tragal Perichondrium Graft after Proper Antifungal Treatment in Fungal Necrotizing Scleritis
- Clinical Features of the Episcleritis and the Scleritis