J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2005 Dec;12(4):358-364.
Anterior Debridement and Strut Graft with Pedicle Screw Fixation for Tuberculous Spondylitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang Univ. Bucheon Hospital.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ljhos@medimail.co.kr
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: This is a retrospective study.
OBJECTIVE
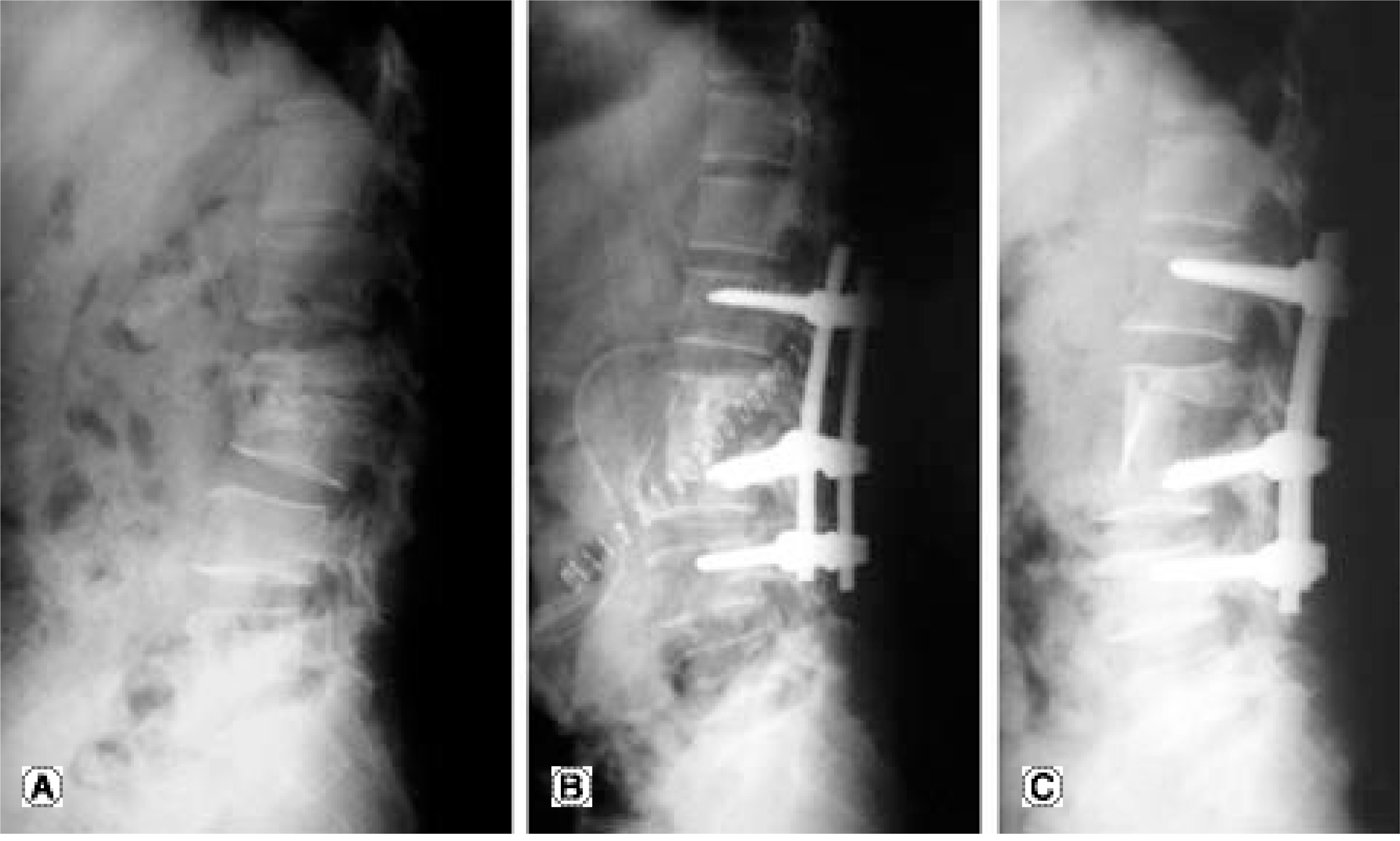
We analyzed the clinical and radiographic results of surgical treatment for patients with tuberculous spondylitis. MATERIAL AND METHODS: Our study included 18 active tuberculous spondylitis patients (12 males and 6 females) who underwent anterior curettage, strut bone grafting and posterior instrumentation. Their average age was 50.1 years (age range: 24-76 years). The mean follow-up was 43 months. Vertebral bodies from T5 to L5 were involved. The anterior column support was iliac autograft in 10 patients and titanium mesh in 4. All the patients had transpedicular instrumentation with an additional hook in 3 and anterior instrumentation in 1. Except for one paraplegic patient, all the others were able to ambulate wearing TLSO. The mean duration of Anti-Tbc medication was 13.3 months (range: 12 to 18 months). The clinical and radiographic results were analyzed, and they included the segmental kyphotic angle and the complications of instrumentation on the involved vertebrae. RESULT: The subjective satisfaction was greater than good except for 2 patients. These 2 patients' satisfaction was fair due to incomplete neurologic recovery and persistent BG-donor site pain. The three paraplegic patients fully recovered postoperatively. The mean correction of the segmental kyphosis was 13 degrees. The mean correction loss was 0.7 degrees at the final follow-up. Pedicle screws were inserted in the involved vertebrae for 10 patients (n = 30). There was no loosening of instrumentation nor spread or recurrence of infection. One case was complicated by pneumonia.
CONCLUSION
For the surgical treatment of active tuberculous spondylitis, anterior column support with strut grafting and posterior instrumentation is mandatory in the destabilized spine after anterior debridement or the correction of kyphosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Moon MS, Woo YK, Park YO. Conservative treatment of tuberculosis of the spine. J of Kor Orthop Assoc. 1986; 21:571–584.
Article2). Wilkinson MC. The treatment of tuberculosis of the spine by evacuation of the paravertebral abscess and curettage of the vertebral bodies. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1955; 37:382–391.
Article3). Chen WJ, Wu CC, Jung CH, Chen LH, Niu CC, Lai P L. Combined anterior and posterior surgeries in the treatment of spinal tuberculous spondylitis. Clin Orthop. 2002; 398:50–59.
Article4). Safran O, Rand N, Kaplan L, Sagiv S, Floman Y. Sequential or simultaneous, same-day anterior decompression and posterior stabilization in the management of vertebral osteomyelitis of the lumbar spine. Spine. 1998; 23:1885–1890.
Article5). MacNab I. Negative disc exploration: An analysis of the causes of nerve-root involvement in sixty-eight patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971; 53:891–903.6). Lenke Lawrence G, Hanson Darrell S, Bridwell Keith H, Rhee John M. Dowel Fibular Strut Grafts for High-Grade Dysplastic Isthmic Spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2002; 27:1982–1988.
Article7). Medical Research Council Working Party on Tuberculosis of the Spine. A 10 year assessment of a controlled trial comparing debridement and anterior spinal fusion in the management of tuberculosis of the spine in patients on standard chemotherapy in Hong Kong. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1982; 64:393–398.8). Medical Research Council Working Party on Tubercuosis of the Spine. A controlled trial of ambulant outpatient treatment and in-patient rest in bed in the management of tuberculosis of the spine in young Korea patients on standard chemotherapy: A study in Masan, Korea. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1973; 50:678–697.9). Korkusuz F, Islam C, Korkusuz Z. Prevention of posterior late kyphosis in Pott’s disease by anterior decompression and intervertebral grafting. World J Surg. 1997; 21:524–528.10). Lindh M. Biomechanics of the Lumbar Spine. In Nordin M, Frankel VH(eds). Basic Biomechanics of the Musculoskeletal System. Philadelphia, Lea & Febiger. 1989; 2:183–207.11). Hodgson AR, Stock FE. Anterior spine fusion for the treatment of tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1960; 42:295–310.
Article12). Yilmaz, Cengiz, Selek, Hakan Y, Gurkan, Ilksen, Erdemli, Bulent, Korkusuz, Zeki. Anterior instrumentation for the treatment of spinal tuberculosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:1261–1267.13). Rajasekaran S, Shanmugsundaram TK. Prediction of the angle of gibbus deformity in tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987; 69:503–509.
Article14). Moon MS, Woo YK, Lee KS, et al. Posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculosis kyphosis of dorsal and lumbar spines. Spine. 1995; 20:1910–1916.15). Bailey HL, Gabriel M, Hodgson AR, Shin JS. Tuberculosis of the spine in children: Operative findings results in one hundred consecutive patients treated by removal of the lesion and anterior grafting. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972; 54:1633–1657.16). Chen WJ, Chen CH, Shin CH. Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylitis: 50 patients followed for 2-8 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 1995; 66:137–142.
Article17). Oga M, Arizono T, Takasita M, Sugioka Y. Evaluation of the risk of instrumentation as a foreign body in spinal tuberculosis. Spine. 1993; 18:1890–1894.
Article18). Chung YG, Ha KY. Adherence and biofilm formation of staphylococcus epidermidis and mycobacterium tubercu - losis on spinal implant. J Kor Spine Surg. 1999; 6:47–56.19). Connolly PJ, Von Schroeder HP, Johnson GE, Kostuik JP. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Long term effect of instrumentation extending to the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77:1210–1216.20). Thompson JP, Transfeldt EE, Bradford Ds, Ogilvie JW, Bouchie-Adjei O. Decompression after Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation of idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 1990; 15:927–931.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Safety and Efficacy of Pedicle Screws and Titanium Mesh Cage in the Treatments of Tuberculous Spondylitis of the Thoracolumbar Spine
- Anterior Debridement and Strut Graft with Pedicle Screw Fixation for Pyogenic Spondylitis
- The Role of Early or Late Pedicle Screw Fixation for Pyogeinc Spondylitis in the Duration of Intravenous Antibiotic Use and the Period of Hospitalization
- Vascularized Fibular Bone Graft for Tuberculous Spondylitis: Case Report
- Simultaneous Anterior and Posterior Surgery in the Management of Tuberculous Spondylitis with Psoas Abscess in Patients with Neurological Deficits