J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2014 Jun;49(3):177-184.
Lumbar Lordosis Restoration with an Eight Degree Cage in Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Degenerative Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. chokj@inha.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to determine how much lumbar lordosis is restored with an eight degree cage in posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) for degenerative lumbar spinal disease.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 61 patients who underwent PLIF using a metal cage with an eight degree lordotic angle were evaluated. Cases with complications such as subsidence of the cage or instrument failure were excluded from this study. Lumbar lordosis, segmental lordosis, disc height, and bony union were analyzed on the patients' radiographs.
RESULTS
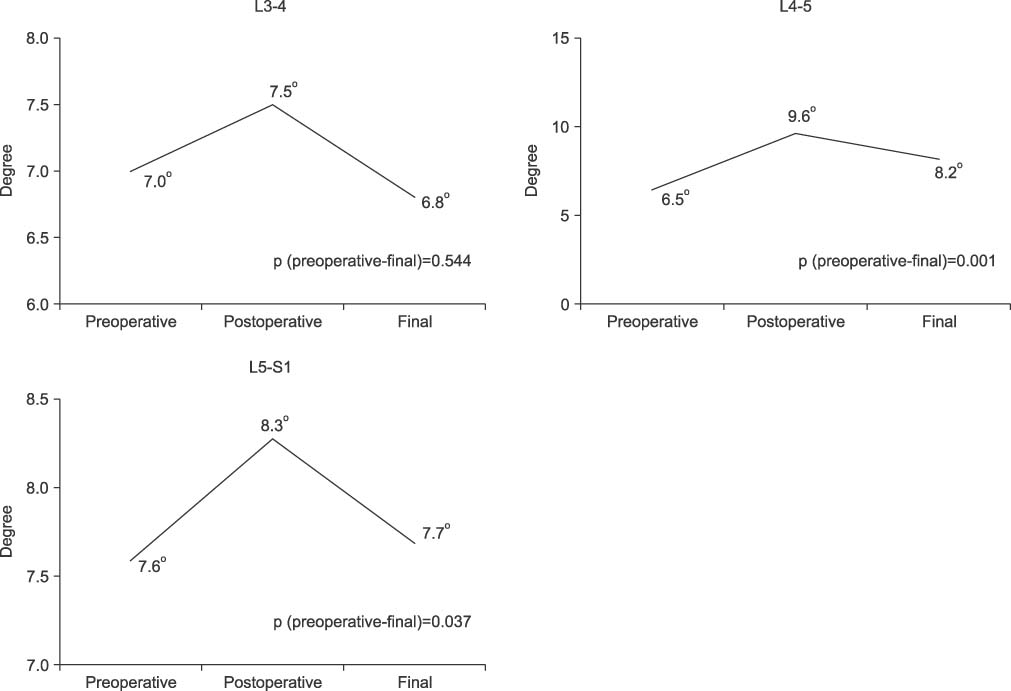
Cages were inserted at L3-4 in 17 patients, L4-5 in 54 patients, and L5-S1 in 20 patients. The number of fused level was 1 segment in 32 patients, 2 segments in 27 patients, and 3 segments in 2 patients. The lumbar lordosis was 33.6degrees before surgery, improved to 37.6degrees after surgery, and then was changed to 37.0degrees at the final follow-up. Segmental lordosis at which the cage was inserted was restored after surgery at L4-5 and L5-S1. Disc height was improved with surgery as well. Satisfactory bony fusion was achieved in 95% of the patients.
CONCLUSION
PLIF using an eight degree lordotic cage for degenerative spinal disease resulted in restoration of lumbar lordosis and segmental lordosis, although these angles showed some loss of correction after surgery.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, Horton W, Berven S, Schwab F. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:2024–2029.
Article2. Cho KJ, Kim KT, Kim WJ, et al. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy in elderly patients with degenerative sagittal imbalance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:E1561–E1566.
Article3. Lagrone MO, Bradford DS, Moe JH, Lonstein JE, Winter RB, Ogilvie JW. Treatment of symptomatic flatback after spinal fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988; 70:569–580.
Article4. Bernhardt M, Bridwell KH. Segmental analysis of the sagittal plane alignment of the normal thoracic and lumbar spines and thoracolumbar junction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989; 14:717–721.
Article5. Lee CS, Oh WH, Chung SS, Lee SG, Lee JY. Analysis of the sagittal alignment of normal spines. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1999; 34:949–954.
Article6. Cho KJ, Kim YT, Park SR, Hong SH. Restoration of lumbar lordosis after posterior lumbar interbody fusion with 4 degree cage in degenerative spinal disease. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2013; 20:51–57.
Article7. Liebensteiner MC, Jesacher G, Thaler M, Gstoettner M, Liebensteiner MV, Bach CM. Restoration and preservation of disc height and segmental lordosis with circumferential lumbar fusion: a retrospective analysis of cage versus bone graft. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011; 24:44–49.8. Yoon YH, Cho KJ, Park SR, Moon KH, Lee TJ, Park HB. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion and unilateral posterolateral fusion with local bone and single cage: comparison with posterolateral lumbar fusion and autologous iliac bone. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2009; 44:102–108.9. Kim JH, Kim SS, Kim JH, Kim BJ. Comparison of monosegment instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion with and without a metal cage in degenerative spine. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2008; 43:143–151.
Article10. Song KJ, Lim YJ, Choi BW, Seo KB. Clinical efficacy of a stand-alone, threaded-titanium fusion cage for single-level degenerative lumbar spinal disorders. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2008; 43:152–159.
Article11. Takahashi H, Suguro T, Yokoyama Y, Iida Y, Terashima F, Wada A. Effect of cage geometry on sagittal alignment after posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative disc disease. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2010; 18:139–142.
Article12. Cho KJ, Moon KH, Kim MK, et al. Changes of clinical outcomes after decompression and fusion for spinal stenosis during 2-year follow-up periods. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2003; 10:113–118.
Article13. Lazennec JY, Ramaré S, Arafati N, et al. Sagittal alignment in lumbosacral fusion: relations between radiological parameters and pain. Eur Spine J. 2000; 9:47–55.
Article14. Kumar MN, Baklanov A, Chopin D. Correlation between sagittal plane changes and adjacent segment degeneration following lumbar spine fusion. Eur Spine J. 2001; 10:314–319.
Article15. Lafage V, Schwab F, Skalli W, et al. Standing balance and sagittal plane spinal deformity: analysis of spinopelvic and gravity line parameters. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33:1572–1578.16. Hioki A, Miyamoto K, Kodama H, et al. Two-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative disc disease: improved clinical outcome with restoration of lumbar lordosis. Spine J. 2005; 5:600–607.
Article17. Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E, Dimnet J. Critères sagittaux de réglaged'une arthrodèse postérieure du rachis. Rachis. 1998; 10:224–226.18. Diedrich O, Perlick L, Schmitt O, Kraft CN. Radiographic spinal profile changes induced by cage design after posterior lumbar interbody fusion preliminary report of a study with wedged implants. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:E274–E280.19. Kim EH, Lee JH, Sihn DH, Kim YE, Jae HW. Factors affecting segmental lordotic angle after posterior lumbar interbody fusion using metal cage. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2005; 12:316–323.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Restoration of Lumbar Lordosis After Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion with 4 Degree Cage in Degenerative Spinal Disease
- Restoration of Segmental Lordosis and Related Factors in Interbody Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Disease
- Minimally Invasive Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Indications, Outcomes and Complications
- Anterior Interbody Fusion using a Horizontal Cylinder Cage in a Degenerative Lumbar Spine
- Efficacy of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion using PEEK Cage and Pedicle Screw Stabilization in Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Disorders: Minimum 3 Years Follow up Results