Korean J Community Nutr.
2016 Jun;21(3):237-246. 10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.3.237.
Effect of a Worksite-based Dietary Intervention Program for the Management of Metabolic Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. hoonyoon@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Research Institute of Human Ecology, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2328092
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2016.21.3.237
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
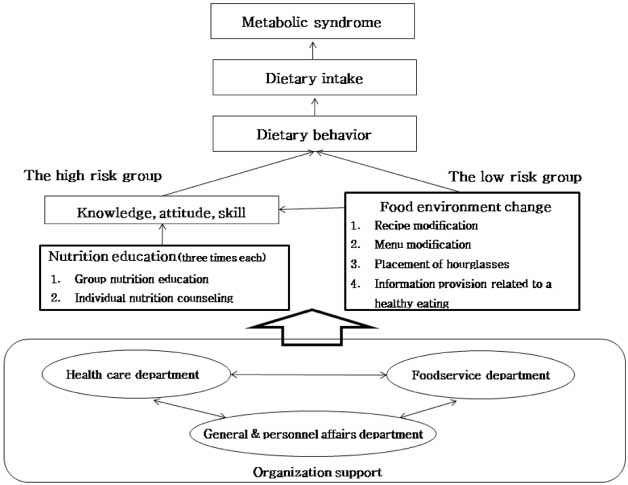
To investigate the effect of a worksite-based dietary intervention program for the management of metabolic syndrome (MS) among male employees.
METHODS
A dietary intervention program combining individual and environmental approach was implemented targeting white-collar employees at a worksite located in Seoul for 10 weeks. Out of 104 employees having agreed to participate in the program, those having three or more out of five components of MS and having two components, including a waist circumference component were classified into "the high risk group" (n=41) and received group nutrition education and individual nutrition counseling three times each. The rest of the study subjects were considered as "the low risk group" (n=63). The food environment at the worksite, where both the high and low risk groups were exposed, was changed to promote healthy eating. Physical data including MS components were collected and a questionnaire on dietary behaviors was administered before and after the intervention. The data from the high risk group (n=17) and the low risk group (n=20), excluding the subjects ineligible for or failed to complete the study (n=67), were analyzed. The difference before and after intervention was tested for significance by Wilcoxon signed-rank tests.
RESULTS
Weight, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, blood pressure, HDL-cholesterol, and HbA1c and the healthy dietary practice score improved significantly after intervention in the high risk group. The median number of MS components decreased significantly from 3.0 to 1.0 in the high risk group. In the low risk group, only HbA1c significantly decreased. Conclusions: The 10-week worksite-based dietary intervention program combining individual and environmental approach was found to be effective for managing MS of male employees.
CONCLUSIONS
The 10-week worksite-based dietary intervention program combining individual and environmental approach was found to be effective for managing MS of male employees.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Inverse association of improved adherence to dietary guidelines with metabolic syndrome: the Seoul Metabolic Syndrome Management program
Dongwoo Ham, YoungYun Cho, Mi-Suk Park, Yun-Sug Park, Sun-Young Kim, Hye-Min Seol, Yoo Mi Park, Sunok Woo, Hyojee Joung, Do-Sun Lim
Nutr Res Pract. 2020;14(6):621-636. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2020.14.6.621.
Reference
-
1. Hong AR, Lim S. Clinical characteristics of metabolic syndrome in Korea, and its comparison with other Asian countries. J Diabetes Investig. 2015; 6(5):508–515.2. Mozumdar A, Liguori G. Persistent increase of prevalence of metabolic syndrome amongadults: NHANES III to NHANES 1999-2006. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34(1):216–219.3. Okafor CI. The metabolic syndrome in Africa: current trends. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 16(1):56–66.4. Lim S, Shin H, Song JH, Kwak SH, Kang SM, Yoon JW. Increasing prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korea - the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for 1998-2007. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34(6):1323–1328.5. Korean Diabetes Association, National Health Insurance Service. Korean Diabetes Fact Sheet 2015 [Internet]. Korean Diabetes Association;2015. cited 2015 Jan 10. Available from: http://www.diabetes.or.kr.6. Ryu S, Song J, Choi BY, Lee SJ, Kim WS, Chang YS. Incidence and risk factors for metabolic syndrome in Korean male workers, ages 30 to 39. Ann Epidemiol. 2007; 17(4):245–252.7. Story M, Kaphingst KM, Robinson-O'Brien R, Glanz K. Creating healthy food and eating environments: policy and environmental approaches. Annu Rev Public Health. 2008; 29:253–272.8. Kim YS. The employment effect of extended working hours limit [internet]. Korea Labor & Society Institute;2015. cited 2015 Nov 29. Available from: http://klsi.org/.9. Lee MS, Kang HJ, Oh HS, Paek YM, Choue RW, Park YK. Effects of worksite nutrition counseling for health promotion; twelve-weeks of nutrition counseling has positive effect on metabolic syndrome risk factors in male workers. Korean J Community Nutr. 2008; 13(1):46–61.10. Oh HS, Jang M, Hwang MO, Cho SW, Paek YM, Choi TI. Effect of 1 year e-mail nutrition education after face-to-face encounter at worksite: changes in cardiovascular risk factors. Korean J Nutr. 2009; 42(6):559–566.11. Park SY, Yang YJ, Kim YR. Effects of nutrition education using a ubiquitous healthcare (u-Health) service on metabolic syndrome in male workers. Korean J Nutr. 2011; 44(3):231–242.12. Kushida O, Murayama N. Effects of environmental intervention in workplace cafeterias on vegetable consumption by male workers. J Nutr Educ Behav. 2014; 46(5):350–358.13. Engbers LH, van Poppel MN, Paw MCA, van Mechelen W. The effects of a controlled worksite environmental intervention on determinants of dietary behavior and self-reported fruit, vegetable and fat intake. BMC Public Health. 2006; 6(1):253.14. Steenhuis I, van Assema P, van Breukelen G, Glanz K, Kok G, de Vries H. The impact of educational and environmental interventions in Dutch worksite cafeterias. Health Promot Int. 2004; 19(3):335–343.15. Sawada K, Takemi Y, Murayama N, Sasaki S, Ishida H. Development and evaluation of a worksite-based nutrition education program integrated with food environmental intervention applying the transtheoretical model. Japanese J Health Educ Promot. 2009; 17(2):54–70.16. Ishida H, Yoshita G, Murayama N. Study on employees' health promotion for the population and the high risk group utilizing foodservice. [In Japanese]. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan;2009. 03.17. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome - an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute scientific statement. Circulation. 2005; 112(17):2735–2752.18. Korean Diabetes Association. Treatment guideline for diabetes 2011. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;2011. p. 10.19. Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Treatment guideline for obesity 2012. Seoul: Korean Society for the Study of Obesity;2012. p. 17.20. Daubert H, Ferko-Adams D, Rheinheimer D, Brecht C. Metabolic risk factor reduction through a worksite health campaign: a case study design. Online J Public Health Inform. 2012; 4(2):1–13.21. Wood PD, Stefanick ML, Williams PT, Haskell WL. The effects on plasma lipoproteins of a prudent weight-reducing diet, with or without exercise, in overweight men and women. N Engl J Med. 1991; 325(7):461–466.22. Park J, Kweon S, Kim Y, Jang M, Oh K. Dietary behaviors related to metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Korean J Community Nutr. 2012; 17(5):664–675.23. Jang JH, Cho SH. Effectiveness of worksite nutrition counseling for hyperlipidemic employees in Kyung-buk area. J Korean Diet Assoc. 1999; 5(1):1–9.24. Lee EH, Kim HK, Lee YH, Moon SY, Ji SH. Effectiveness of lifestyle intervention on the management of metabolic syndrome. Korean J Health Educ Promot. 2007; 24(3):1–19.25. Yoo SH, Kim HK. Program theory evaluation of a lifestyle intervention program for the prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome. Korean J Health Educ Promot. 2010; 27(4):165–175.26. Muto T, Yamauchi K. Evaluation of a multicomponent workplace health promotion program conducted in Japan for improving employees' cardiovascular disease risk factors. Prev Med. 2001; 33(6):571–577.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of a Worksite On-line Health Education Program on Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors and Nutrient Intakes of Male Workers
- A Study on the Development of Method for Measuring Nutrient Intakes at the Worksite
- The effects of the DASH diet education program with omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on metabolic syndrome parameters in elderly women with abdominal obesity
- The Effect of Metabolic Syndrome Management Program in a Public Health Center
- Effect of the Telephone-Delivered Nutrition Education on Dietary Intake and Biochemical Parameters in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome