J Korean Soc Radiol.
2013 May;68(5):407-410.
Hepatic Rupture Caused by Hemolysis, Elevated Liver Enzyme, and Low Platelet Count Syndrome: A Case Report with Computed Tomographic and Conventional Angiographic Findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Asan Foundation, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea. jhahn@gnah.co.kr
Abstract
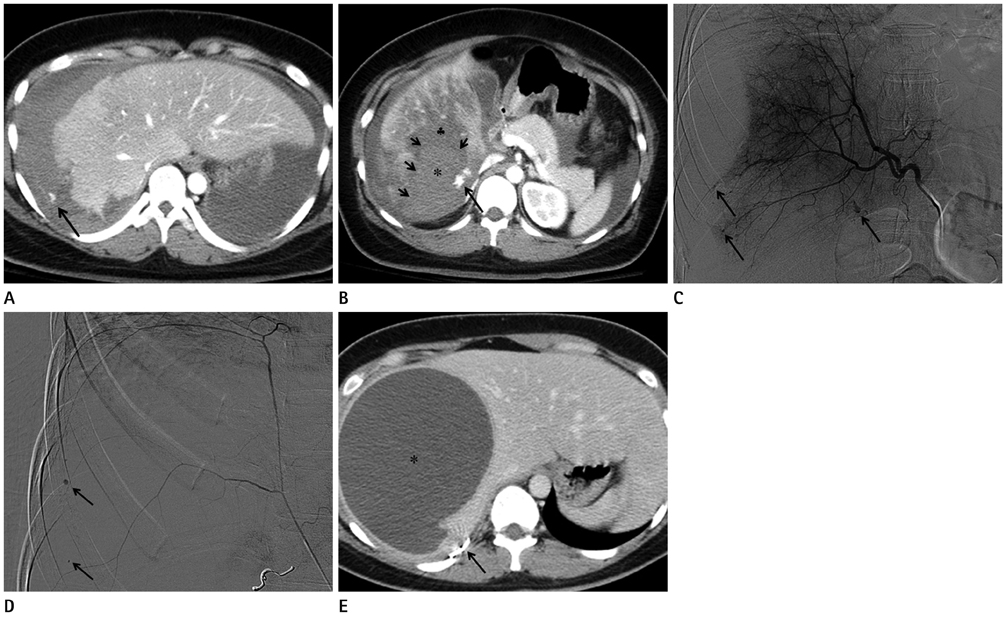
- The authors recently obtained successful clinical outcome after embolization of the hepatic artery and right inferior phrenic artery in a pregnant patient with hemolysis, elevated liver enzyme, and low platelet count (HELLP) syndrome causing hepatic rupture. We report the computed tomographic and conventional angiographic findings in a case of HELLP syndrome, resulting in hepatic infarction and rupture with active bleeding.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Henny CP, Lim AE, Brummelkamp WH, Buller HR, Ten Cate JW. A review of the importance of acute multidisciplinary treatment following spontaneous rupture of the liver capsule during pregnancy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1983. 156:593–598.2. Rinehart BK, Terrone DA, Magann EF, Martin RW, May WL, Martin JN Jr. Preeclampsia-associated hepatic hemorrhage and rupture: mode of management related to maternal and perinatal outcome. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1999. 54:196–202.3. Barton JR, Sibai BM. Hepatic imaging in HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996. 174:1820–1825. discussion 1825-1827.4. Zissin R, Yaffe D, Fejgin M, Olsfanger D, Shapiro-Feinberg M. Hepatic infarction in preeclampsia as part of the HELLP syndrome: CT appearance. Abdom Imaging. 1999. 24:594–596.5. Weinstein L. Syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count: a severe consequence of hypertension in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982. 142:159–167.6. Araujo AC, Leao MD, Nobrega MH, Bezerra PF, Pereira FV, Dantas EM, et al. Characteristics and treatment of hepatic rupture caused by HELLP syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006. 195:129–133.7. Takeuchi Y, Arai Y, Inaba Y, Ohno K, Maeda T, Itai Y. Extrahepatic arterial supply to the liver: observation with a unified CT and angiography system during temporary balloon occlusion of the proper hepatic artery. Radiology. 1998. 209:121–128.8. Yamagami T, Kato T, Tanaka O, Hirota T, Nishimura T. Influence of extrahepatic arterial inflow into the posterior segment or caudate lobe of the liver on repeated hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005. 16:457–463.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Postpartum Spontaneous Intrahepatic Hemorrhage and Hepatic Rupture in the HELLP Syndrome
- An anesthetic experience in severe preeclampsia patient suspected HELLP syndrome with an intraperitoneal hemorrhage caused by a rapidly progressed liver rupture: A case report
- Hepatic Infarction in HELLP Syndrome: A Case Report
- Anesthetic Management of a Patient with Postpartum HELLP Syndrome: A case report
- Delayed Postpartum Hemolysis, Elevated Liver Enzymes, and Low Platelets Syndrome Successfully Treated with Dexamethasone