Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2016 Jun;20(2):120-122. 10.13104/imri.2016.20.2.120.
Nontraumatic Intracystic Hemorrhage of Arachnoid Cyst: CT and MR Findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine and Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea. sartre81@gmail.com
- 3Department of Radiology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine and Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2327424
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.2.120
Abstract
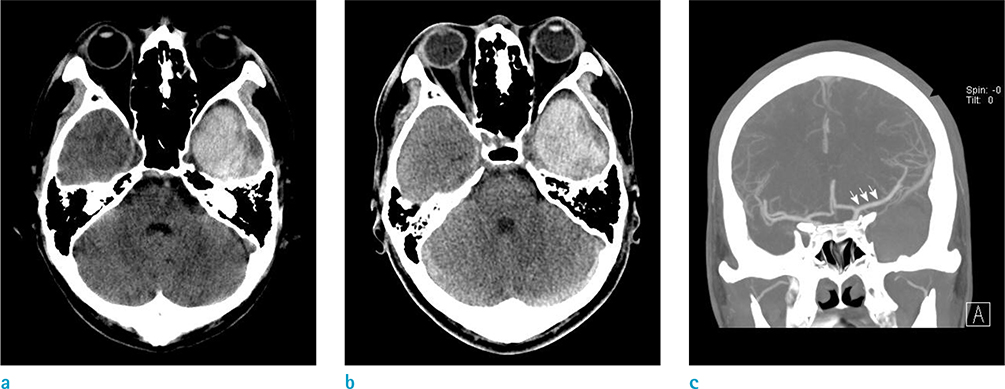
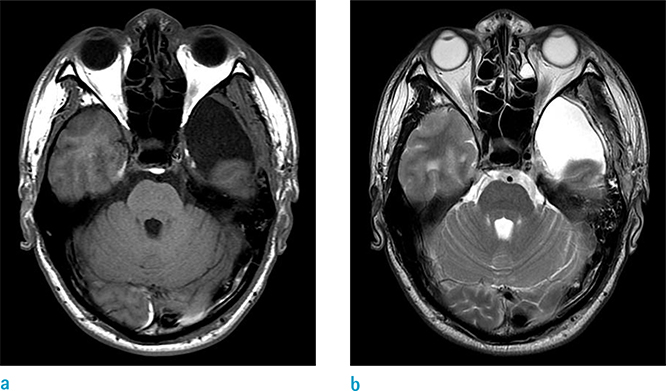
- Arachnoid cysts (AC) are intraarachnoidal cerebrospinal fluid collections, and account for 1% of all intracranial space-occupying lesions. Intracystic hemorrhage of the AC can occur spontaneously, but this is an extremely rare event. Herein, we present a case of hemorrhagic AC in a nontraumatic patient in the left middle cranial fossa. We also performed relevant literature review on this disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wester K. Peculiarities of intracranial arachnoid cysts: location, sidedness, and sex distribution in 126 consecutive patients. Neurosurgery. 1999; 45:775–779.2. Sommer IE, Smit LM. Congenital supratentorial arachnoidal and giant cysts in children: a clinical study with arguments for a conservative approach. Childs Nerv Syst. 1997; 13:8–12.3. Rengachary SS, Watanabe I, Brackett CE. Pathogenesis of intracranial arachnoid cysts. Surg Neurol. 1978; 9:139–144.4. Cincu R, Agrawal A, Eiras J. Intracranial arachnoid cysts: current concepts and treatment alternatives. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2007; 109:837–843.5. Davidoff LM, Dyke CG. RelapsingJuvenilechronic subdural haematoma: a clinical and roentgenographic study. Bull Neurol Inst NY. 1938; 7:95111.6. Passero S, Filosomi G, Cioni R, Venturi C, Volpini B. Arachnoid cysts of the middle cranial fossa: a clinical, radiological and follow-up study. Acta Neurol Scand. 1990; 82:94–100.7. Huang D, Abe T, Kojima K, et al. Intracystic hemorrhage of the middle fossa arachnoid cyst and subdural hematoma caused by ruptured middle cerebral artery aneurysm. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:1284–1286.8. Galassi E, Piazza G, Gaist G, Frank F. Arachnoid cysts of the middle cranial fossa: a clinical and radiological study of 25 cases treated surgically. Surg Neurol. 1980; 14:211–219.9. Kondziolka D, Bernstein M, ter Brugge K, Schutz H. Acute subdural hematoma from ruptured posterior communicating artery aneurysm. Neurosurgery. 1988; 22:151–154.10. Ergun R, Okten AI, Beskonakli E, Anasiz H, Ergungor F, Taskin Y. Unusual complication of arachnoid cyst: spontaneous rupture into the subdural space. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1997; 139:692–694.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intracystic Hemorrhage of an Arachnoid Cyst: a Case with Prediagnostic Imaging of an Intact Cyst
- Arachnoid Cyst with Spontaneous Intracystic Hemorrhage and Chronic Subdural Hematoma
- A Case of Arachnoid Cyst in the Middle Cranial Fossa
- Hemorrhagic Complications of Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Head Injury: Report of 5 Cases
- A Clinical Analysis of 4 Cases of Arachnoid Cysts in Middle Cranial Fossa, Associated with Chronic Subdural Hematoma