J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2002 Jun;9(2):106-114.
Tactics for Surgical Treatment of the Double Thoracic Scoliosis: Significance of T1 tilt, first rib elevation and correction ratio
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University Medical College, Seoul, Korea. choonki@plaza.snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Medical College, Bucheon, Korea.
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: A retrospective clinical and radiographic review.
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study is to suggest the indications and more ideal objective amount of corrections of for upper and lower curves. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: There are many controversies exist about the diagnosis and treatment of double thoracic scoliosis yet.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
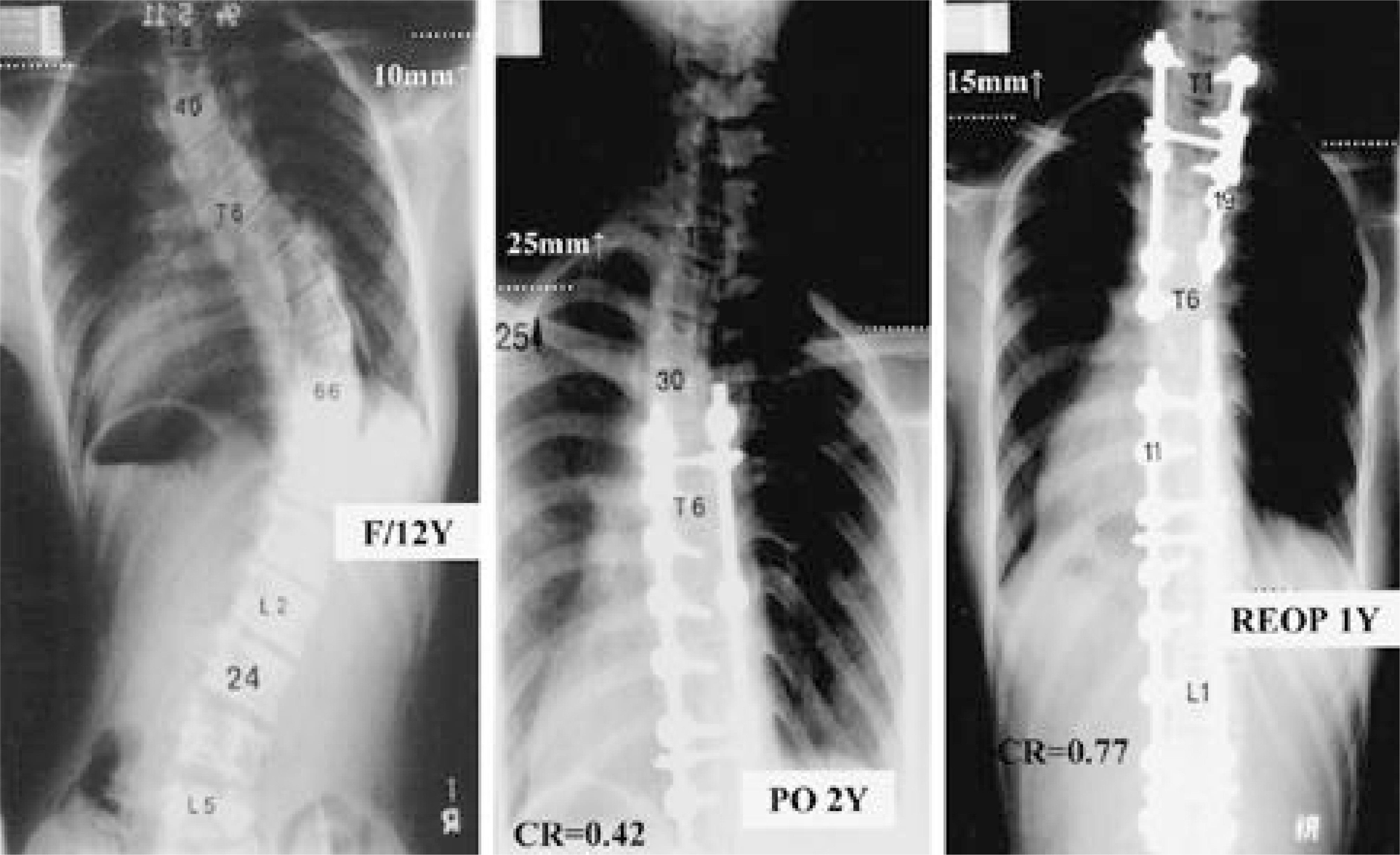
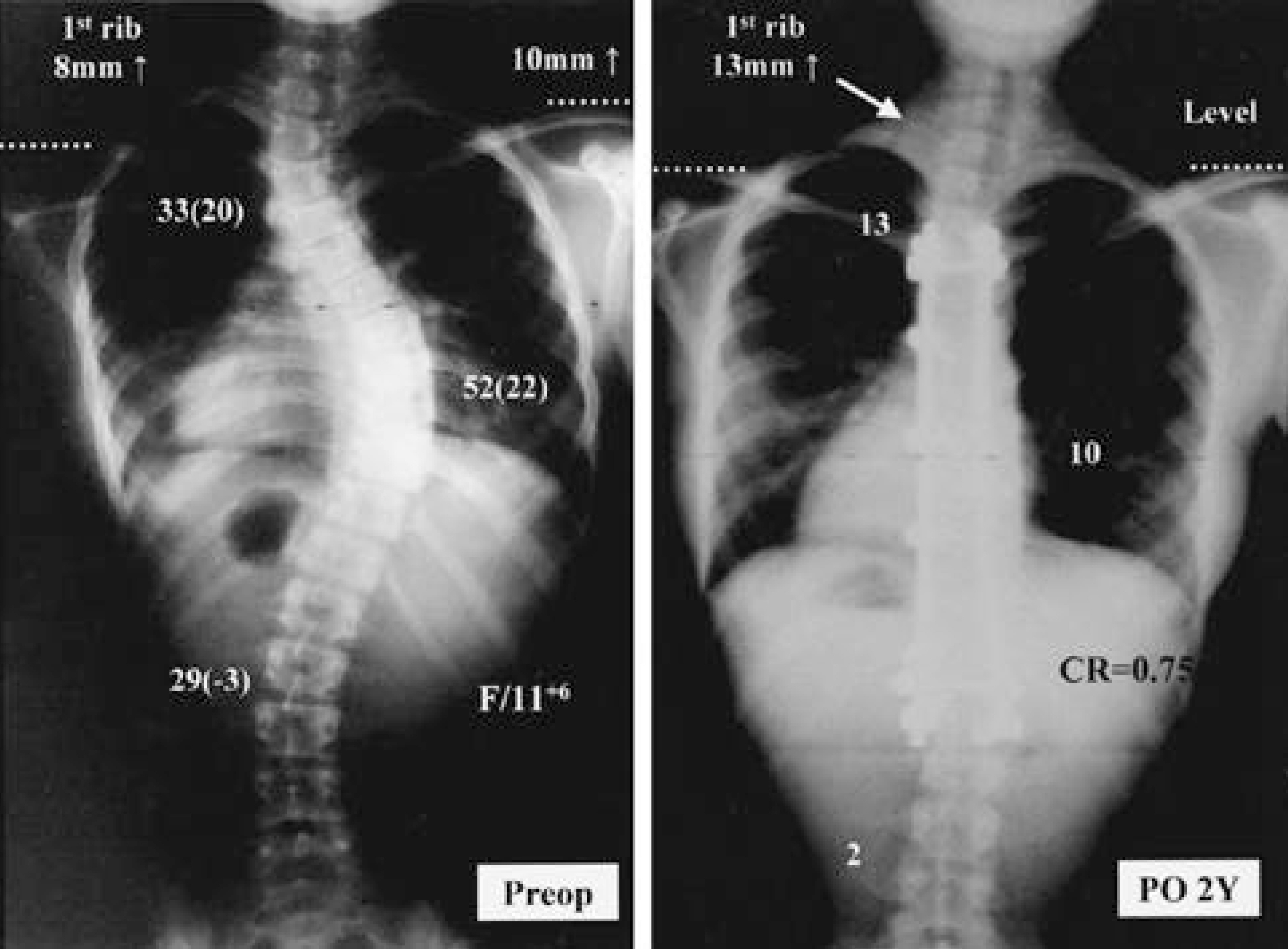
Thirty-nine double thoracic scoliosis patients with left shoulder elevation and/or positive T1 tilt and an upper curve of 25 degrees or more were divided into two groups. Group I (24 patients) underwent fusion on both curves, and Group II (15 patients), on the lower curve alone. Cobb angles, T1 tilt, left first rib elevation (represents trapezial prominence), and shoulder level difference were measured from standing on pre- and post-operative standing films. The correction ratio [Upper curve correction(%)/Lower curve correction(%)] was used to represent describe how much the upper curve was had been corrected compared to versus the lower curve.
RESULTS
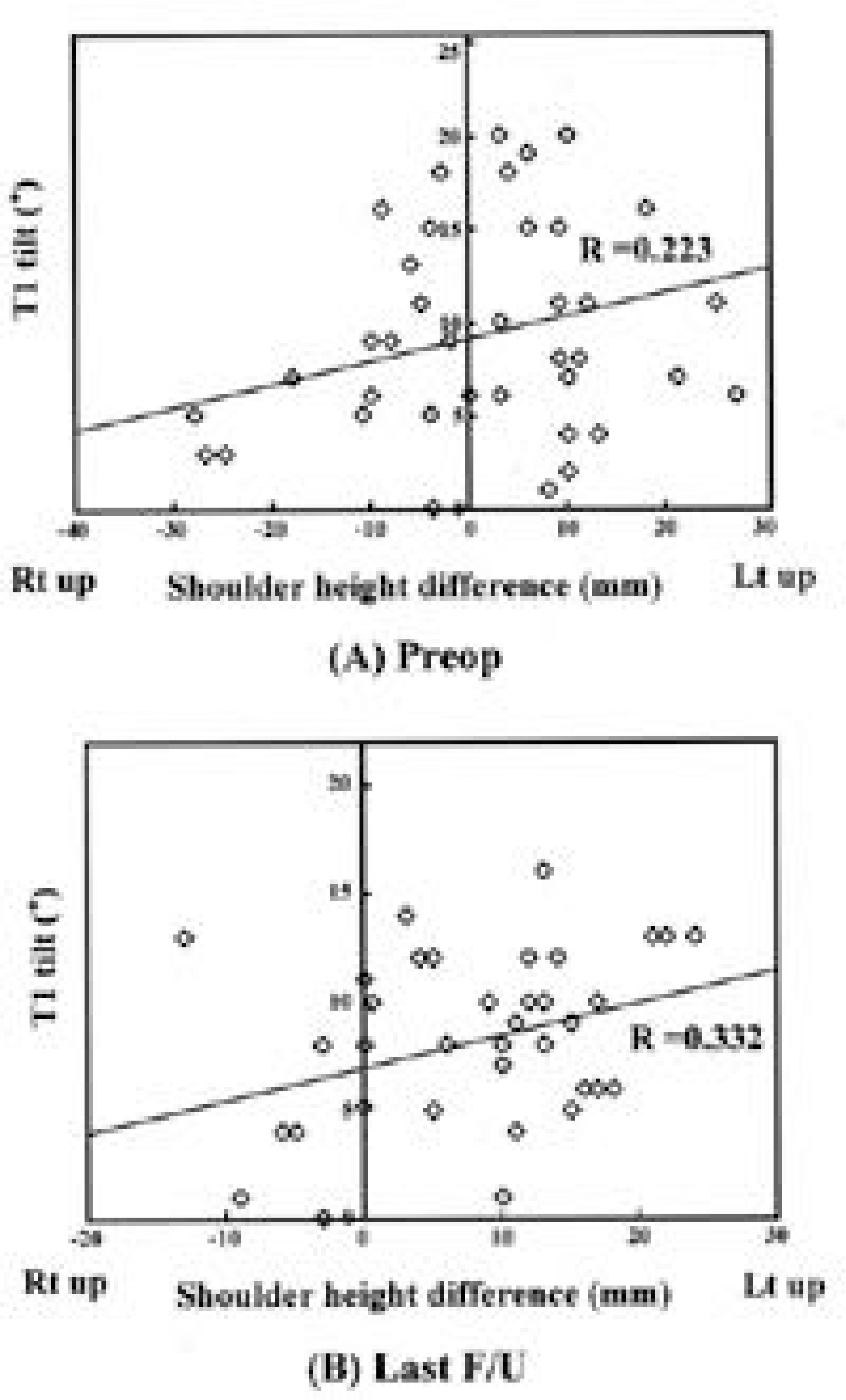
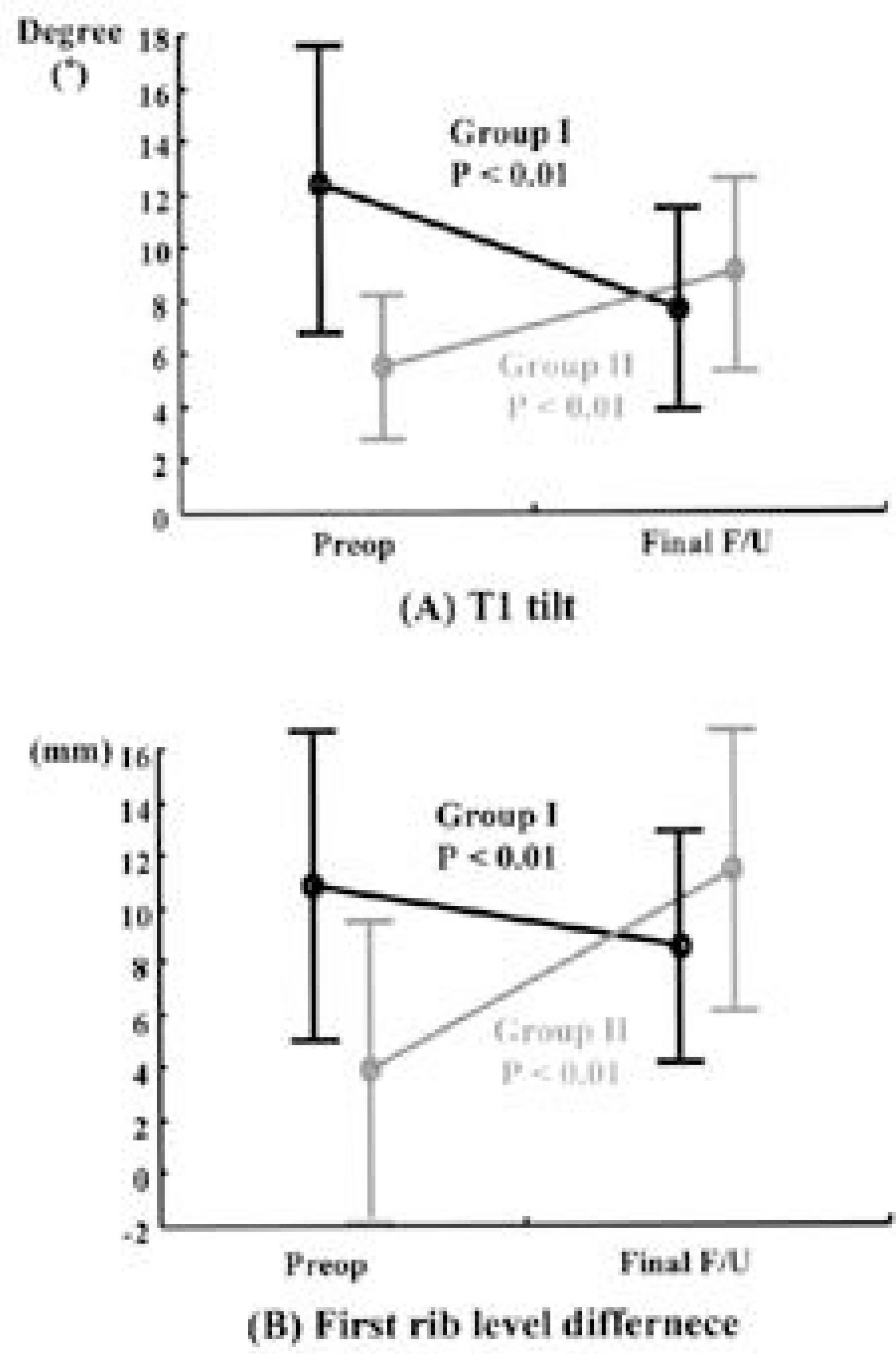
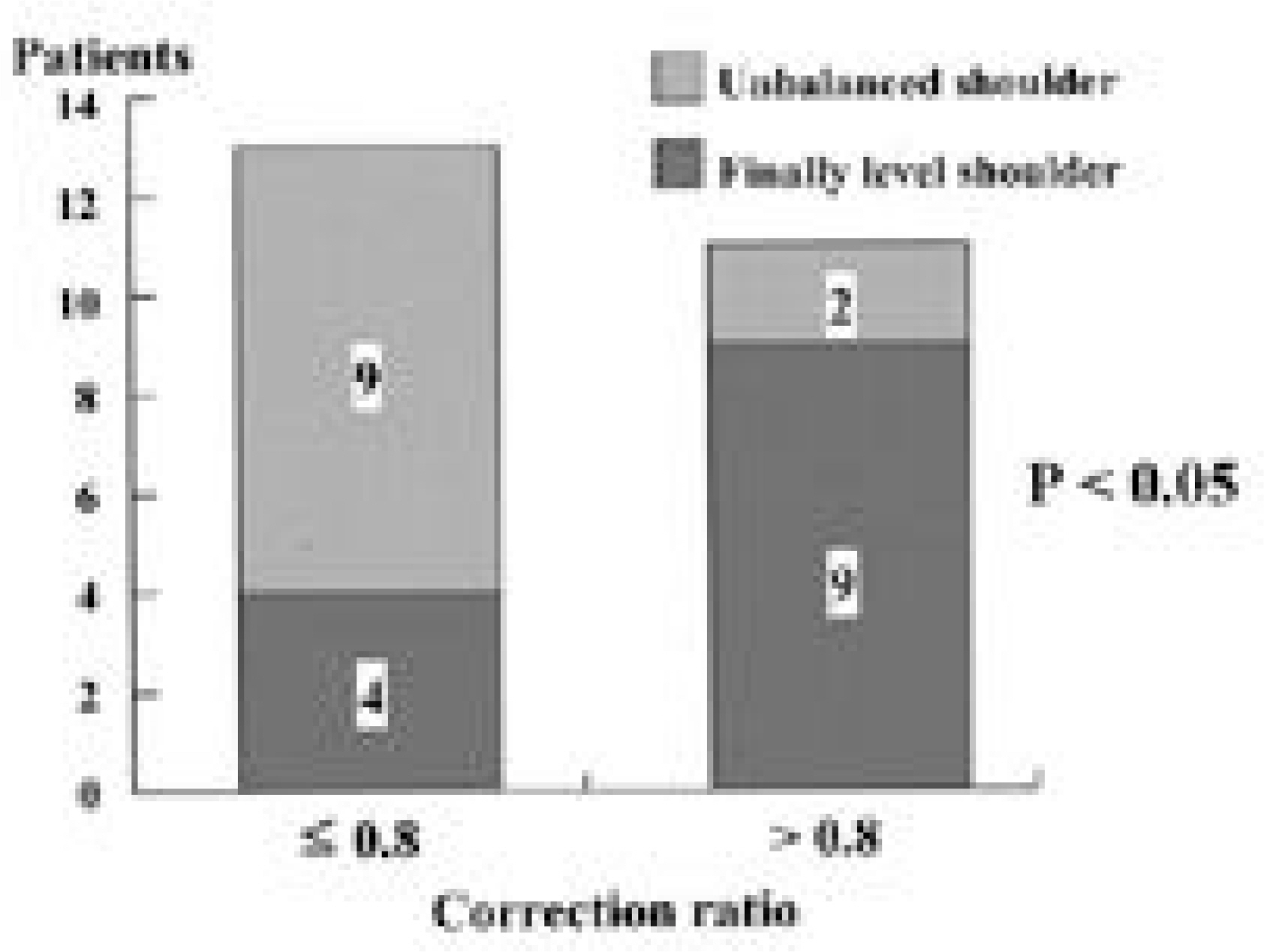
T1 tilt did not correlate well with left shoulder elevation, but correlated with left first rib elevation. In Group I, T1 tilt and left first rib elevation improved significantly after fusion of the upper curve, whereas these were aggravated in Group II. In Group I, most of the patients with the a correction ratio of more than 0.8, showed balanced shoulder levels finally.
CONCLUSIONS
In double thoracic scoliosis patients, T1 tilt and left first rib elevation should be considered in addition to not only left shoulder elevation and the rigidity of upper curve, but also the T1 tilt and left first rib elevation should be considered as the indication of the extension of fusion to upper curve. The amount of upper curve correction should be more than at least 80% of that of the lower curve for a balanced correction in the treatment of double thoracic scoliosis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1). Ginsburg H, Goldstein L, De Vanny J, Haake P. An evaluation of the upper thoracic curve in idiopathic scoliosis: guidelines in selection of the fusion area. Presented at the Annual Meeting of the. Scoliosis Research Society: Hong Kong;October 1977.2). King HA, Moe JH, Bradford DS, Winter RB. The selection of fusion levels in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg. 65-A:1302–1313. 1983.
Article3). Lee CK, Denis F, Winter RB, Lonstein JE. Analysis of the upper thoracic curve in surgically treated idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 18:1599–1608. 1993.
Article4). Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, O’ Brien MF, Baldus C, Blanke K. Recognition and treatment of the proximal thoracic curve in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis treated with Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation. Spine. 19:1589–1597. 1994.
Article5). Moe JH, Kettleson DN. Idiopathic scoliosis: analy -sis of curve patterns and the preliminary results Milwau -kee brace treatment in one hundred sixty-nine patients. J Bone Joint Surg. 52-A:1509–1533. 1970.6). Ponseti IV, Friedman B. Prognosis of idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg. 32-A:381–395. 1950.7). Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee CS, Lee SM, Kim JH, Chung ER, Lee JH. Indications of proximal thoracic curve fusion in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 25:2342–2349. 2000.
Article8). Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, Chung YJ, Park YB. Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 20(12):1399–1405. 1995.
Article9). Suk SI, Lee CK, Min HJ, Cho KH, Oh JH. Comparison of Cotrel-Dubousset pedicle screws and hooks in the treatment of idiopathic scoliosis. Int Orthop. 18(6):341–346. 1994.
Article10). Winter RB. The idiopathic double thoracic curve pat -tern: its recognition and surgical management. Spine. 14:1287–1292. 1989.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Proximal Fusion to T1 or T2 in Double Thoracic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
- Spontaneous Rib Fracture during Boston Brace Treatment for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
- The Incidence of Scoliosis in Korea Part II : The Incidence of Scoliosis in the Middle and High School Male Students
- Correction of Double Thoracic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Using PedicleScrew Instrumentation: Comparison with Translation and Rod Derotation
- Costoclavicular Syndrome: A Case Report