J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Jan;55(1):143-148.
A Case of Oxaliplatin-Related Ocular Toxicity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kangbuk Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jhbae94@hotmail.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report a case of oxaliplatin (Eloxatin(R))-related ocular toxicity in a patient with advanced stomach cancer.
CASE SUMMARY
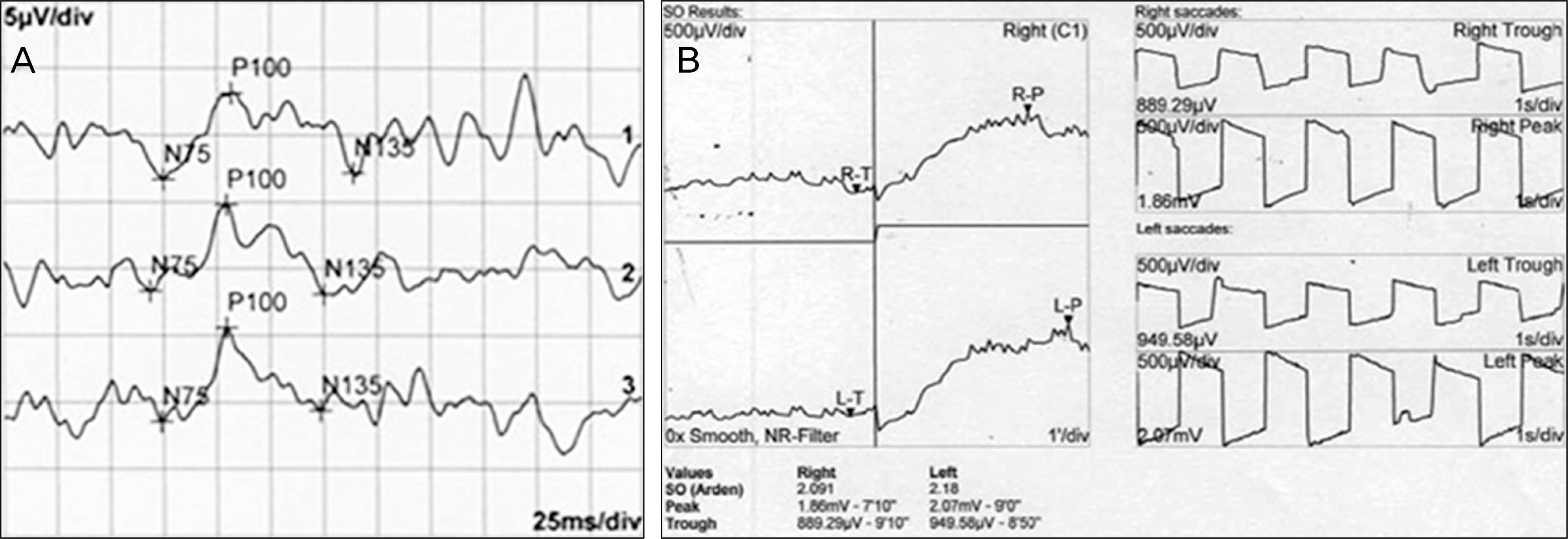
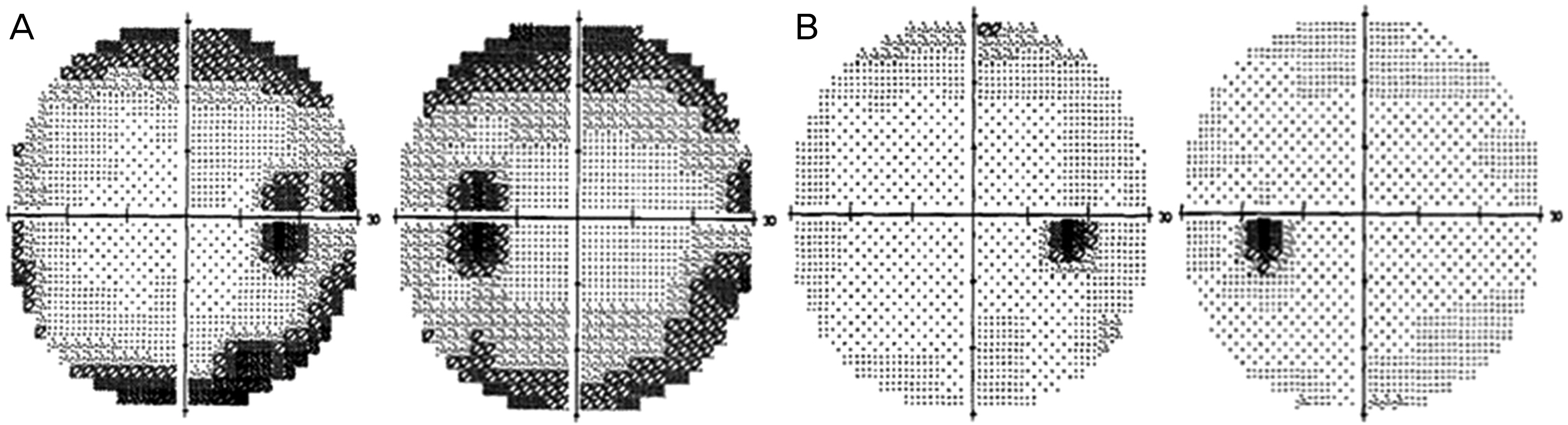
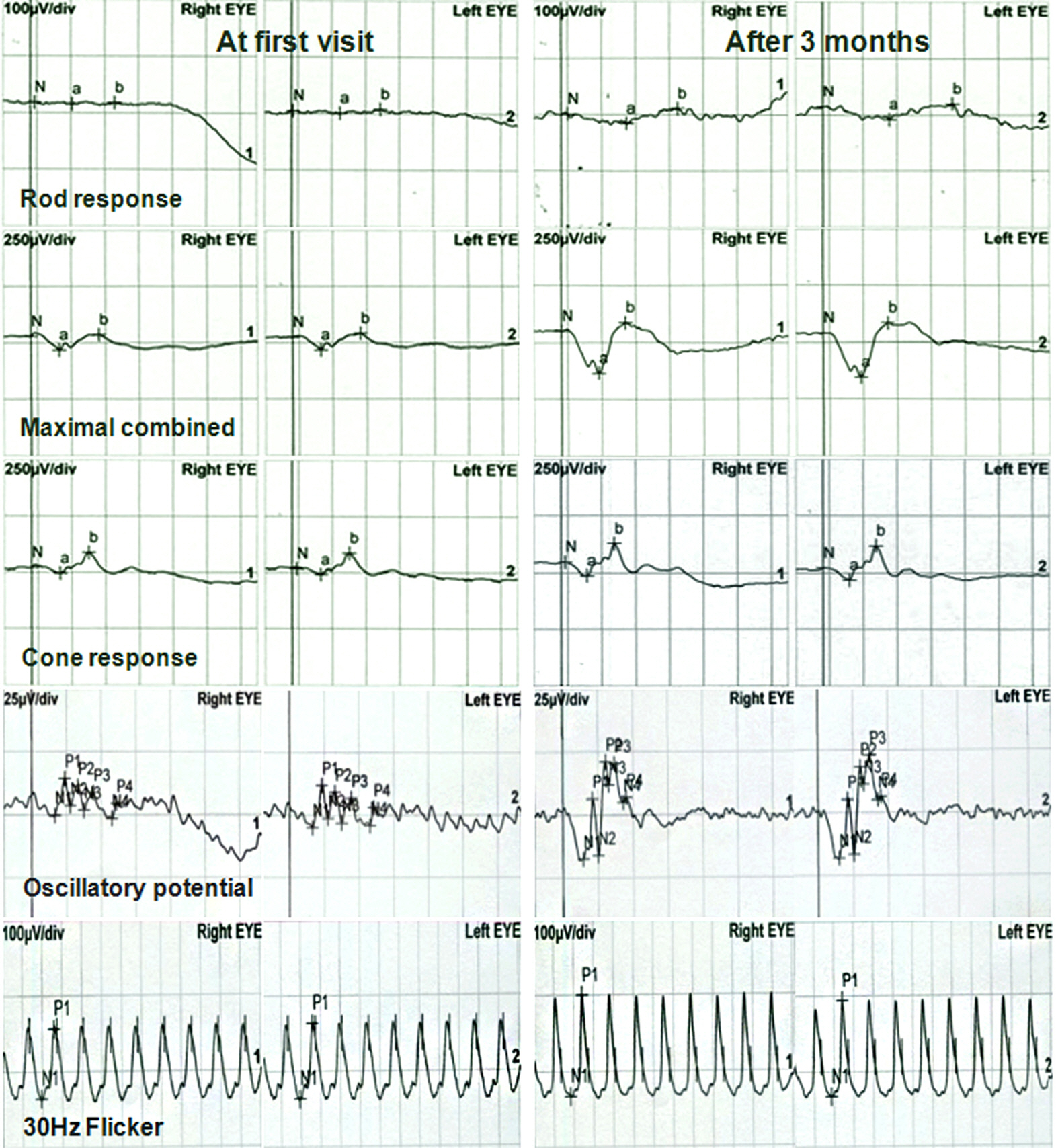
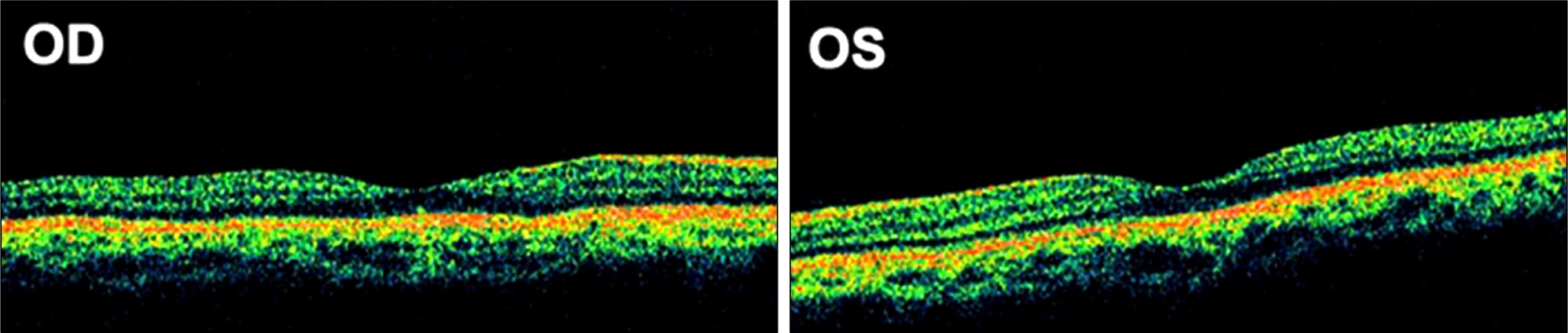
A 43-year-old female with advanced stomach cancer experienced visual symptoms during the treatment with oxaliplatin on a XELOX schedule (a combination of oxaliplatin and capecitabine). After 1 cycle of chemotherapy, she complained of blurred vision and visual field defects in both eyes. Visual field tests showed a bilateral concentric field defect and the electroretinogram revealed a marked reduction of responses in both eyes. On the second cycle of chemotherapy, oxaliplatin was discontinued due to suspicious ocular toxicity. Her visual symptoms improved and visual field test showed normal results 1 month after oxaliplatin discontinuation. However, 3 months after oxaliplatin discontinuation, electroretinogram remained abnormal despite the progressive improvement.
CONCLUSIONS
Platinum-based antineoplastic agents such as oxaliplatin should be administered with caution because oxaliplatin can cause damage to the retinal photoreceptors and the optic nerve. Early detection of ocular toxicity and discontinuation of oxaliplatin therapy could prevent severe and irreversible visual loss.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Raymond E, Buquet-Fagot C, Djelloul S. . Antitumor activity of oxaliplatin in combination with 5-fluorouracil and the thymidy-late synthase inhibitor AG337 in human colon, breast and ovarian cancers. Anticancer Drugs. 1997; 8:876–85.
Article2. André T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L. . Oxaliplatin, fluorour-acil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2343–51.
Article3. Bang YJ, Kim YW, Yang HK. . Adjuvant capecitabine and ox-aliplatin for gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy (CLASSIC): a phase 3 open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012; 379:315–21.4. Mathé G, Kidani Y, Triana K. . A phase I trial of trans-1-dia-minocyclohexane oxalato-platinum (l-OHP). Biomed Pharmacother. 1986; 40:372–6.5. Extra JM, Espie M, Calvo F. . Phase I study of oxaliplatin in pa-tients with advanced cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1990; 25:299–303.
Article6. Cassidy J, Misset JL.Oxaliplatin-related side effects: character-istics and management. Semin Oncol. 2002; 29(5 Suppl 15):11–20.
Article7. Gamelin E, Gamelin L, Bossi L, Quasthoff S.Clinical aspects and molecular basis of oxaliplatin neurotoxicity: current management and development of preventive measures. Semin Oncol. 2002; 29(5 Suppl 15):21–33.
Article8. Hartmann JT, Lipp HP.Toxicity of platinum compounds. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2003; 4:889–901.
Article9. Simpson D, Dunn C, Curran M, Goa KL.Oxaliplatin: a review of its use in combination therapy for advanced metastatic colorectal cancer. Drugs. 2003; 63:2127–56.10. Imperia PS, Lazarus HM, Lass JH.Ocular complications of sys-temic cancer chemotherapy. Surv Ophthalmol. 1989; 34:209–30.
Article11. Rixe O, Ortuzar W, Alvarez M. . Oxaliplatin, tetraplatin, cisplatin, and carboplatin: spectrum of activity in drug-resistant cell lines and in the cell lines of the National Cancer Institute's Anticancer Drug Screen panel. Biochem Pharmacol. 1996; 52:1855–65.
Article12. Raymond E, Faivre S, Woynarowski JM, Chaney SG.Oxaliplatin: mechanism of action and antineoplastic activity. Semin Oncol. 1998; 25(2 Suppl 5):4–12.13. Schmid KE, Kornek GV, Scheithauer W, Binder S.Update on ocu-lar complications of systemic cancer chemotherapy. Surv Ophthalmol. 2006; 51:19–40.
Article14. Siu SW, Chan RT, Au GK.Hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin: experience in a single institute. Ann Oncol. 2006; 17:259–61.
Article15. Mesquida M, Sanchez-Dalmau B, Ortiz-Perez S. . Oxaliplatin- related ocular toxicity. Case Rep Oncol. 2010; 3:423–7.16. O'Dea D, Handy CM, Wexler A.Ocular changes with oxaliplatin. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2006; 10:227–9.17. Wilson RH, Lehky T, Thomas RR. . Acute oxaliplatin-induced peripheral nerve hyperexcitability. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:1767–74.
Article18. Gamelin L, Capitain O, Morel A. . Predictive factors of ox-aliplatin neurotoxicity: the involvement of the oxalate outcome pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:6359–68.
Article19. Lecomte T, Landi B, Beaune P. . Glutathione S-transferase P1 polymorphism (Ile105Val) predicts cumulative neuropathy in pa-tients receiving oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12:3050–6.
Article20. Webster RG, Brain KL, Wilson RH. . Oxaliplatin induces hy-perexcitability at motor and autonomic neuromuscular junctions through effects on voltage-gated sodium channels. Br J Pharmacol. 2005; 146:1027–39.
Article21. Grolleau F, Gamelin L, Boisdron-Celle M. . A possible explanation for a neurotoxic effect of the anticancer agent oxaliplatin on neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels. J Neurophysiol. 2001; 85:2293–7.
Article22. Smith BJ, Côté PD.Reduced retinal function in the absence of Na(v)1.6. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e31476.
Article23. Adelsberger H, Quasthoff S, Grosskreutz J. . The chemo-therapeutic oxaliplatin alters voltage-gated Na(+) channel kinetics on rat sensory neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000; 406:25–32.
Article24. Dong CJ, Hare WA.Contribution to ischemic injury of rat optic nerves by intracellular sodium overload. Doc Ophthalmol. 2005; 110:15–23.
Article25. Osborne NN, Wood JP, Chidlow G. . Effectiveness of levobe-taxolol and timolol at blunting retinal ischaemia is related to their calcium and sodium blocking activities: relevance to glaucoma. Brain Res Bull. 2004; 62:525–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Oxaliplatin-induced Sudden Hearing Loss in a Patient with Pancreatic Cancer
- Diffuse alveolar damage during chemotherapy with oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin
- Ocular Toxicity Induced by Topical Antivirals: Clinical Manifestation and Follow-up of 6 Case Series
- Oxaliplatin-induced Pulmonary Fibrosis: Two Case Reports
- Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Combination Chemotherapy of Oxaliplatin, 5-Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin