J Periodontal Implant Sci.
2013 Dec;43(6):301-307.
The effect of pretreating resorbable blast media titanium discs with an ultrasonic scaler or toothbrush on the bacterial removal efficiency of brushing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate School of Clinical Dental Science, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Periodontics, Seoul St Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ko_y@catholic.ac.kr
- 3Department of Oral Microbiology and Immunology, Seoul National University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
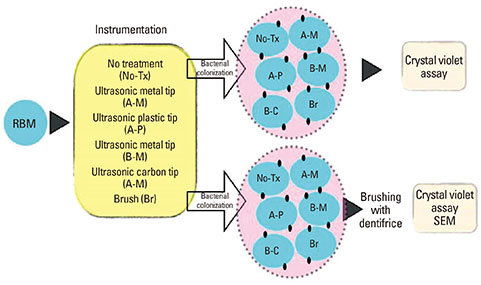
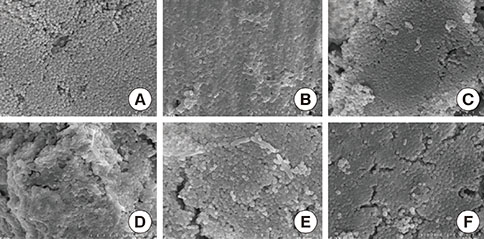
This in vitro study was performed to assess the adherence of Porphyromonas gingivalis to a resorbable blast media (RBM) titanium surface pretreated with an ultrasonic scaler or toothbrush and to evaluate the effects of the treatment of the RBM titanium discs on the bacterial removal efficiency of brushing by crystal violet assay and scanning electron microscopy.
METHODS
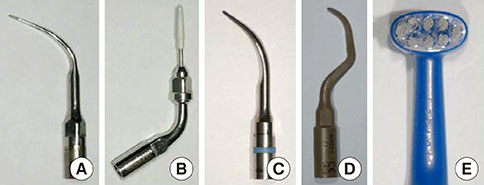
RBM titanium discs were pretreated with one of several ultrasonic scaler tips or cleaned with a toothbrush. Then the titanium discs were incubated with P. gingivalis and the quantity of adherent bacteria was compared. The disc surfaces incubated with bacteria were brushed with a toothbrush with dentifrice. Bacteria remaining on the disc surfaces were quantified.
RESULTS
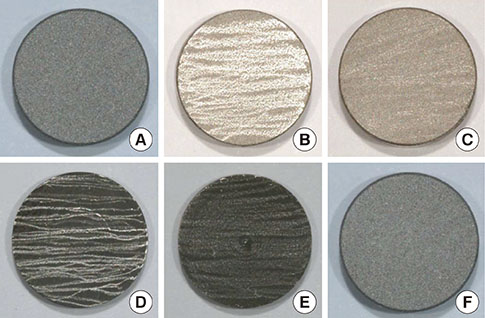
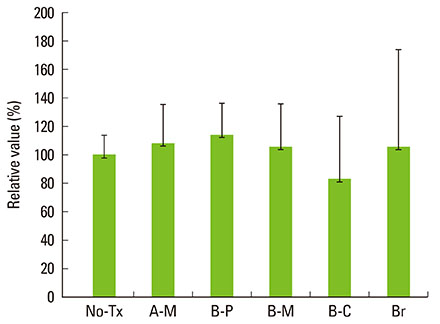
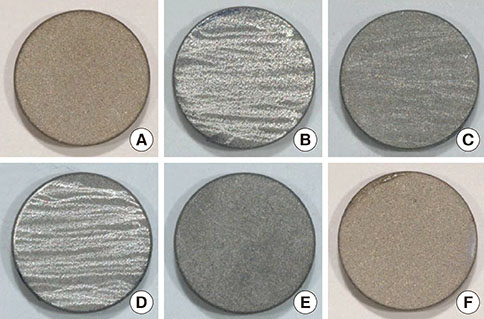
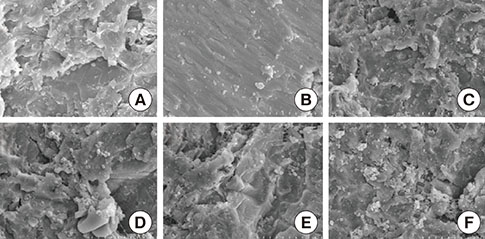
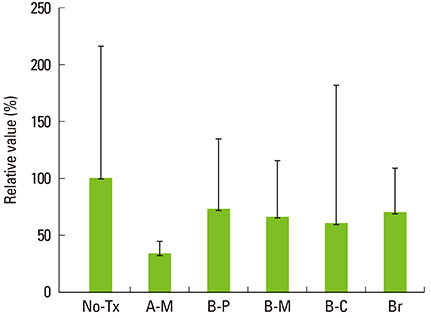
A change in morphology of the surface of the RBM titanium discs after different treatments was noted. There were no significant differences in the adherence of bacteria on the pretreated discs according to the treatment modality. Pretreatment with various instruments did not produce significant differences in the bacterial removal efficiency of brushing with dentifrice.
CONCLUSIONS
Within the limits of this study, various types of mechanical instrumentation were shown to cause mechanical changes on the RBM titanium surface but did not show a significant influence on the adherence of bacteria and removal efficiency of brushing.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lindholm-Sethson B, Ardlin BI. Effects of pH and fluoride concentration on the corrosion of titanium. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008; 86:149–159.
Article2. Groessner-Schreiber B, Hannig M, Duck A, Griepentrog M, Wenderoth DF. Do different implant surfaces exposed in the oral cavity of humans show different biofilm compositions and activities? Eur J Oral Sci. 2004; 112:516–522.
Article3. Alhag M, Renvert S, Polyzois I, Claffey N. Re-osseointegration on rough implant surfaces previously coated with bacterial biofilm: an experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008; 19:182–187.
Article4. Baffone W, Sorgente G, Campana R, Patrone V, Sisti D, Falcioni T. Comparative effect of chlorhexidine and some mouthrinses on bacterial biofilm formation on titanium surface. Curr Microbiol. 2011; 62:445–451.
Article5. Cooper LF. A role for surface topography in creating and maintaining bone at titanium endosseous implants. J Prosthet Dent. 2000; 84:522–534.
Article6. Elias CN, Meirelles L. Improving osseointegration of dental implants. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2010; 7:241–256.
Article7. Franco M, Rigo L, Viscione A, De Santis B, Tropina E, Brunelli G, et al. CaPO4 blasted implants inserted into iliac crest homologue frozen grafts. J Oral Implantol. 2009; 35:176–180.
Article8. Sanz A, Oyarzun A, Farias D, Diaz I. Experimental study of bone response to a new surface treatment of endosseous titanium implants. Implant Dent. 2001; 10:126–131.
Article9. Nishimoto SK, Nishimoto M, Park SW, Lee KM, Kim HS, Koh JT, et al. The effect of titanium surface roughening on protein absorption, cell attachment, and cell spreading. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008; 23:675–680.10. Pae A, Kim SS, Kim HS, Woo YH. Osteoblast-like cell attachment and proliferation on turned, blasted, and anodized titanium surfaces. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011; 26:475–481.11. Piattelli M, Scarano A, Paolantonio M, Iezzi G, Petrone G, Piattelli A. Bone response to machined and resorbable blast material titanium implants: an experimental study in rabbits. J Oral Implantol. 2002; 28:2–8.
Article12. Gonshor A, Goveia G, Sotirakis E. A prospective, multicenter, 4-year study of the ACE Surgical resorbable blast media implant. J Oral Implantol. 2003; 29:174–180.
Article13. Badihi Hauslich L, Sela MN, Steinberg D, Rosen G, Kohavi D. The adhesion of oral bacteria to modified titanium surfaces: role of plasma proteins and electrostatic forces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013; 24:Suppl A100. 49–56.
Article14. Drake DR, Paul J, Keller JC. Primary bacterial colonization of implant surfaces. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999; 14:226–232.15. Takasaki AA, Aoki A, Mizutani K, Kikuchi S, Oda S, Ishikawa I. Er:YAG laser therapy for peri-implant infection: a histological study. Lasers Med Sci. 2007; 22:143–157.
Article16. Kawashima H, Sato S, Kishida M, Yagi H, Matsumoto K, Ito K. Treatment of titanium dental implants with three piezoelectric ultrasonic scalers: an in vivo study. J Periodontol. 2007; 78:1689–1694.
Article17. Park JB, Kim N, Ko Y. Effects of ultrasonic scaler tips and toothbrush on titanium disc surfaces evaluated with confocal microscopy. J Craniofac Surg. 2012; 23:1552–1558.
Article18. Sato S, Kishida M, Ito K. The comparative effect of ultrasonic scalers on titanium surfaces: an in vitro study. J Periodontol. 2004; 75:1269–1273.
Article19. Rupf S, Idlibi AN, Marrawi FA, Hannig M, Schubert A, von Mueller L, et al. Removing biofilms from microstructured titanium ex vivo: a novel approach using atmospheric plasma technology. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e25893.
Article20. Pereira da Silva CH, Vidigal GM Jr, de Uzeda M, de Almeida Soares G. Influence of titanium surface roughness on attachment of Streptococcus sanguis: an in vitro study. Implant Dent. 2005; 14:88–93.
Article21. Park JB, Jang YJ, Koh M, Choi BK, Kim KK, Ko Y. In vitro analysis of the efficacy of ultrasonic scalers and a toothbrush for removing bacteria from resorbable blast material titanium disks. J Periodontol. 2013; 84:1191–1198.
Article22. Hotta M, Sekine I, Imade S, Sano A. Evaluation of tapered-end toothbrush bristles regarding efficacy of access to occlusal fissures. J Clin Dent. 2002; 13:225–227.23. Stiller S, Bosma ML, Shi X, Spirgel CM, Yankell SL. Interproximal access efficacy of three manual toothbrushes with extended, x-angled or flat multitufted bristles. Int J Dent Hyg. 2010; 8:244–248.
Article24. Fais LM, Fernandes-Filho RB, Pereira-da-Silva MA, Vaz LG, Adabo GL. Titanium surface topography after brushing with fluoride and fluoride-free toothpaste simulating 10 years of use. J Dent. 2012; 40:265–275.
Article25. Molina C, Nogues L, Martinez-Gomis J, Peraire M, Salsench J, Sevilla P, et al. Dental casting alloys behaviour during power toothbrushing with toothpastes of various abrasivities. Part II: corrosion and ion release. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008; 19:3015–3019.
Article26. Hossain A, Okawa S, Miyakawa O. Effect of toothbrushing on titanium surface: an approach to understanding surface properties of brushed titanium. Dent Mater. 2006; 22:346–352.
Article27. Siirila HS, Kononen M. The effect of oral topical fluorides on the surface of commercially pure titanium. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1991; 6:50–54.28. Hossain A, Okawa S, Miyakawa O. Surface texture and composition of titanium brushed with toothpaste slurries of different pHs. Dent Mater. 2007; 23:186–192.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A comparative study for the efficacy of plaque removal of two powered toothbrushes and a manual toothbrush
- The effect of working parameters on removal of casting gold alloy using a piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler with scaler tip in vitro
- Research on plaque removal by sonic toothbrush for patients with a fixed orthodontic appliance
- The Effect of a Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Scaler with Curette Tip on Casting Gold Removal in Vitro
- The Effects of a Er:YAG Laser on Machined, Sand-Blasted and Acid-Etched, and Resorbable Blast Media Titanium Surfaces Using Confocal Microscopy and Scanning Electron Microscopy