J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 Apr;52(4):401-406.
Pupil Size in the Normal Korean Population According to Age and Illuminance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. wcpark@dau.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report the change of pupil sizes according to age and illuminance in the normal Korean population.
METHODS
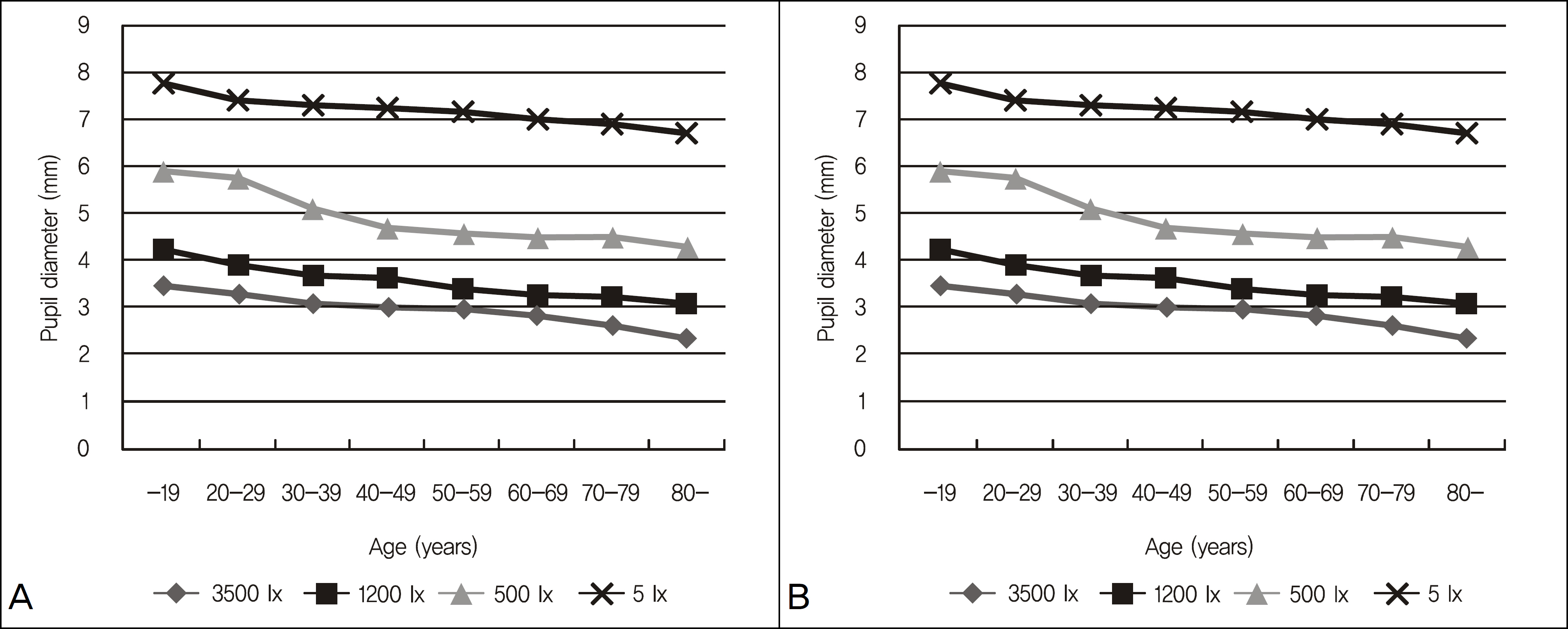
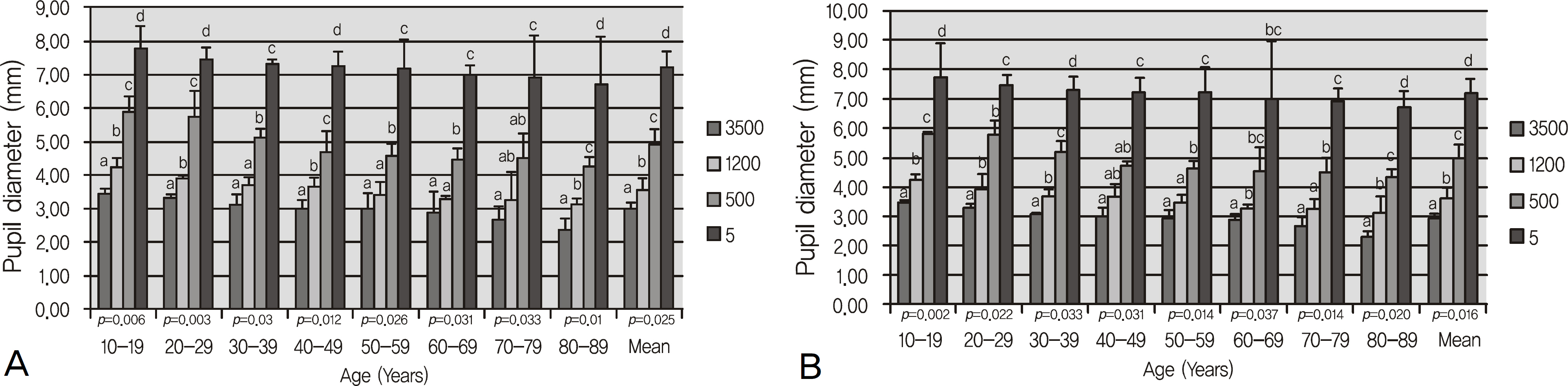
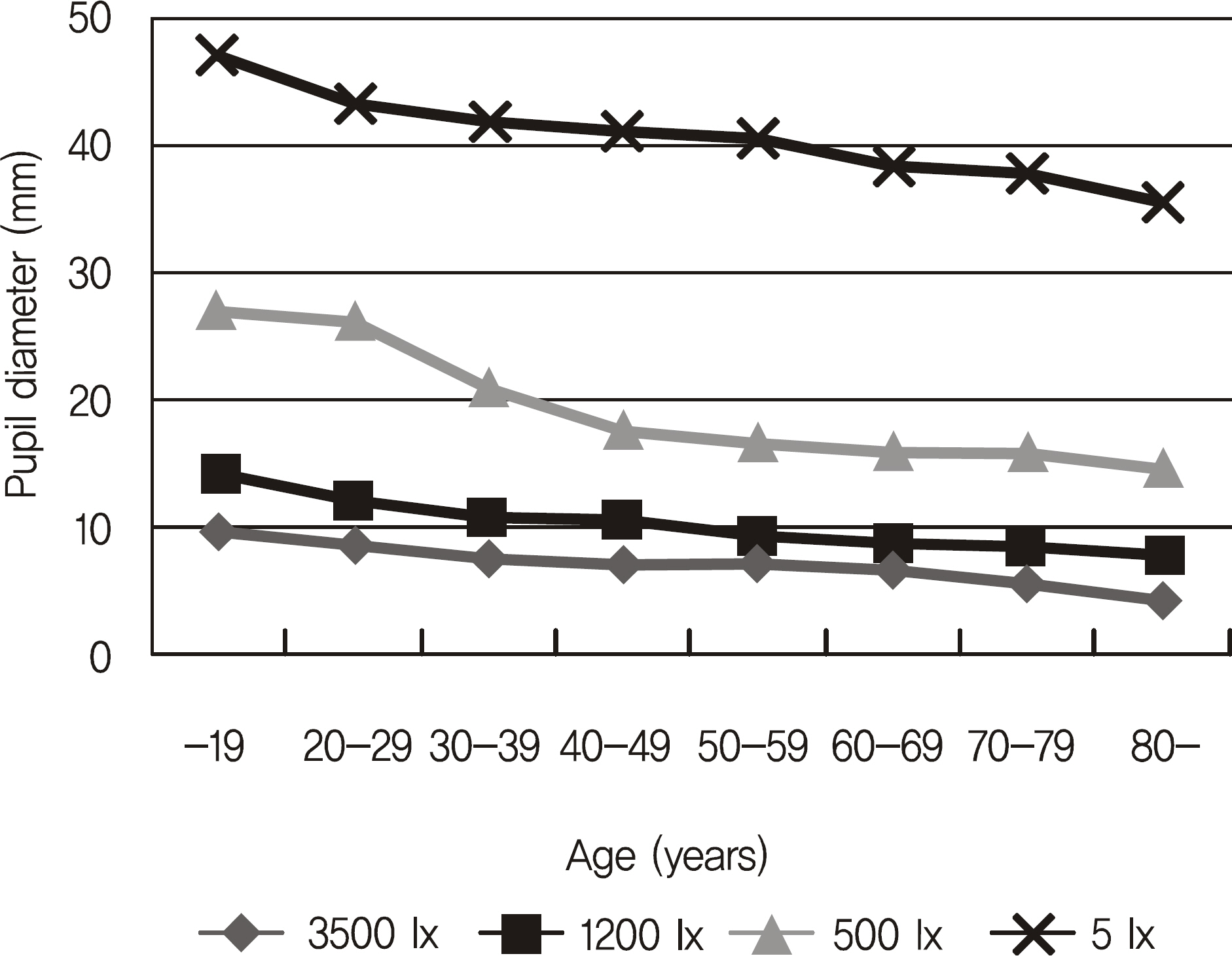
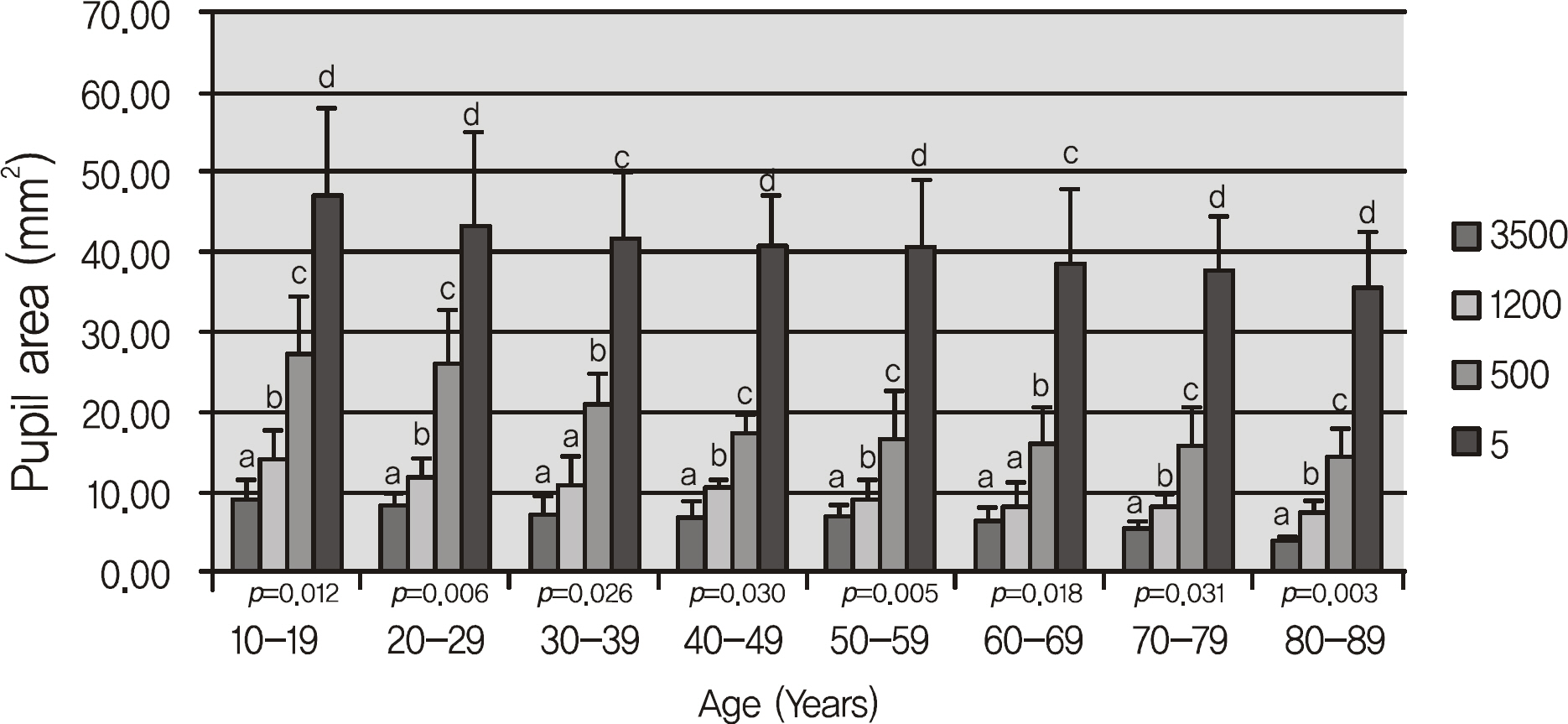
Normal Koreans outpatients who never had a history of ophthalmic disease were examined. The patients consisted of 320 eyes of 160 patients, which were classified into 8 age decades (teenage to 80's) with 40 eyes in each age group. The vertical and horizontal pupil size and area under 4 different illuminances (3,500, 1,200, 500, 5 lux) were measured using the Colvard pupillometer(R) (OASIS Medical, Glendora, CA, USA).
RESULTS
The pupil size was significantly decreased as the age increased under each illuminance. The pupil area measured after dark adaptation was 47.30 mm2 in the teenage group, 43.32 mm2 in the 20's group, 41.94 mm2 in the 30's group, 40.98 mm2 in the 40's group, 40.61 mm2 in the 50's group, 38.60 mm2 in the 60's group, 37.78 mm2 in the 70's group and 35.45 mm2 in the 80's group. The decrease in pupil area was statistically significant.
CONCLUSIONS
In the normal Korean population, a significant decrease in pupil size and area was observed with aging. The present study results provide good basic data for cataract and presbyopia refractive surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Endl MJ, Martinez CE, Klyce SD, et al. Effect of larger ablation zone and transition zone on corneal optical aberrations after photorefractive keratectomy. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001; 119:1159–64.
Article2. Martínez CE, Applegate RA, Klyce SD, et al. Effect of pupillary dilation on corneal optical aberrations after photorefractive keratectomy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998; 116:1053–62.
Article3. Roberts CW, Koester CJ. Optical zone diameters for photorefractive corneal surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993; 34:2275–81.4. Nixon WS. Pupil size refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:1435–6.5. Nakamura K, Bissen-Miyajima H, Oki S, Onuma K. Pupil sizes in different Japanese age groups and the implications for intraocular lens choice. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:134–8.
Article6. Oshika T, Tokunaga T, Samejima T, et al. Influence of pupil diameter on the relation between ocular higher-order aberration and contrast sensitivity after laser in situ keratomileusis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006; 47:1334–8.
Article7. Knorz MC, Koch DD, Martinez-Franco C, Lorger CV. Effect of pupil size and astigmatism on contrast acuity with monofocal and bifocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1994; 20:26–33.
Article8. Freedman KA, Brown SM, Mathews SM, Young RS. Pupil size and the ablation zone in laser refractive surgery: considerations based on geometric optics. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:1924–31.
Article9. Wachler BS, Hiatt D, Chou B, Christie JP. Reduction of pupil size and halos with minus lenses after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Refract Surg. 2004; 20:149–54.
Article10. Helgesen A, Hjortdal J, Ehlers N. Pupil size and night vision dis-turbances after LASIK for myopia. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2004; 82:454–60.
Article11. Koch DD, Samuelson SW, Villarreal R, et al. Changes in pupil size induced by phacoemulsification and posterior chamber lens implantation: consequences for multifocal lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:579–84.
Article12. Koch DD, Samuelson SW, Haft EA, Merin LM. Pupillary size and responsiveness. Implications for selection of a bifocal intraocular lens. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:1030–5.13. Schnitzler EM, Baumeister M, Kohnen T. Scotopic measurement of normal pupils: Colvard versus Video Vision Analyzer infrared pupillometer. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:859–66.
Article14. Rosen ES, Gore CL, Taylor D, et al. Use of a digital infrared pupillometer to assess patient suitability for refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:1433–8.
Article15. Boxer Wachler BS, Krueger RR. Agreement and repeatability of pupillometry using videokeratography and infrared devices. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:35–40.
Article16. Wickremasinghe SS, Smith GT, Stevens JD. Comparison of dynamic digital pupillometry and static measurements of pupil size in determining scotopic pupil size before refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:1171–6.
Article17. Kosaka K, Negishi K, Onuma K, et al. Measurement of pupil diameter under photopic and scotopic conditions using a handheld open-view type digital pupillometer. Atarashii Ganka. 2004; 21:1281–4.18. Kohnen T, Terzi E, Kasper T, et al. Correlation of infrared pupillometers and CCD-camera imaging from aberrometry and videokeratography for determining scotopic pupil size. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:2116–23.
Article19. Chaglasian EL, Akbar S, Probst LE, et al. Pupil measurement using the Colvard pupillometer and a standard pupil card with a cobalt blue filter penlight. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:255–60.
Article20. McDonnell C, Rolincova M, Venter J. Comparison of measurement of pupil sizes among the colvard pupillometer, procyon pupillometer, and NIDEK OPD-scan. J Refract Surg. 2006; 22:S1027–30.
Article21. Hsieh YT, Hu FR. The correlation of pupil size measured by Colvard pupillometer and Orbscan II. J Refract Surg. 2007; 23:789–95.
Article