Tuberc Respir Dis.
2014 Aug;77(2):94-97. 10.4046/trd.2014.77.2.94.
Empyema Necessitatis in a Patient on Peritoneal Dialysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym Kidney Research Institute, Seoul, Korea. km2071@unitel.co.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2320546
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.77.2.94
Abstract
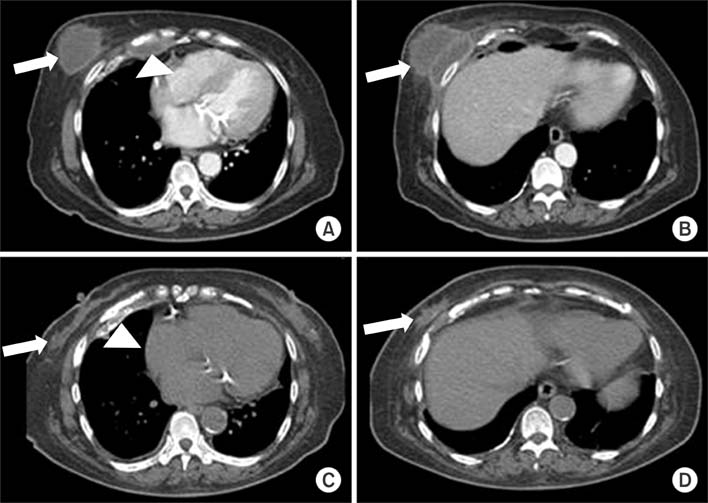
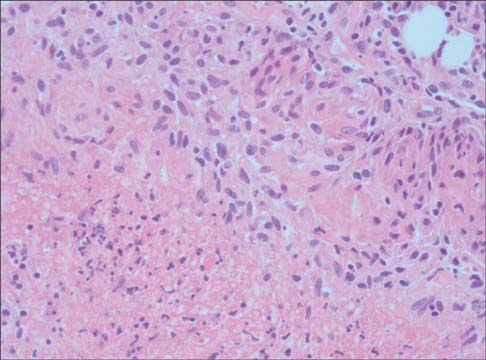
- Empyema necessitatis is a rare complication of an empyema. Although the incidence is thought to be decreased in the post-antibiotic era, immunocompromised patients such as patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis are still at a higher risk. A 56-year-old woman on peritoneal dialysis presented with an enlarging mass on the right anterior chest wall. The chest computed tomography scan revealed an empyema necessitatis and the histopathologic findings revealed a granulomatous inflammation with caseation necrosis. The patient was treated with anti-tuberculous medication.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jover F, Andreu L, Cuadrado JM, Montagud J, Merino J. Tuberculous empyema necessitatis in a man infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. South Med J. 2002; 95:751–752.2. Aylk S, Qakan A, Aslankara N, Ozsoz A. Tuberculous abscess on the chest wall. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2009; 71:39–42.3. Llamas-Velasco M, Dominguez I, Ovejero E, Perez-Gala S, Garcia-Diez A. Empyema necessitatis revisited. Eur J Dermatol. 2010; 20:115–119.4. Sindel EA. Empyema necessitates. Q Bull Sea View Hosp. 1940; 6:1–49.5. Freeman AF, Ben-Ami T, Shulman ST. Streptococcus pneumoniae empyema necessitatis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004; 23:177–179.6. Hussein MM, Mooij JM, Roujouleh H. Tuberculosis and chronic renal disease. Semin Dial. 2003; 16:38–44.7. el-Shahawy MA, Gadallah MF, Campese VM. Tuberculosis of the spine (Pott's disease) in patients with end-stage renal disease. Am J Nephrol. 1994; 14:55–59.8. Akgul AG, Orki A, Orki T, Yuksel M, Arman B. Approach to empyema necessitatis. World J Surg. 2011; 35:981–984.9. Reyes CV. Cutaneous tumefaction in empyema necessitatis. Int J Dermatol. 2007; 46:1294–1297.10. Noyes BE, Michaels MG, Kurland G, Armitage JM, Orenstein DM. Pseudomonas cepacia empyema necessitatis after lung transplantation in two patients with cystic fibrosis. Chest. 1994; 105:1888–1891.11. Tonna I, Conlon CP, Davies RJ. A case of empyema necessitatis. Eur J Intern Med. 2007; 18:441–442.12. Reyes CV, Thompson KS, Jensen J. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of mastitis secondary to empyema necessitatis: a report of two cases. Acta Cytol. 1999; 43:873–876.13. Glicklich M, Mendelson DS, Gendal ES, Teirstein AS. Tuberculous empyema necessitatis. Computed tomography findings. Clin Imaging. 1990; 14:23–25.14. Chaiyasate K, Hramiec J. Images in clinical medicine. Tuberculosis empyema necessitatis. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:e8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tuberculous Empyema Necessitatis with Osteomyelitis, a Rare Case in the 21st Century
- Peritoneal-pleural leak improved by switching from continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis to automated peritoneal dialysis
- Ultrasonographic findings of tuberculous empyema necessitatis
- Treatment of Huge Chronic Tuberculous Empyema with Cardiopulmonary Dysfunction: 1 case report
- New dialysis treatment options for patients with end-stage chronic kidney disease