J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 Sep;65(3):267-270.
Spontaneous Perforation of Common Bile Duct in a Child with a Clinical Manifestation of Acute Abdominal Distension: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. nksook1004@hallym.or.kr
Abstract
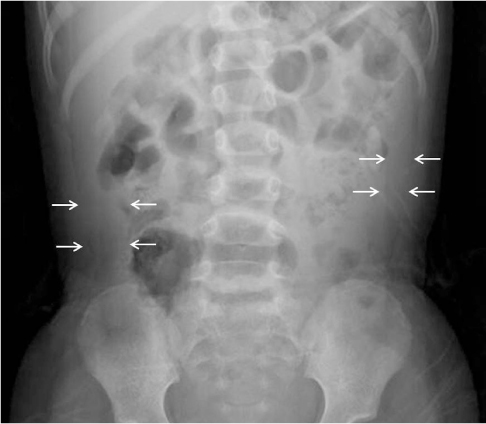
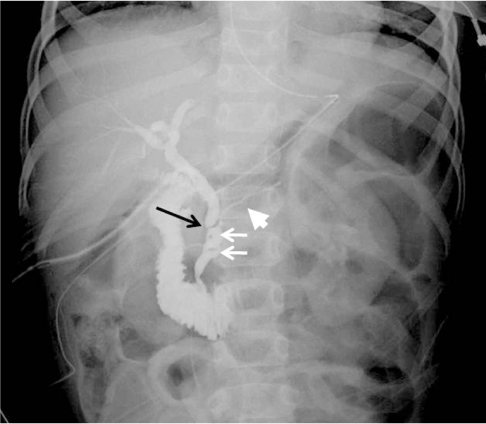
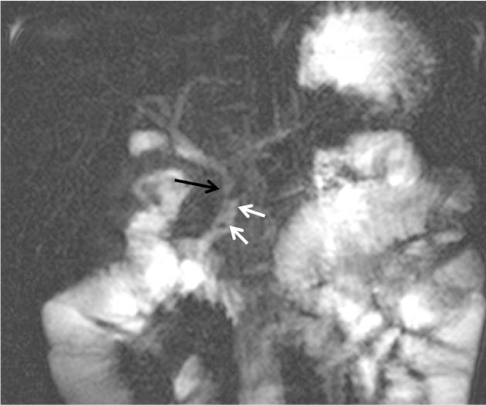
- Spontaneous perforation of common bile duct (CBD) is extremely rare in children, but potentially a fatal disorder that requires an emergency laparotomy. Most of the patients present with insidious symptoms including slowly progressive abdominal distension with accumulation of the ascites, fluctuating mild jaundice, and clay-colored stools. We report a case of surgically confirmed spontaneous perforation of the CBD in a 3-year-old girl who presented with acute abdominal distension with no biliary symptoms or signs, and who showed imaging findings consistent with anomalous pancreaticobiliary ductal union with a focal stenosis in the CBD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Karrer FM, Hall RJ, Stewart BA, Lilly JR. Congenital biliary tract disease. Surg Clin North Am. 1990; 70:1403–1418.2. Haller JO, Condon VR, Berdon WE, Oh KS, Price AP, Bowen A, et al. Spontaneous perforation of the common bile duct in children. Radiology. 1989; 172:621–624.3. Chardot C, Iskandarani F, De Dreuzy O, Duquesne B, Pariente D, Bernard O, et al. Spontaneous perforation of the biliary tract in infancy: a series of 11 cases. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 1996; 6:341–346.4. Vijay BB, Kumar R, Gupta DK, Ragavan M, Mohapatra T, Dhanpathi H, et al. Spontaneous biliary perforation in an infant: an unusual chronic presentation. Clin Nucl Med. 2008; 33:273–275.5. Carubelli CM, Abramo TJ. Abdominal distention and shock in an infant. Am J Emerg Med. 1999; 17:342–344.6. Lee MJ, Kim MJ, Yoon CS. MR cholangiopancreatography findings in children with spontaneous bile duct perforation. Pediatr Radiol. 2010; 40:687–692.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Spontaneous Perforation of the Common Bile Duct in Infant
- A Case of Spontaneous Perforation of the Right Intrahepatic Duct - An ERCP Diagnosis
- Spontaneous Rupture of the Hepatic Duct
- Spontaneous Perforation of the Bile Duct
- Spontaneous Perforation of Common Bile Duct: Abscess Formation Presenting as a Choledochal Cyst