Tuberc Respir Dis.
2014 Aug;77(2):81-84. 10.4046/trd.2014.77.2.81.
A Case of Venlafaxine-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. sicha@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2320543
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.77.2.81
Abstract
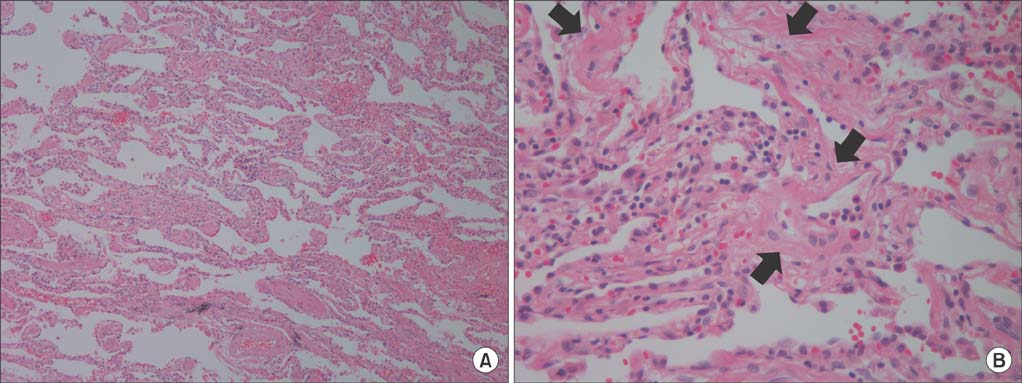
- A patient treated with venlafaxine for major depression developed an interstitial lung disease (ILD) with the characteristic clinical, radiological and pathological features of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. A high resolution computed tomography scan demonstrated ground glass opacity, mosaic perfusion with air-trapping and traction bronchiectasis in both lungs. The pathological findings were consistent with a nonspecific interstitial pneumonia pattern. Clinical and radiological improvements were noted after the discontinuation of venlafaxine and the administration of a corticosteroid. This report provides further evidence that the anti-depressant venlafaxine can cause ILD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Paparrigopoulos T, Tzavellas E, Karaiskos D, Ilias I, Liappas I. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia after venlafaxine overdose. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2011; 31:258–259.2. Turner RC, Nelson JE, Roberts BT, Gillam DM. Venlafaxine-associated interstitial pneumonitis. Pharmacotherapy. 2005; 25:626–629.3. Feighner JP. The role of venlafaxine in rational antidepressant therapy. J Clin Psychiatry. 1994; 55:Suppl A. 62–68.4. Andrews JM, Ninan PT, Nemeroff CB. Venlafaxine: a novel antidepressant that has a dual mechanism of action. Depression. 1996; 4:48–56.5. Melien O, Skaali T, Myhr K, Brors O. Venlafaxine and asthma. Nord J Psychiatry. 2005; 59:538–540.6. Tsigkaropoulou E, Hatzilia D, Rizos E, Christodoulou C, Loukides S, Papiris S, et al. Venlafaxine-induced acute eosinophilic pneumonia. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2011; 33:411.e7–411.e9.7. Fleisch MC, Blauer F, Gubler JG, Kuhn M, Scherer TA. Eosinophilic pneumonia and respiratory failure associated with venlafaxine treatment. Eur Respir J. 2000; 15:205–208.8. Drent M, Singh S, Gorgels AP, Hansell DM, Bekers O, Nicholson AG, et al. Drug-induced pneumonitis and heart failure simultaneously associated with venlafaxine. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 167:958–961.9. Arias SA, Cohen P, Kwon JS. Clozapine-induced lymphocytic alveolitis. Am J Psychiatry. 2011; 168:210–211.10. Gonzalez-Rothi RJ, Zander DS, Ros PR. Fluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac)-induced pulmonary disease. Chest. 1995; 107:1763–1765.11. Borderias Clau L, Marigil Gomez MA, Val Adan P, Marcen Letosa M, Biescas Lopez R, Garrapiz Lopez FJ. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis due to venlafaxine. Arch Bronconeumol. 2008; 44:571–573.12. Patel RA, Sellami D, Gotway MB, Golden JA, Webb WR. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: patterns on high-resolution CT. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2000; 24:965–970.13. Barrera L, Mendoza F, Zuniga J, Estrada A, Zamora AC, Melendro EI, et al. Functional diversity of T-cell subpopulations in subacute and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 177:44–55.14. Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, Sandor P, Ruiz I, Roberts EA, et al. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981; 30:239–245.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Low dose Venlafaxine-Induced Hypertension
- Vaginal Bleeding Associated with Venlafaxine Add-On Therapy: A Case Report
- Multiple Cancers in a Patient with Systemic Sclerosis and Aggravated Interstitial Lung Disease by Chemotherapy
- A Case Report of Rare Adverse Events Associated with Venlafaxine Administration: Hypoglycemia and Lactic Acidosis
- Carbamazepine-induced Acute Interstitial Lung Disease