J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2010 Oct;36(5):360-365.
Demyelination of neurofilament protein 200 immune positive never fibers in human pulp
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. shalee@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral Histology and Anatomy, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
Abstract
- INTRODUCTION
Mammalian tooth pulp is densely innervated by sensory nerves that are mostly C fibers and A delta fibers. However, there is evidence suggesting that many unmyelinated axons in the pulp are in fact parent meylinated axons.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
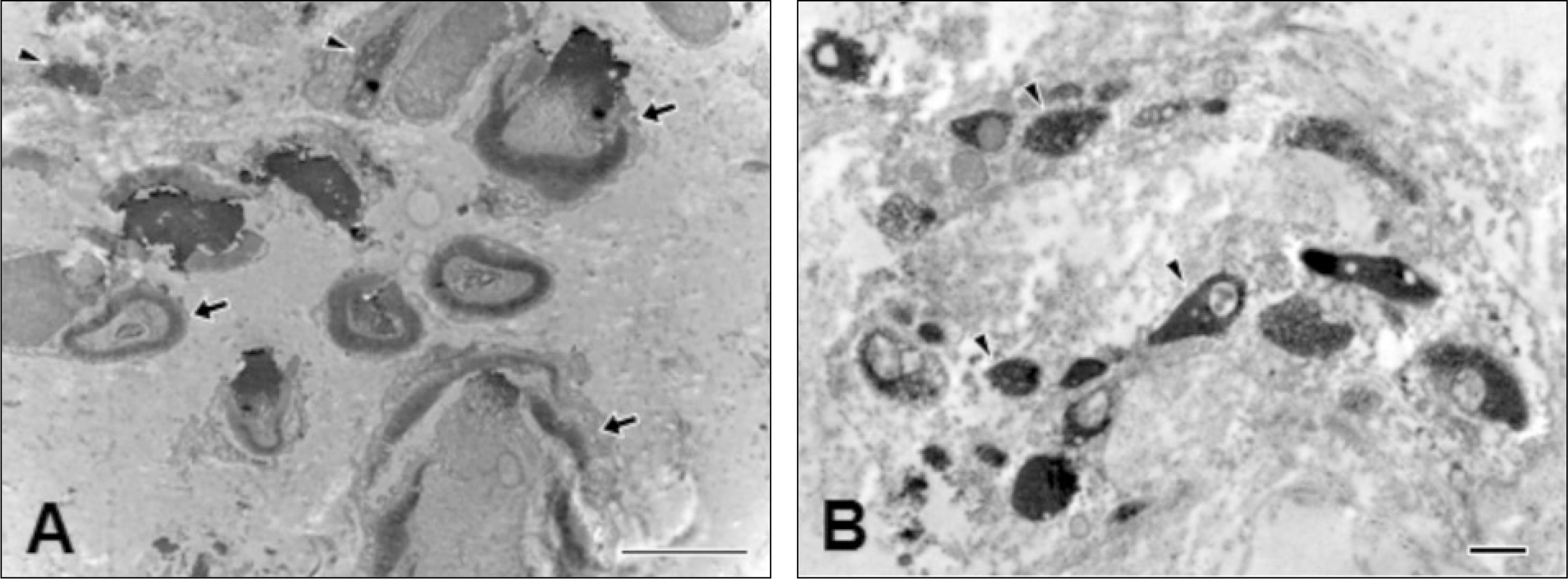
The pulp was removed from healthy premolars and 3rd molars extracted from juveniles and adults undergoing orthodontic treatment, and immunohistochemical staining were applied with NPF200 antibodies, which specifically dye myelinated axons. The specimens underwent an electron microscopy examination with diaminobenzidine (DAB) immunostaining after observation and analysis by fluorescence and confocal laser scanning microscopy.
RESULTS
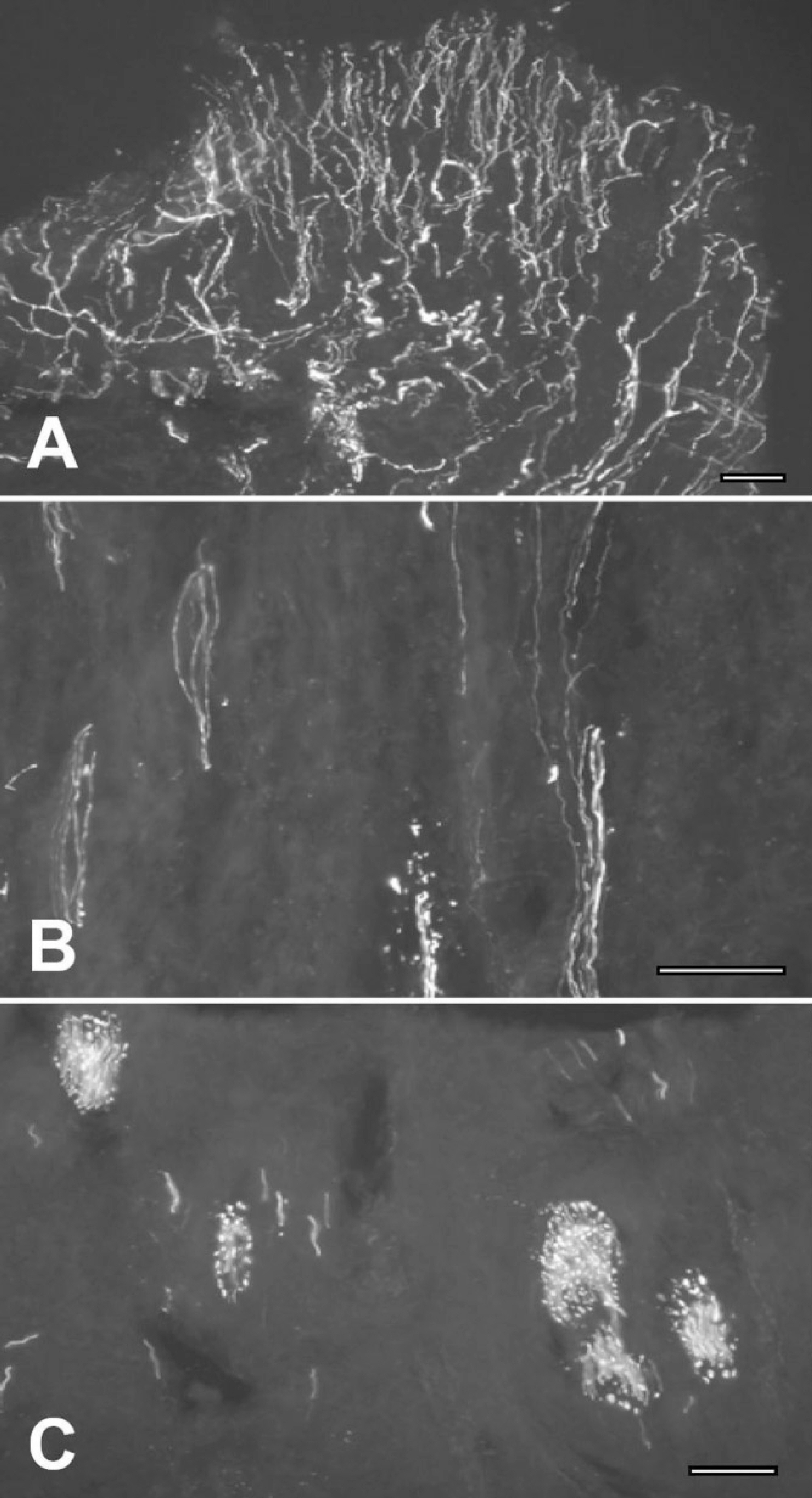
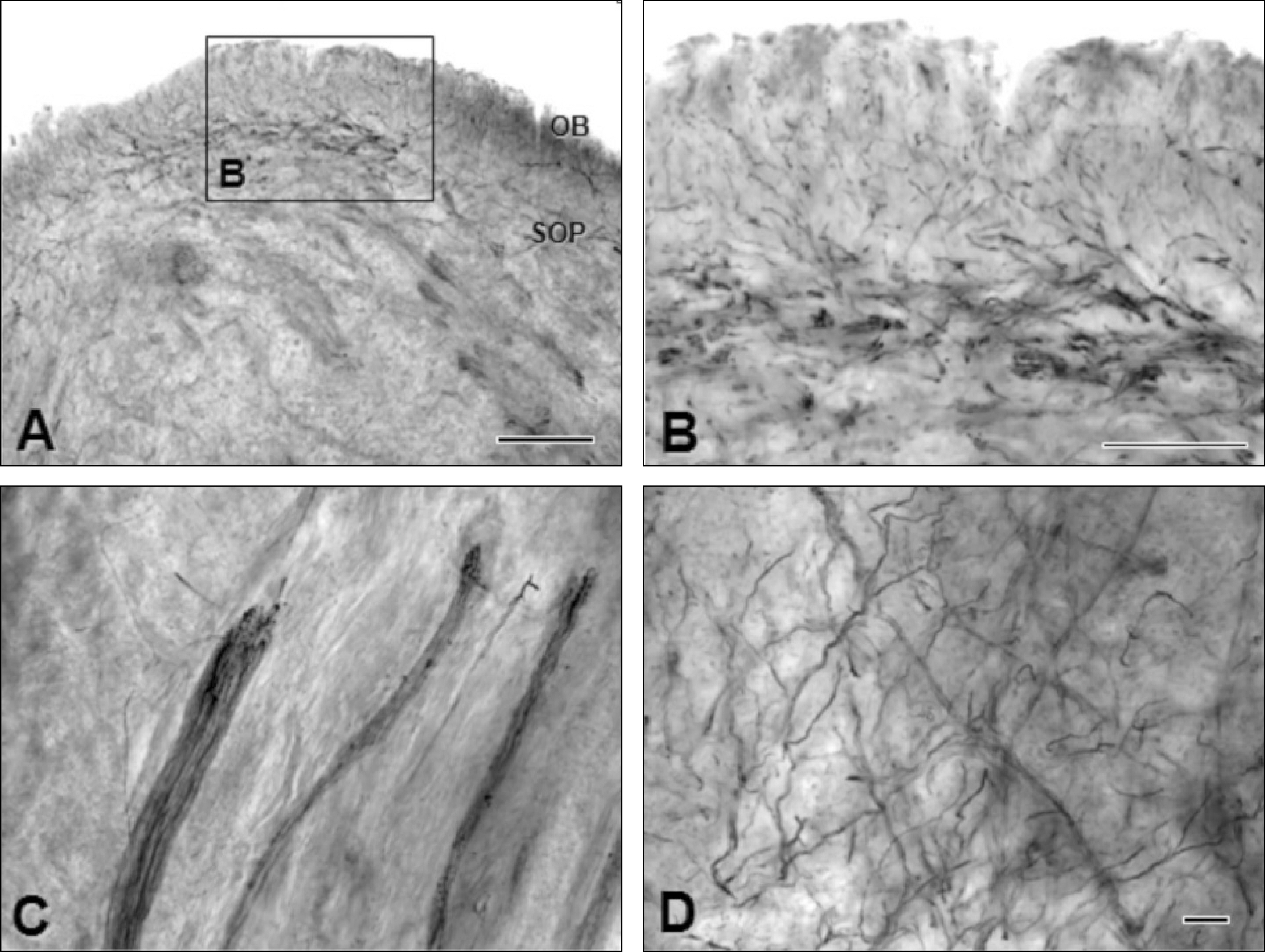
The NPF200 immuno-positive axons in the radicular pulp areas were observed as bundles of many nerve fibers. Many small bundles were formed with fewer axons when firing to the coronal pulp areas and then reachrd a different direction.
CONCLUSION
Myelinated fibers innervated to the dental pulp maintain their myelins in the radicular portion, but these fibers lost myelins in the coronal portion. Afterthe loss of myelin, the size of the axoplasm also decreased.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Byers MR. Detal sensory receptors. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1984; 25:39–94.2. Hildebrand C, Fried K, Tuisku F, Johansson CS. Teeth and tooth nerves. Prog Neurobiol. 1995; 45:165–222.
Article3. Holland GR, Robinson PP. The number and size of axons at the apex of the cat's canine tooth. Anat Rec. 1983; 205:215–22.
Article4. Reader A, Foreman DW. An ultrastructural quantitative investigation of human intradental innervation. J Endod. 1981; 7:493–9.
Article5. Holje L, Hildebrand C, Fried K. Proportion of unmyelinated axons in the rat inferior alveolar nerve and mandibular molar pulps after neonatal administration of capsaicin. Brain Res. 1983; 266:133–6.
Article6. Horiuchi H. A study of pulp-nerve excitation through a silver-wire electrode. J Dent Res. 1965; 44:1257–63.
Article7. Lisney SJ. Some anatomical and electrophysiological properties of tooth-pulp afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1978; 284:19–36.
Article8. Cadden SW, Lisney SJ, Matthews B. Thresholds to electrical stimulation of nerves in cat canine tooth-pulp with A beta-, A delta- and C-fibre conduction velocities. Brain Res. 1983; 261:31–41.9. Fried K, Hildebrand C. Axon number and size distribution in the developing feline inferior alveolar nerve. J Neurol Sci. 1982; 53:169–80.
Article10. Johansson CS, Hildebrand C, Povlsen B. Anatomy and developmental chronology of the rat inferior alveolar nerve. Anat Rec. 1992; 234:144–52.
Article11. Paik SK, Park KP, Lee SK, Ma SK, Cho YS, Kim YK, et al. Light and electron microscopic analysis of the somata and parent axons innervating the rat upper molar and lower incisor pulp. Neuroscience. 2009; 162:1279–86.
Article12. Holland GR. Fibre numbers and sizes in the inferior alveolar nerve of the cat. J Anat. 1978; 127:343–52.13. Hirvonen TJ. A quantitative electron-microscopic analysis of the axons at the apex of the canine tooth pulp in the dog. Acta Anat (Basel). 1987; 128:134–9.
Article14. Nair PN, Luder HU, Schroeder HE. Number and size-spectra of myelinated nerve fibers of human premolars. Anat Embryol (Berl). 1992; 186:563–71.
Article15. Naftel JP, Bernanke JM, Qian XB. Quantitative study of the apical nerve fibers of adult and juvenile rat molars. Anat Rec. 1994; 238:507–16.
Article16. Elder GA, Friedrich VL Jr, Bosco P, Kang C, Gourov A, Tu PH, et al. Absence of the mid-sized neurofilament subunit decreases axonal calibers, levels of light neurofilament (NF-L), and neurofilament content. J Cell Biol. 1998; 141:727–39.
Article17. Lawson SN, Waddell PJ. Soma neurofilament immunoreactivity is related to cell size and fibre conduction velocity in rat primary sensory neurons. J Physiol. 1991; 435:41–63.
Article18. Dirajlal S, Pauers LE, Stucky CL. Differential response properties of IB(4)-positive and -negative unmyelinated sensory neurons to protons and capsaicin. J Neurophysiol. 2003; 89:513–24.
Article19. Amaya F, Decosterd I, Samad TA, Plumpton C, Tate S, Mannion RJ, et al. Diversity of expression of the sensory neuron-specific TTX-resistant voltage-gated sodium ion channels SNS and SNS2. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2000; 15:331–42.
Article20. Beland B, Fitzgerald M. Mu- and delta-opioid receptors are downregulated in the largest diameter primary sensory neurons during postnatal development in rats. Pain. 2001; 90:143–50.
Article21. Bennett DL, Michael GJ, Ramachandran N, Muson JB, Averill S, Yan Q, et al. A distinct subgroup of small DRG cells express GDNF receptor components and GDNF is protective for these neurons after nerve injury. J Neurosci. 1998; 18:3059–72.
Article22. Benn SC, Costigan M, Tate S, Fitzgerald M, Woolf CJ. Developmental expression of the TTX-resistant voltage-gated sodium channels Nav1.8 (SNS) and Nav1.9 (SNS2) in primary sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 2001; 21:6077–85.
Article23. Naftel JP, Richards LP, Pan M, Bernanke JM. Course and composition of the nerves that supply the mandibular teeth of the rat. Anat Rec. 1999; 256:433–47.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Neurofilament Protein in the Nerve of Human Cornea
- The Ultrastructure of TRPV1-positive Nerve Terminals in the Human Tooth Pulp
- Neurochemical Properties of Dental Primary Afferent Neurons
- Expression of Neurofilament in Human Retinal Horizontal Cell by Immunogold Labeling
- Expression of P2X3 and its colocalization with trpv1 in the human dental pulp