J Korean Acad Periodontol.
2009 Aug;39(Suppl):261-268.
Prevalence of periodontitis and associated risk factors in Korean adults: Korean National Oral Health Survey 2006
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Korea.
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, College of Medicine, Dankook University, Korea. leevan@dankook.ac.kr
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To estimate the prevalence of periodontitis in Korean adults and to examine the associations between periodontitis and known risk factors.
METHODS
Using Korean National Oral Health Survey 2006 data, a total of 4,263 people who had taken oral examination, interviewed by questionnaire, and aged 18 or older were sampled. The prevalence of periodontitis measured by Community Periodontal Index (CPI) was calculated and the differences in prevalence according to known risk factors (age, sex, monthly income, education, residential area, tooth-brushing frequency, regular dental visit, smoking, and diabetes) were examined with chi-square test. Logistic regression analysis was performed to see the effects of each risk factor on the risk of having periodontitis. All statistical approaches were reflected national sampling design using Survey procedures in SAS 9.1.
RESULTS
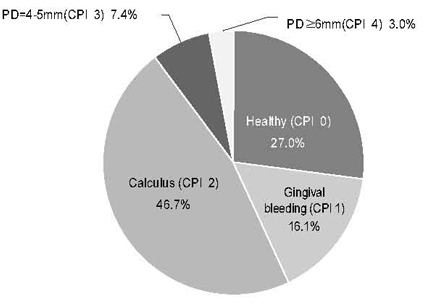
The overall prevalence of periodontitis in Korean adults was 10.3%. There existed statistically significant differences in crude prevalence for periodontitis according to the all risk factors. In logistic regression, older age groups (O.R.:2.94-3.71), people living in rural area (O.R.:1.87), and current smokers (O.R.:1.77) were significantly prone to have periodontitis. People who earned monthly income of more than 2 million Korean won (O.R.:0.64) and brushed their teeth two or more times per day (O.R.:0.60-0.62) had significantly lower risk of having periodontitis.
CONCLUSIONS
About 10% of Korean adults had periodontitis in 2006. People who were older, living in rural region, in lower income status, smoking, less tooth brushing were more likely to have periodontitis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burt B. Position paper: epidemiology of periodontal diseases. J Periodontol. 2005. 76:1406–1419.2. Page RC, Beck JD. Risk assessment for periodontal diseases. Int Dent J. 1997. 47:61–87.
Article3. Gordis L. Measuring the occurrence of disease: I. Morbidity. Epidemiology. 2009. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier;43.4. Albandar JM, Brunelle JA, Kingman A. Destructive periodontal disease in adults 30 years of age and older in the United States, 1988-1994. J Periodontol. 1999. 70:13–29.
Article5. Dowsett SA, Archila L, Kowolik MJ. Oral health status of an indigenous adult population of Central America. Community Dent Health. 2001. 18:162–166.6. Gjermo P, Rosing CK, Susin C, Oppermann R. Periodontal diseases in Central and South America. Periodontol 2000. 2002. 29:70–78.
Article7. Taani DS. Oral health in Jordan. Int Dent J. 2004. 54:395–400.
Article8. Cobb CM, Williams KB, Gerkovitch MM. Is the prevalence of periodontitis in the USA in decline? Periodontol 2000. 2009. 50:13–24.
Article9. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korean National Oral Health Survey 2000. 2001. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare;28–30.10. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korean National Oral Health Survey 2006. 2007. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare;23–24.11. Ainamo J, Barmes D, Beagrie G, et al. Development of the World Health Organization (WHO) community periodontal index of treatment needs (CPITN). Int Dent J. 1982. 32:281–291.12. Borrell LN, Kunzel C, Lamster I, Lalla E. Diabetes in the dental office: using NHANES III to estimate the probability of undiagnosed disease. J Periodontal Res. 2007. 42:559–565.
Article13. Cook S, Auinger P, Li C, Ford ES. Metabolic syndrome rates in United States adolescents, from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999-2002. J Pediatr. 2008. 152:165–170.
Article14. Demmer RT, Jacobs DR Jr., Desvarieux M. Periodontal disease and incident type 2 diabetes: results from the First National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and its epidemiologic follow-up study. Diabetes Care. 2008. 31:1373–1379.15. Noble JM, Borrell LN, Papapanou PN, et al. Periodontitis is associated with cognitive impairment among older adults: analysis of NHANES-III. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009. Forthcoming.
Article16. Goodson JM. Diagnosis of periodontitis by physical measurement: interpretation from episodic disease hypothesis. J Periodontol. 1992. 63:373–382.
Article17. Jeffcoat MK, Reddy MS. Advances in measurements of periodontal bone and attachment loss. Monogr Oral Sci. 2000. 17:56–72.
Article18. Haffajee AD, Socransky SS. Attachment level changes in destructive periodontal diseases. J Clin Periodontol. 1986. 13:461–475.
Article19. Oliver RC, Brown LJ, Löe H. Periodontal diseases in the United States population. J Periodontol. 1998. 69:269–278.
Article20. Bacić M, Plancak D, Granić M. CPITN assessment of periodontal disease in diabetic patients. J Periodontol. 1988. 59:816–822.
Article21. Ojima M, Hanioka T, Tanaka K, Inoshita E, Aoyama H. Relationship between smoking status and periodontal conditions: findings from national databases in Japan. J Periodontal Res. 2006. 41:573–579.
Article22. Papapanou PN. Periodontal diseases: epidemiology. Ann Periodontol. 1996. 1:1–36.
Article23. Nunn ME. Understanding the etiology of periodontitis: an overview of periodontal risk factors. Periodontol 2000. 2003. 32:11–23.
Article24. Taylor GW, Borgnakke WS. Self-reported periodontal disease: validation in an epidemiological survey. J Periodontol. 2007. 78:1407–1420.
Article25. Haber J, Wattles J, Crowley M, et al. Evidence for cigarette smoking as a major risk factor for periodontitis. J Periodontol. 1993. 64:16–23.
Article26. Hujoel PP, Drangsholt M, Spiekerman C, DeRouen TA. Periodontitis-systemic disease associations in the presence of smoking--causal or coincidental? Periodontol 2000. 2002. 30:51–60.
Article27. Laxman VK, Annaji S. Tobacco use and its effects on the periodontium and periodontal therapy. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2008. 9:97–107.
Article28. Nibali L, D'Aiuto F, Griffiths G, et al. Severe periodontitis is associated with systemic inflammation and a dysmetabolic status: a case-control study. J Clin Periodontol. 2007. 34:931–937.
Article29. Tsai C, Hayes C, Taylor GW. Glycemic control of type 2 diabetes and severe periodontal disease in the US adult population. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2002. 30:182–192.
Article30. Merchant A, Pitiphat W, Douglass CW, Crohin C, Joshipura K. Oral hygiene practices and periodontitis in health care professionals. J Periodontol. 2002. 73:531–535.
Article31. Williams KB, Cobb CM, Taylor HJ, Brown AR, Bray KK. Effect of sonic and mechanical toothbrushes on subgingival microbial flora: a comparative in vivo scanning electron microscopy study of 8 subjects. Quintessence Int. 2001. 32:147–154.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence and risk factors of periodontitis among adults with or without diabetes mellitus
- A study on the relationship between food insecurity and periodontitis in Korean adults: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VII) from 2016-2018
- Risk factors for dental caries and severe periodontitis in Korean adults: analysis with the 2016-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data
- The association between periodontitis and systemic disease among Korean adults
- Association between Vitamin D Level in Blood and Periodontitis in Korean Elderly