Tuberc Respir Dis.
2015 Oct;78(4):371-374. 10.4046/trd.2015.78.4.371.
Pulmonary Pneumatocele in a Pneumonia Patient Infected with Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase Producing Proteus mirabilis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dankook University Hospital, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. hkh0519@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2320709
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2015.78.4.371
Abstract
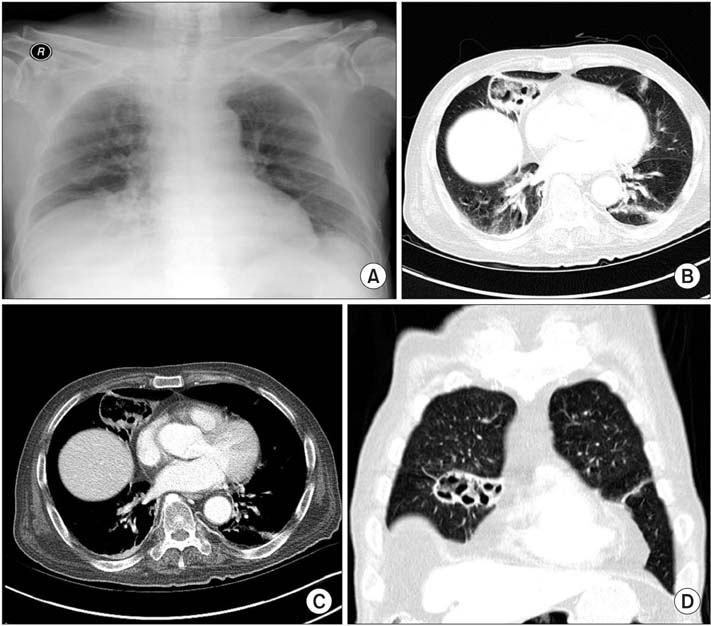
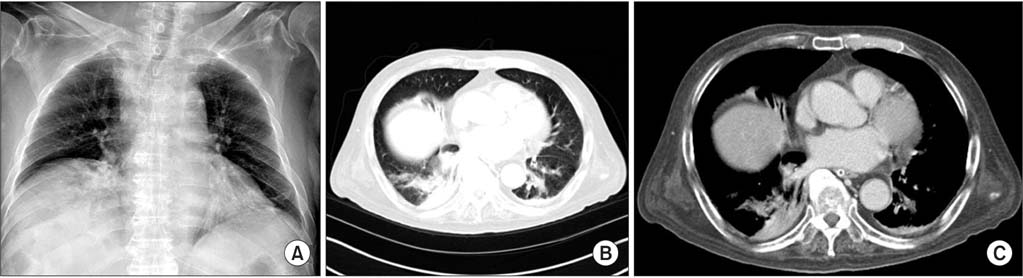
- Pulmonary pneumatoceles are air-filled thin-walled spaces within the lung and are rare in adult cases of pneumonia. We report the case of a 74-year-old male who was admitted with a cough and sputum production. He had been treated with oral dexamethasone since a brain tumorectomy 6 months prior. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) of the chest revealed a large pneumatocele in the right middle lobe and peripheral pneumonic consolidation. Bronchoalveolar lavage was performed; cultures identified extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Proteus mirabilis. A 4-week course of intravenous ertapenem was administered, and the pneumatocele with pneumonia resolved on follow-up chest CT. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of pulmonary pneumatocele caused by ESBL-producing P. mirabilis associated with pneumonia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lysy J, Werczberger A, Globus M, Chowers I. Pneumatocele formation in a patient with Proteus mirabilis pneumonia. Postgrad Med J. 1985; 61:255–257.2. McGarry T, Giosa R, Rohman M, Huang CT. Pneumatocele formation in adult pneumonia. Chest. 1987; 92:717–720.3. Meyers HI, Jacobson G. Staphylococcal pneumonia in children and adults. Radiology. 1959; 72:665–671.4. Ceruti E, Contreras J, Neira M. Staphylococcal pneumonia in childhood: long-term follow-up including pulmonary function studies. Am J Dis Child. 1971; 122:386–392.5. Thapa BR, Kumar L, Mitra SK. Proteus mirabilis pneumonia with giant pneumatocele. Indian J Pediatr. 1987; 54:593–597.6. Wu JJ, Chen HM, Ko WC, Wu HM, Tsai SH, Yan JJ. Prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in Proteus mirabilis in a Taiwanese university hospital, 1999 to 2005: identification of a novel CTX-M enzyme (CTX-M-66). Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008; 60:169–175.7. Endimiani A, Luzzaro F, Brigante G, Perilli M, Lombardi G, Amicosante G, et al. Proteus mirabilis bloodstream infections: risk factors and treatment outcome related to the expression of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005; 49:2598–2605.8. O'Hara CM, Brenner FW, Miller JM. Classification, identification, and clinical significance of Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2000; 13:534–546.9. Sturenburg E, Mack D. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: implications for the clinical microbiology laboratory, therapy, and infection control. J Infect. 2003; 47:273–295.10. de Champs C, Bonnet R, Sirot D, Chanal C, Sirot J. Clinical relevance of Proteus mirabilis in hospital patients: a two year survey. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000; 45:537–539.11. Okimoto N, Hayashi T, Ishiga M, Nanba F, Kishimoto M, Yagi S, et al. Clinical features of Proteus mirabilis pneumonia. J Infect Chemother. 2010; 16:364–366.12. Kim JY, Park YJ, Kim SI, Kang MW, Lee SO, Lee KY. Nosocomial outbreak by Proteus mirabilis producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamase VEB-1 in a Korean university hospital. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004; 54:1144–1147.13. Quigley MJ, Fraser RS. Pulmonary pneumatocele: pathology and pathogenesis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988; 150:1275–1277.14. Zuhdi MK, Spear RM, Worthen HM, Peterson BM. Percutaneous catheter drainage of tension pneumatocele, secondarily infected pneumatocele, and lung abscess in children. Crit Care Med. 1996; 24:330–333.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Use of Boronic Acid Disks for the Detection of Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase and AmpC beta-lactamase in Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca and Proteus mirabilis
- Isolation Frequency of Extended Spectrum beta-Lactamase Producing Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, and Proteus mirabilis
- Epidemiology of Ciprofloxacin Resistance and Its Relationship to Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase Production in Proteus mirabilis Bacteremia
- Two Cases of Neonatal Osteomyelitis due to Extended Spectrum beta-lactamase Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Detection and Occurrence of Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase-Producing Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter spp., Proteus spp., and Serratia marcescens Isolates