Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2016 Dec;20(4):254-258. 10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.254.
Spontaneous Perforation of Common Bile Duct: Abscess Formation Presenting as a Choledochal Cyst
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Gyeonggi-do, Korea. choikim75@gmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- KMID: 2366408
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.254
Abstract
- Spontaneous perforation of the bile duct without any traumatic or iatrogenic injury is extremely rare. We report a case of abscess formation related to spontaneous perforation of the common bile duct by a gallstone, mimicked a cholecochal cyst.
MeSH Terms
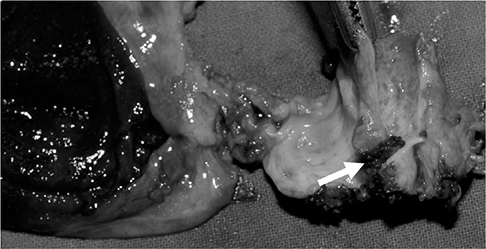
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kang SB, Han HS, Min SK, Lee HK. Nontraumatic perforation of the bile duct in adults. Arch Surg. 2004; 139:1083–1087.2. Wiseman K, Buczkowski AK, Chung SW, Francoeur J, Schaeffer D, Scudamore CH. Epidemiology, presentation, diagnosis, and outcomes of choledochal cysts in adults in an urban environment. Am J Surg. 2005; 189:527–531. discussion 531.3. Freeland J. Rupture of the hepatic duct. Lancet. 1882; 1:731–732.4. Mizutani S, Yagi A, Watanabe M, et al. T tube drainage for spontaneous perforation of the extrahepatic bile duct. Med Sci Monit. 2011; 17:CS8–CS11.5. Lee HK, Han HS, Lee JH, Min SK. Nontraumatic perforation of the bile duct treated with laparoscopic surgery. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2005; 15:329–332.6. Piotrowski JJ, Van Stiegmann G, Liechty RD. Spontaneous bile duct rupture in pregnancy. HPB Surg. 1990; 2:205–209.7. Thompson CM, Saad NE, Quazi RR, Darcy MD, Picus DD, Menias CO. Management of iatrogenic bile duct injuries: role of the interventional radiologist. Radiographics. 2013; 33:117–134.8. Ouaissi M, Kianmanesh R, Belghiti J, et al. Todani Type II congenital bile duct cyst: European Multicenter Study of the French Surgical Association and literature review. Ann Surg. 2015; 262:130–138.9. Qayyum A. Diffusion-weighted imaging in the abdomen and pelvis: concepts and applications. Radiographics. 2009; 29:1797–1810.10. Megison SM, Votteler TP. Management of common bile duct obstruction associated with spontaneous perforation of the biliary tree. Surgery. 1992; 111:237–239.