J Nutr Health.
2014 Oct;47(5):374-384. 10.4163/jnh.2014.47.5.374.
Design of service delivery for a child obesity prevention and management program using technology convergence
- Affiliations
-
- 1Nutrition Education Major, Graduate School of Education, Sangmyung University, Seoul 110-743, Korea.
- 2Institute of Health and Environment, Graduate School of Public Health, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea.
- 3Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Dankook University, Cheonan 330-714, Korea.
- 4Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea.
- 5Department of Food and Nutrition, Daejeon University, Daejeon 300-716, Korea. jshim@dju.kr
- KMID: 2327170
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4163/jnh.2014.47.5.374
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Health professionals and policy makers confront the failure of provider-administered, conventional behavioral interventions in the fight against obesity epidemic. The aim of this study was to develop a tailored, cost-effective delivery system for a child obesity prevention and management program through technology convergence using Web-enabled smart cellular phones.
METHODS
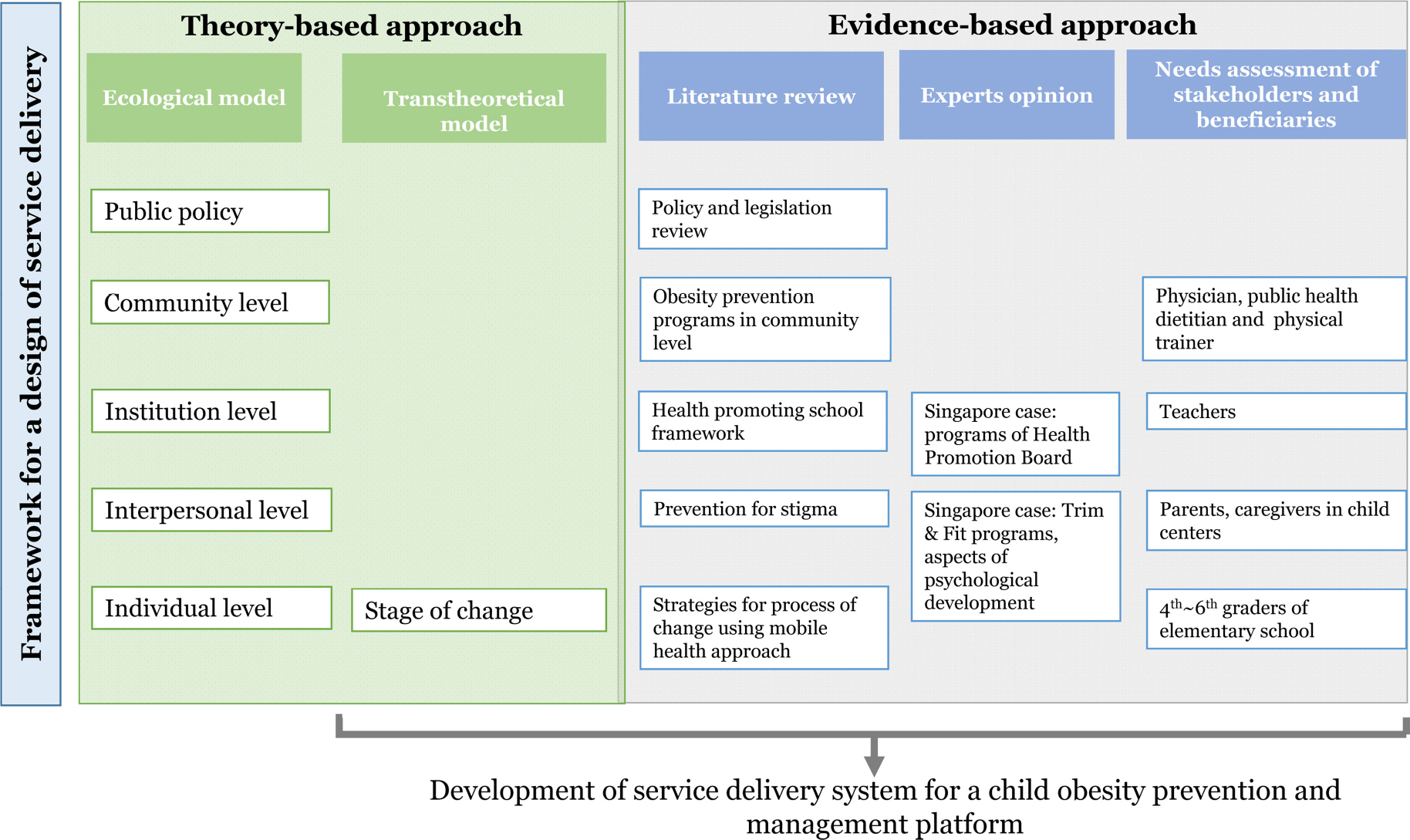
Assessment of service needs and development of a delivery system for the program were based on a comprehensive literature review and expert reviews, and results from in-depth interviews and a need-assessment survey.
RESULTS
The user- and site- centered service delivery system using Web-enabled cellular telephones as the hardware platform for obesity prevention and management has been developed. A tailored informational service and intervention will be provided interactively between stakeholders through the platform. The potential legal issues associated with the service design have also been considered.
CONCLUSION
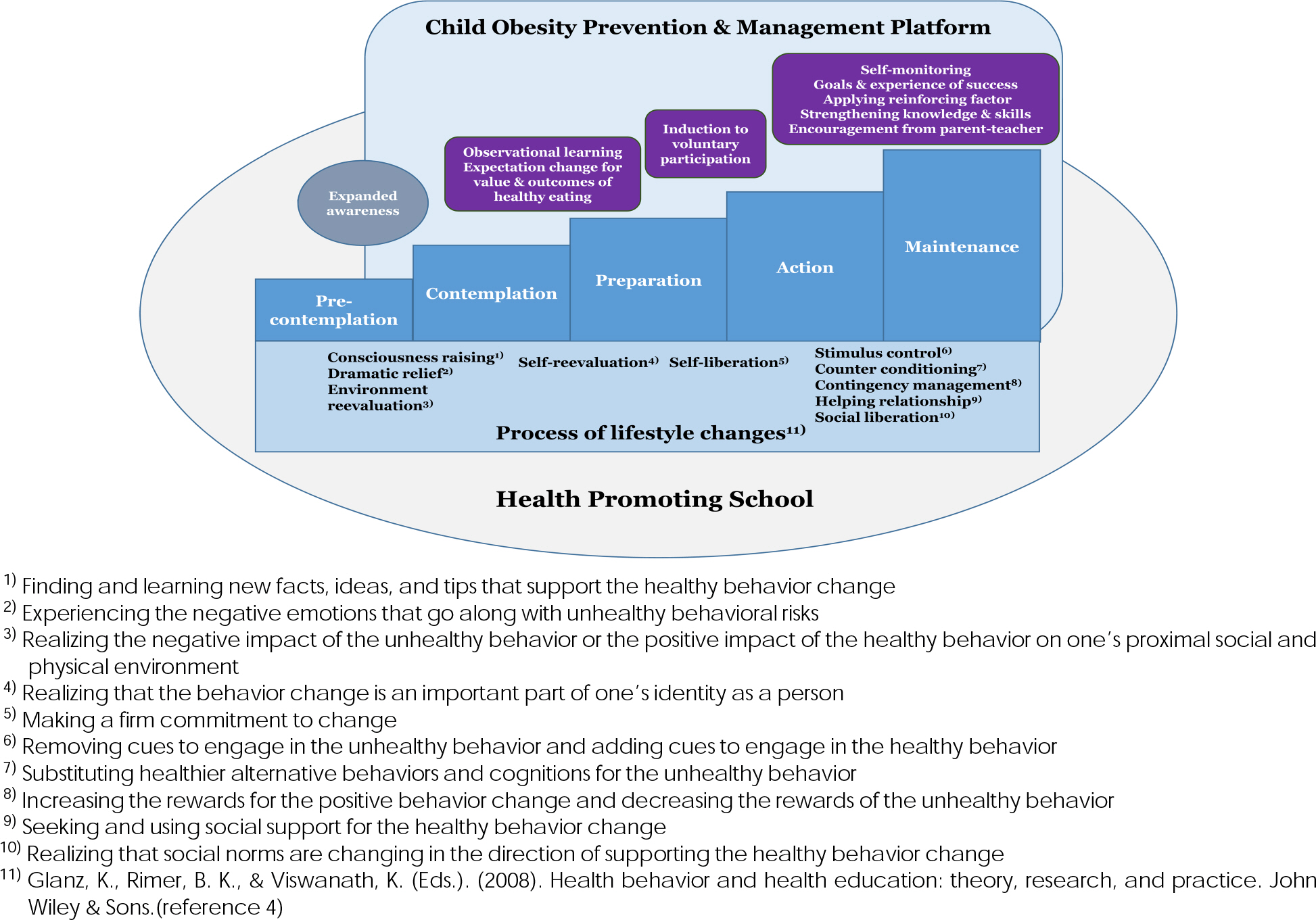
The user-centered convergence design and platform based on principles of Transtheoretical Model and Stages of Change using the Health Promoting School framework could enable effective intervention and promote acceptance in the long-run.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
A Qualitative Study on the Potential Utilization of a Mobile Phone for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children : Parents Perspective
Bo Young Lee, Mi-Young Park, Kirang Kim, Jea Eun Shim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean J Community Nutr. 2019;24(2):117-126. doi: 10.5720/kjcn.2019.24.2.117.Leveraging Multimodal Supports using Mobile Phones for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children: Program Providers' Perspective from a Qualitative Study
Mi-Young Park, Jae Eun Shim, Kirang Kim, Ji-Yun Hwang
Korean J Community Nutr. 2017;22(3):238-247. doi: 10.5720/kjcn.2017.22.3.238.
Reference
-
References
1. Yoon N, Kwon S. Impact of obesity on health care utilization and expenditure. Korean J Health Econ Policy. 2013; 19(2):61–80.2. Kim H. Multi-sectoral coordination strategy for policies and programs on nutrition service and obesity prevention. Korean J Health Educ Promot. 2013; 30(4):57–67.
Article3. Tate EB, Spruijt-Metz D, O'Reilly G, Jordan-Marsh M, Gotsis M, Pentz MA, Dunton GF. mHealth approaches to child obesity prevention: Successes, unique challenges, and next directions. Transl Behav Med. 2013; 3(4):406–415.
Article4. Glanz K., Rimer BK, Viswanath K, editors. Health behavior and health education: theory, research, and practice. San Francisco: John Wiley & Sons;2008.5. Langford R, Bonell CP, Jones HE, Pouliou T, Murphy SM, Waters E, Komro KA, Gibbs LF, Magnus D, Campbell R. The WHO Health Promoting School framework for improving the health and wellbeing of students and their academic achievement (Review). The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 2014, Issue 4.6. Kim M. Problems and solutions for health promoting schools in Korea. Korean Pub Health Res. 2013; 39(1):57–67.7. Report of School Health Examination Survey 2013. Press release. Ministry of Education, [cited 2014 Sep 25]. Available from:. http://. www.moe.go.kr/web/45859/ko/board/view.do?bbsId=294&board-Seq. =52706.8. Repetti RL, Taylor SE, Seeman TE. Risky families: family social environments and the mental and physical health of offspring. Psychol Bull. 2002; 128(2):330–366.
Article9. Lissau I, S⊘rensen TI. Parental neglect during childhood and increased risk of obesity in young adulthood. Lancet. 1994; 343(8893):324–327.
Article10. Kumar S1. Nilsen WJ, Abernethy A, Atienza A, Patrick K, Pavel M, Riley WT, Shar A, Spring B, Spruijt-Metz D, Hedeker D, Honavar V, Kravitz R, Lefebvre RC, Mohr DC, Murphy SA, Quinn C, Shusterman V, Swendeman D. Mobile health technology evaluation: the mHealth evidence workshop. Am J Prev Med. 2013; 45(2):228–236.11. Burke LE, Styn MA, Sereika SM, Conroy MB, Ye L, Glanz K, Ewing LJ. Using mHealth technology to enhance self-monitoring for weight loss: a randomized trial. Am J Prev Med. 2012; 43(1):20–26.12. de Niet J, Timman R, Bauer S, van den Akker E, de Klerk C, Kordy H, Passchier J, Short message service reduces dropout in childhood obesity treatment: A randomized controlled trial. Health Psychology. 2012; 31(6):797–805.13. Mamun AA, O'Callaghan MJ, Williams GM, Najman JM. Adolescents bullying and young adults body mass index and obesity: a longitudinal study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2013; 37(8):1140–1146.
Article14. Jansen PW, Verlinden M, Dommisse-van Berkel A, Mieloo CL, Raat H, Hofman A, Jaddoe VW, Verhulst FC, Jansen W, Tiemeier H. Teacher and peer reports of overweight and bullying among young primary school children. Pediatrics. 2014; 134(3):473–480.
Article15. Yang, Hwajin (School of social science, Singapore Management University, Singapore). Conversation with: Jae Eun Shim (Department of food and Nutrition, Daejeon University, Daejeon, Korea), Ji-Yoon Hwang (The graduate school of education, Sangmyung University, Seoul, Korea), Kirang Kim (Department of food and Nutrition, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea). 2014 Jun 30.16. Haapala I, Barengo NC, Biggs S, Surakka L, Manninen P. Weight loss by mobile phone: a 1-year effectiveness study. Public Health Nutr. 2009; 12(12):2382–2391.
Article17. Turner-McGrievy GM, Beets MW, Moore JB, Kaczynski AT, Barr-Anderson DJ, Tate DF. Comparison of traditional versus mobile app self-monitoring of physical activity and dietary intake among overweight adults participating in an mHealth weight loss program. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2013; 20:513–518.
Article18. Woolford SJ, Clark SJ, Strecher VJ, Resnicow K. Tailored mobile phone text messages as an adjunct to obesity treatment for adolescents. J Telemed Telecare. 2010; 16(8):458–461.
Article19. Bechhofer L, Flis B, Guerrant K, and Kovalchick K. USA: The Michigan Journey Toward Coordinated School Health. Whitman CB, Aldinger CE, editors. editors.Case Studies in Global School Health Promotion from research to practice. New York: Springer;2009. p. 171–186.20. Vaithinathan R, Yee CL, Loke WM, Leow K. Singapore: Health-Promoting Schools: The CHERISH Award. Whitman CB, Aldinger CE, editors. editors.Case Studies in Global School Helath Promotion from research to practice. New York: Springer;2009. p. 349–364.21. Case Study-Obesity Prevention and Control Efforts in Singapore. The National Bureau of Asian Research; [cited 2014 June 22]. Available from:. http://www.pacifichealthsummit.org/down-loads/Obesity. %20Prevention%20and%20 Control%20Efforts% 20in%20Singapore%20-%202008%20Case%20Study.pdf.22. Lee HY, Lee EL, Pathy P, Chan YH. Anorexia nervosa in Singapore: an eight-year retrospective study. Singapore Med J. 2005; 46(6):275–281.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of Child-Teen Obesity Treatment Service Platform
- A Study for the Model Development of 'Child Health Management Program'
- Leveraging Multimodal Supports using Mobile Phones for Obesity Management in Elementary-School Children: Program Providers' Perspective from a Qualitative Study
- Effects of Obesity Management Program for Obese Elementary School Children
- Current Status and Needs Assessment for Obesity Prevention and Management Project at Public Health Centers