J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2011 Oct;37(5):380-385.
Bone regeneration of the fluoridated hydroxyapatite and the bio-glass in the rabbit cranium defect model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea. kkwoms@dku.edu
Abstract
- INTRODUCTION
Hydroxyapatite (Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, HA) is the main inorganic phase of human hard tissue that is used widely as the repair material for bones. When HA is applied to a bony defect, however, it can be encapsulated with fibrous tissue and float in the implanted area due to a lack of consolidation. Bioceramics as allogenic graft materials are added to HA to improve the rate and bone healing capacity. Fluoridated hydroxyapatite (Ca10(PO4)6(OH,F)2, FHA), where F- partially replaces the OH- in hydroxyapatite, is considered a good alternative material for bone repair owing to its solubility and biocompatibility.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was designed to determine the bone healing capacity of FHA newly produced as a nanoscale fiber in the laboratory. HA and FHA with bioglass was implanted in a rabbit cranium defect and the specimen was analysed histologically.
RESULTS
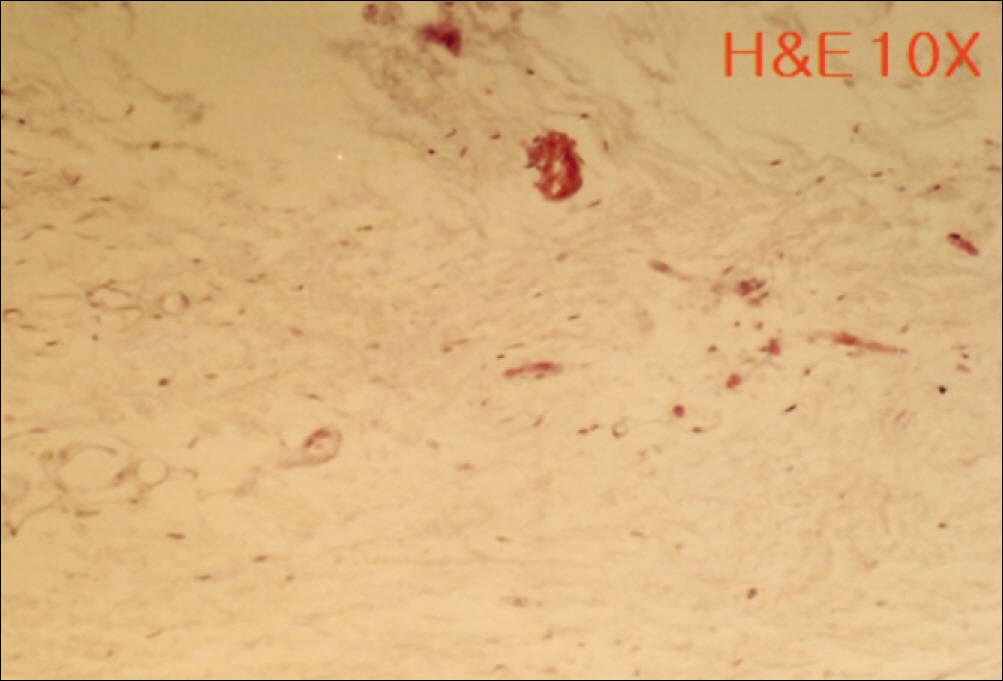
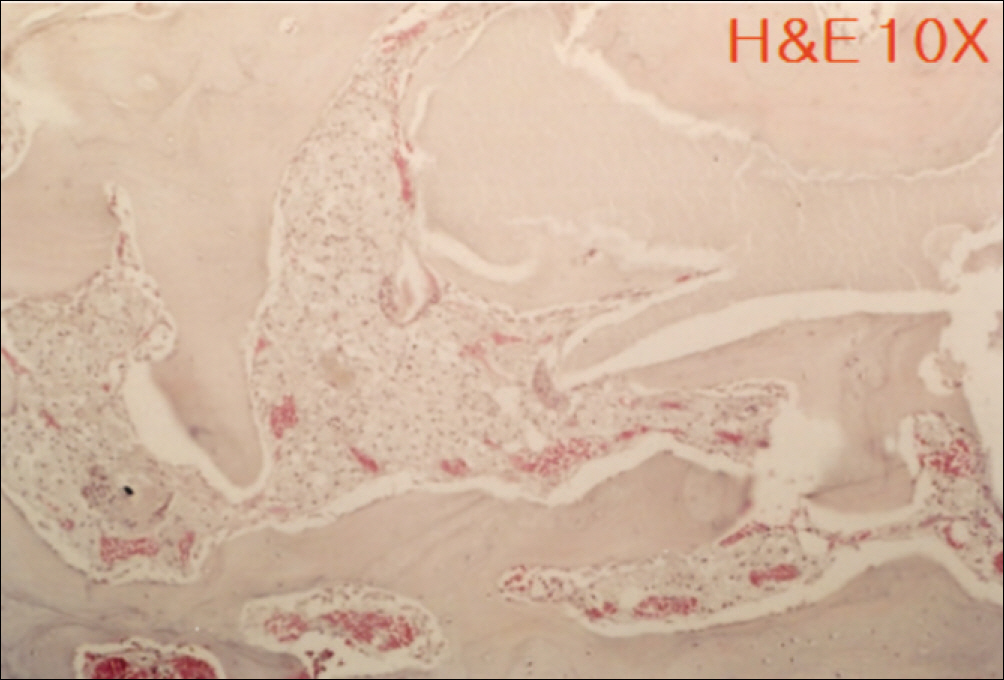
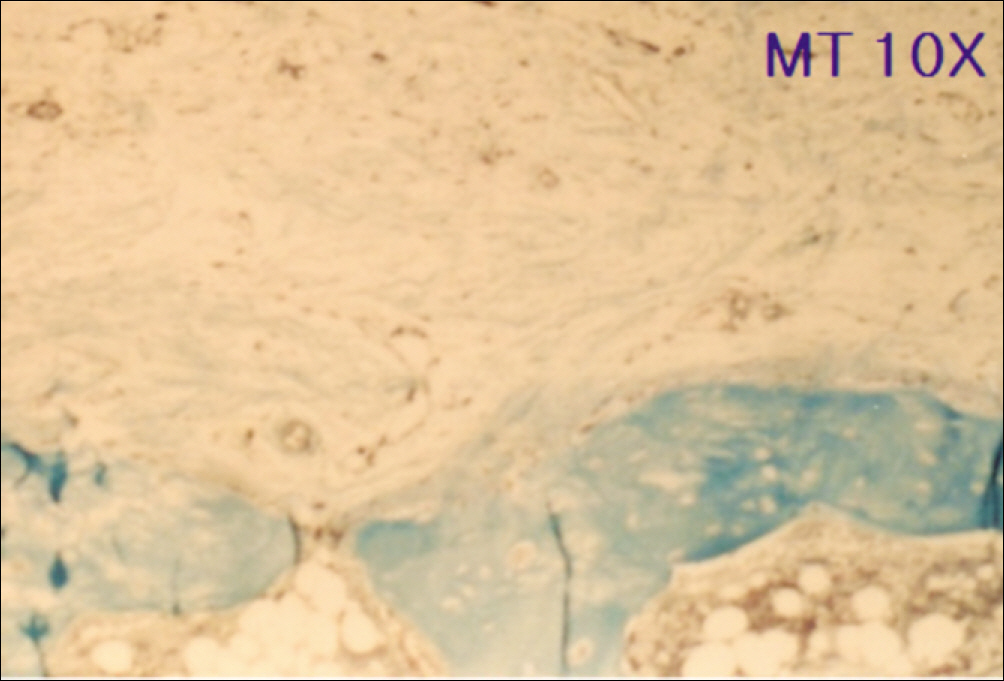
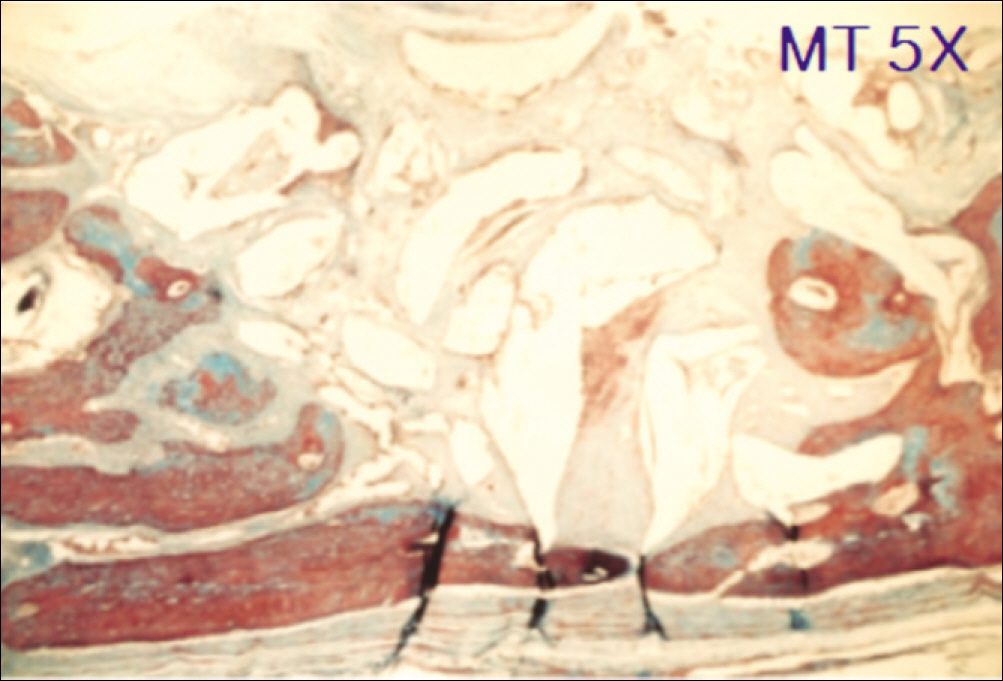
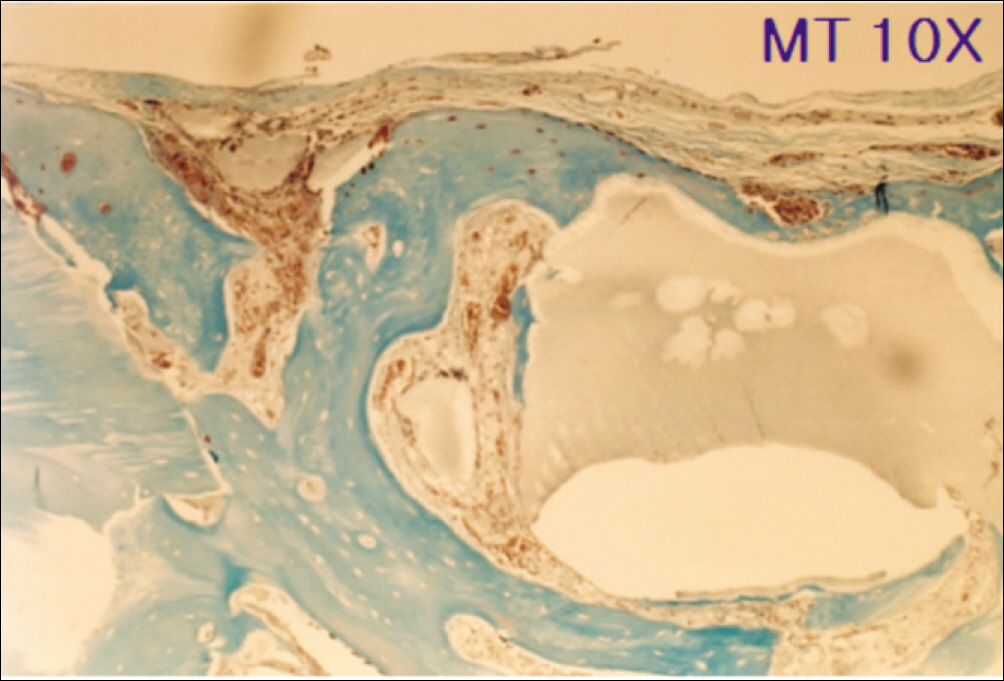
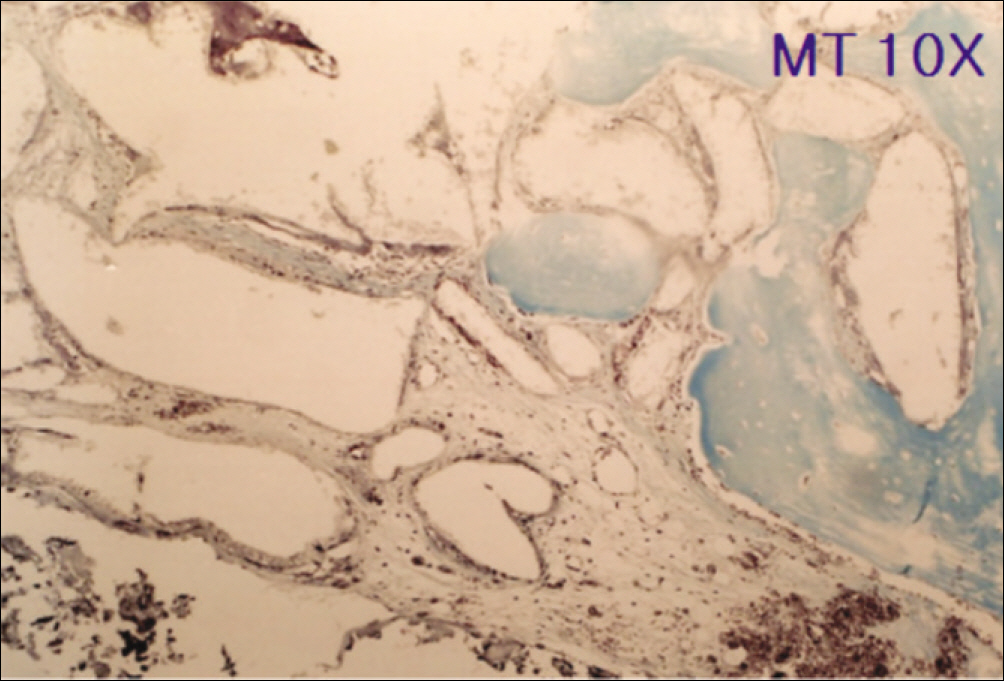
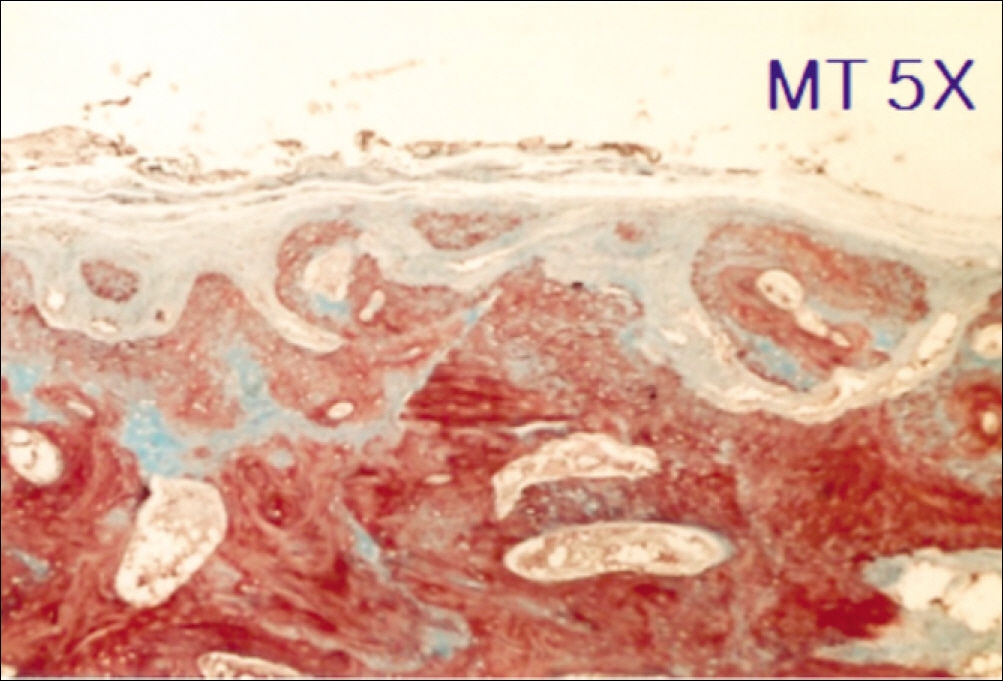
1. At 4 weeks, fibrous connective tissue and little bone formation was observed around the materials of the experimental group I implanted HA and bioglass. Newly formed bone was observed around the materials in the experimental group II implanted FHA and bioglass. 2. At 8 weeks, the amount of newly formed and matured bone was higher in experimental group II than in experimental group I and the control group.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that FHA and bioglass is a relatively favorable bone substitute with biocompatibility and better bone healing capacity than pure HA and bioglass.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Boyne PJ. Induction of bone repair by various bone grafting materials. Elliott K, Fitzsimons DW, Boyne PJ, editors. Hard Tissue Growth, Repair and Remineralization(Ciba Foundation Symposium 11). New York: Associated Scientific Publishers;1973. p. 121–5.2. Costantino PD, Friedman CD. Synthetic bone graft substitutes. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1994; 27:1037–42.
Article3. Oreamuno S, Lekovic V, Kenney EB, Carranza FA Jr, Takei HH, Prokic B. Comparative clinical study of porous hydroxyapatite and decalcified freeze-dried bone in human periodontal defects. J Periodontol. 1990; 61:399–405.
Article4. Papay FA, Morales L Jr, Ahmed OF, Neth D, Reger S, Zins J. Comparison of ossification of demineralized bone, hydroxyapatite, Gelfoam, and bone wax in cranial defect repair. J Craniofac Surg. 1996; 7:347–51.
Article5. Driessens FC. Relation between apatite solubility and anti-cariogenic effect of fluoride. Nature. 1973; 243:420–1.
Article6. Okazaki M, Miake Y, Tohda H, Yanagisawa T, Matsumoto T, Takahashi J. Functionally graded fluoridated apatites. Biomaterials. 1999; 20:1421–6.
Article7. LeGeros RZ, Silverstone LM, Daculsi G, Kerebel LM. In vitro caries-like lesion formation in F-containing tooth enamel. J Dent Res. 1983; 62:138–44.
Article8. Marie PJ, De Vernejoul MC, Lomri A. Stimulation of bone formation in osteoporosis patients treated with fluoride associated with increased DNA synthesis by osteoblastic cells in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 1992; 7:103–13.
Article9. Kim HW, Kim HE. Nanofiber generation of hydroxyapatite and fluor-hydroxyapatite bioceramics. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2006; 77:323–8.
Article10. Katagiri T, Takahashi N. Regulatory mechanisms of osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. Oral Dis. 2002; 8:147–59.
Article11. Lynch SE, Genco RJ, Marx RE. Tissue Engineering. Applications in Maxillofacial Surgery and Periodontics. Chicargo: Quintessence Publishing Group;1999.12. Frost HM. Bone remodelling Dynamics. Springfield: Thomas CC;1963.13. Frost HM. Intermediary Organization of the Skeleton. BocaRaton: CRC Press;1986.14. Robling AG, Castillo AB, Turnern CH. Biomechanical and molecular regulation of bone remodeling. Ann Rev Biomed Eng. 2006; 8:455–98.
Article15. Canalis E, Economides AN, Gazzerro E. Bone morphogenetic proteins, their antagonists, and the skeleton. Endocr Rev. 2003. 24. : 218–35.
Article16. Glowacki J, Mulliken JB. Induced osteogenesis for repair and construction in the craniofacial region. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1980; 65:553–60.17. Kaban LB, Mulliken JB, Glowacki J. Treatment of jaws defects with demineralized bone implants. J Oral Maxillfac Surg. 1982; 40:623–6.18. Einhorn TA, Lane JM, Burstein AH, Kopman CR, Vigorita VJ. The healing of segmental bone defects induced by demineralized bone matrix. A radiographic and biomechanical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984; 66:274–9.
Article19. Fenter AE, Hartigan MS, Low SB. Periodontal repair using PerioGlas in nonhuman primates: clinical and histologic observations. Compendium. 1994; 15(932):935–8.21. Rho KS, Han SJ, Kim CH, Kim KW. Bone healing capacity of the new fluoridated hydroxyapatite in the rabbit cranium defect. J Korean Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 33:464–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bone healing capacity of the new fluoridated hydroxyapatite in the rabbit cranium defect
- The effects of bone regeneration in rabbit calvarial defect with particulated and block type of hydroxyapatite
- The Effect of a Hydroxyapatite and 4-hexylresorcinol Combination Graft on Bone Regeneration in the Rabbit Calvarial Defect Model
- A Comparative Study on Regeneration of Bone Defects after the Grafts of Demineralized Bone Matrix and Hydroxyapatite
- THE EFFECT OF BIOACTIVE GLASS AND A RESORBABLE MEMBRANE ON BONE REGENERATION OF THE MANDIBULAR BONE DEFECTS IN RABBIT