Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Aug;75(2):59-66.
Elevated Prx1 Provides Resistance to Docetaxel, But Is Not Associated with Predictive Significance in Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Institute of Wonkwang Medical Science, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. kshryj@wonkwang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
This study was conducted in order to elucidate the effects of docetaxel on the growth of peroxiredoxin 1 (Prx1) knockdown A549 xenograft tumors and further tested the role of Prx1 as a predictor for how a patient would respond to docetaxel treatment.
METHODS
Effects of docetaxel on the growth of scrambled- and shPrx1-infected A549 xenograft tumors in nude mice were measured. Moreover, immunohistochemical expression of Prx1 was evaluated in paraffin-embedded tissues from 24 non-small cell lung cancer patients who had received docetaxel-cisplatin regimens as a first-line treatment.
RESULTS
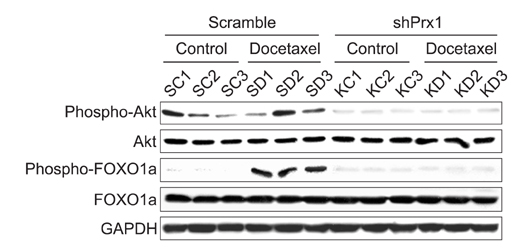
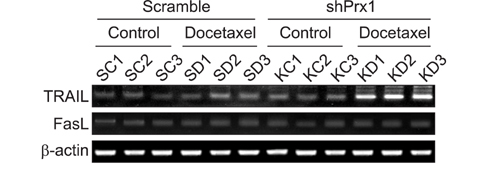
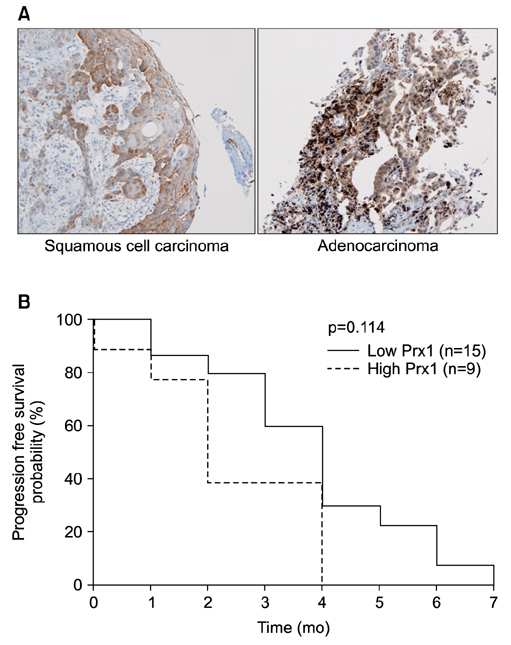
Docetaxel treatment in Prx1 knockdown xenograft tumor resulted in reduced tumors growth compared with other groups. Prx1 knockdown increased the production of cleaved caspases-8 and -9 in the control itself compared to scramble tumors. Moreover, docetaxel treatment in Prx1 knockdown tissue led to an increased protein band. Phosphorylated Akt was found in Prx1 scramble tissues. Phosphorylated FOXO1 was detected in the docetaxel treatment group. On the other hand, Prx1 knockdown completely suppressed the Akt-FOXO1 axis. The median progression-free survival (PFS) of patients with low Prx1 expression was 7 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 6.0-7.7), whereas the median progression-free survival of patients with high Prx1 expression was 4 months (95% CI, 4.0-5.0). However, high Prx1 expression was not associated with decreased PFS (p=0.114).
CONCLUSION
Our findings suggest that elevated Prx1 provides resistance to docetaxel treatment through suppression of FOXO1-induced apoptosis in A549 xenograft tumors, but may not be related with the predictive significance for response to docetaxel treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010; 60:277–300.2. Rigas JR. Do newer chemotherapeutic agents improve survival in non-small cell lung cancer? Semin Oncol. 1998; 25:3 Suppl 8. 5–9.3. Posner MR. Docetaxel in squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. Anticancer Drugs. 2001; 12:Suppl 1. S21–S24.4. Rowinsky EK. The development and clinical utility of the taxane class of antimicrotubule chemotherapy agents. Annu Rev Med. 1997; 48:353–374.5. Bhalla KN. Microtubule-targeted anticancer agents and apoptosis. Oncogene. 2003; 22:9075–9086.6. Haldar S, Chintapalli J, Croce CM. Taxol induces bcl-2 phosphorylation and death of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1996; 56:1253–1255.7. Haldar S, Basu A, Croce CM. Bcl2 is the guardian of microtubule integrity. Cancer Res. 1997; 57:229–233.8. Lee LF, Li G, Templeton DJ, Ting JP. Paclitaxel (Taxol)-induced gene expression and cell death are both mediated by the activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK/SAPK). J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:28253–28260.9. Amato SF, Swart JM, Berg M, Wanebo HJ, Mehta SR, Chiles TC. Transient stimulation of the c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase/activator protein 1 pathway and inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase are early effects in paclitaxel-mediated apoptosis in human B lymphoblasts. Cancer Res. 1998; 58:241–247.10. Mhaidat NM, Zhang XD, Jiang CC, Hersey P. Docetaxel-induced apoptosis of human melanoma is mediated by activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and inhibited by the mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:1308–1314.11. Mhaidat NM, Wang Y, Kiejda KA, Zhang XD, Hersey P. Docetaxel-induced apoptosis in melanoma cells is dependent on activation of caspase-2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007; 6:752–761.12. Iwao-Koizumi K, Matoba R, Ueno N, Kim SJ, Ando A, Miyoshi Y, et al. Prediction of docetaxel response in human breast cancer by gene expression profiling. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:422–431.13. Rhee SG, Kang SW, Chang TS, Jeong W, Kim K. Peroxiredoxin, a novel family of peroxidases. IUBMB Life. 2001; 52:35–41.14. Yanagawa T, Ishikawa T, Ishii T, Tabuchi K, Iwasa S, Bannai S, et al. Peroxiredoxin I expression in human thyroid tumors. Cancer Lett. 1999; 145:127–132.15. Yanagawa T, Iwasa S, Ishii T, Tabuchi K, Yusa H, Onizawa K, et al. Peroxiredoxin I expression in oral cancer: a potential new tumor marker. Cancer Lett. 2000; 156:27–35.16. Noh DY, Ahn SJ, Lee RA, Kim SW, Park IA, Chae HZ. Overexpression of peroxiredoxin in human breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2001; 21:2085–2090.17. Lehtonen ST, Svensk AM, Soini Y, Paakko P, Hirvikoski P, Kang SW, et al. Peroxiredoxins, a novel protein family in lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2004; 111:514–521.18. Kim HJ, Chae HZ, Kim YJ, Kim YH, Hwangs TS, Park EM, et al. Preferential elevation of Prx I and Trx expression in lung cancer cells following hypoxia and in human lung cancer tissues. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2003; 19:285–298.19. Chang JW, Lee SH, Jeong JY, Chae HZ, Kim YC, Park ZY, et al. Peroxiredoxin-I is an autoimmunogenic tumor antigen in non-small cell lung cancer. FEBS Lett. 2005; 579:2873–2877.20. Chen MF, Keng PC, Shau H, Wu CT, Hu YC, Liao SK, et al. Inhibition of lung tumor growth and augmentation of radiosensitivity by decreasing peroxiredoxin I expression. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 64:581–591.21. Kim JH, Bogner PN, Ramnath N, Park Y, Yu J, Park YM. Elevated peroxiredoxin 1, but not NF-E2-related factor 2, is an independent prognostic factor for disease recurrence and reduced survival in stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:3875–3882.22. Kim JH, Bogner PN, Baek SH, Ramnath N, Liang P, Kim HR, et al. Up-regulation of peroxiredoxin 1 in lung cancer and its implication as a prognostic and therapeutic target. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:2326–2333.23. Chhipa RR, Lee KS, Onate S, Wu Y, Ip C. Prx1 enhances androgen receptor function in prostate cancer cells by increasing receptor affinity to dihydrotestosterone. Mol Cancer Res. 2009; 7:1543–1552.24. Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951; 193:265–275.25. Suhara T, Kim HS, Kirshenbaum LA, Walsh K. Suppression of Akt signaling induces Fas ligand expression: involvement of caspase and Jun kinase activation in Akt-mediated Fas ligand regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 2002; 22:680–691.26. Dijkers PF, Medema RH, Lammers JW, Koenderman L, Coffer PJ. Expression of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member Bim is regulated by the forkhead transcription factor FKHR-L1. Curr Biol. 2000; 10:1201–1204.27. Tannock IF, de Wit R, Berry WR, Horti J, Pluzanska A, Chi KN, et al. Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:1502–1512.28. Montgomery RB, Bonham M, Nelson PS, Grim J, Makary E, Vessella R, et al. Estrogen effects on tubulin expression and taxane mediated cytotoxicity in prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 2005; 65:141–150.29. Yu D, Jing T, Liu B, Yao J, Tan M, McDonnell TJ, et al. Overexpression of ErbB2 blocks Taxol-induced apoptosis by upregulation of p21Cip1, which inhibits p34Cdc2 kinase. Mol Cell. 1998; 2:581–591.30. Wu JD, Haugk K, Coleman I, Woodke L, Vessella R, Nelson P, et al. Combined in vivo effect of A12, a type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor antibody, and docetaxel against prostate cancer tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12(20 Pt 1):6153–6160.31. Xing H, Weng D, Chen G, Tao W, Zhu T, Yang X, et al. Activation of fibronectin/PI-3K/Akt2 leads to chemoresistance to docetaxel by regulating survivin protein expression in ovarian and breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2008; 261:108–119.32. Kosaka T, Miyajima A, Shirotake S, Suzuki E, Kikuchi E, Oya M. Long-term androgen ablation and docetaxel up-regulate phosphorylated Akt in castration resistant prostate cancer. J Urol. 2011; 185:2376–2381.33. Biggs WH 3rd, Meisenhelder J, Hunter T, Cavenee WK, Arden KC. Protein kinase B/Akt-mediated phosphorylation promotes nuclear exclusion of the winged helix transcription factor FKHR1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:7421–7426.34. Kops GJ, Burgering BM. Forkhead transcription factors: new insights into protein kinase B (c-akt) signaling. J Mol Med (Berl). 1999; 77:656–665.35. Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, et al. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell. 1999; 96:857–868.36. Modur V, Nagarajan R, Evers BM, Milbrandt J. FOXO proteins regulate tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand expression. Implications for PTEN mutation in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:47928–47937.37. Lee YJ, Park MY, Kang YA, Kwon SY, Yoon HI, Lee JH, et al. Enhancement of sensitivity of human lung cancer cell line to TRAIL and gefitinib of IGF-1R blockade. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2007; 63:42–51.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cell Death Induction Mechanism of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Line, NCI-H1703 by Docetaxel
- Comparison of Gefitinib versus Docetaxel in Patients with Pre-Treated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- A Case of Subungal Abscess And Onycholysis Related to Docetaxel
- A Case of Patient with Coincident Lung Cancer and Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Docetaxel-Cisplatin Chemotherapy
- Docetaxel as Second-line Monotherapy for Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer