Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Aug;75(2):52-58.
Clinical Features and Prognostic Factors in Elderly Koreans with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in a Tertiary Referral Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Medical Center and Ewha Medical Research Institute, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. medyon@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Ewha Medical Center and Ewha Medical Research Institute, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
More than half of cases for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) occur in elderly patients with a median age at diagnosis of 70 years. The aim of our study was to examine the clinical features and prognostic factors contributing to mortality in elderly patients with advanced NSCLC.
METHODS
Following a retrospective review of clinical data, 122 patients aged 70 years and over with a histopathological diagnosis of locally advanced (stage IIIB, n=32) and metastatic (stage IV, n=90) NSCLC between 2005 and 2011 were enrolled.
RESULTS
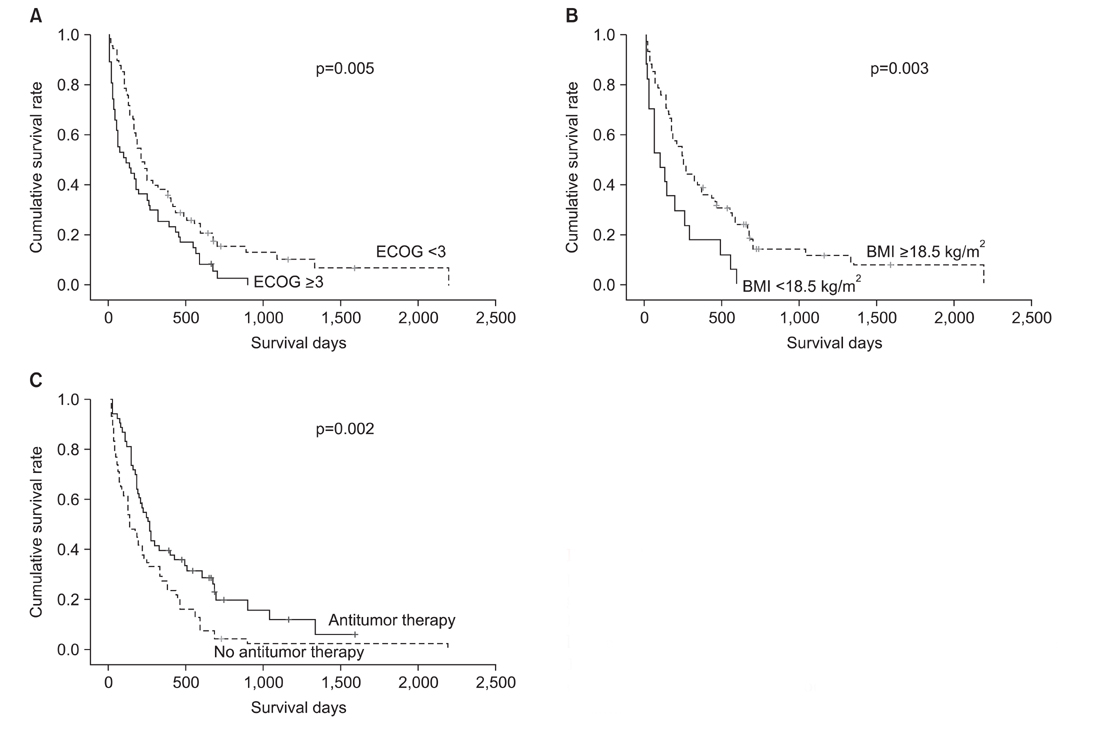
The median age was 76 years (interquartile range, [IQR], 72-80 years), and 85 (70%) patients were male. Fifty-seven (46%) patients had never smoked, and 17 (19%) were in a malnourished state with a body mass index (BMI) of <18.5 kg/m2. The initial treatments included chemotherapy (40%) and radiotherapy (7%), but 57% of the patients received supportive care only. The 1-year survival rate was 32%, and the 3-year survival rate was 4%, with a median survival duration of 6.2 months (IQR, 2.5-15.3 months). Male gender (hazard ratio [HR], 2.2; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.3-3.9; p=0.005), low BMI (HR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.3-3.9; p=0.004), and supportive care only (HR, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.2-2.9; p=0.007) were independent predictors of shorter survival based on a Cox proportional hazards model.
CONCLUSION
Elderly patients with advanced NSCLC had a poor prognosis, particularly male patients, those with a low BMI, and those who received supportive care only.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung KW, Park S, Kong HJ, Won YJ, Lee JY, Park EC, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2008. Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 43:1–11.2. Kim YC, Kwon YS, Oh IJ, Kim KS, Kim SY, Ryu JS, et al. National survey of lung cancer in Korea, 2005. J Lung Cancer. 2007; 6:67–73.3. Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM Classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2007; 2:706–714.4. Jung SY, Park DI, Park MR, Jung SS, Kim JO, Kim SY, et al. Clinical characteristics of patients older than 76 with lung cancer. Korean J Med. 2012; 82:562–568.5. Gridelli C, Perrone F, Gallo C, Cigolari S, Rossi A, Piantedosi F, et al. Chemotherapy for elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: the Multicenter Italian Lung Cancer in the Elderly Study (MILES) phase III randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003; 95:362–372.6. Schild SE, Stella PJ, Geyer SM, Bonner JA, McGinnis WL, Mailliard JA, et al. The outcome of combined-modality therapy for stage III non-small-cell lung cancer in the elderly. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:3201–3206.7. The World Health Organization histological typing of lung tumours. Second edition. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982; 77:123–136.8. Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012; 62:10–29.9. Kim HS, Hyun DS, Kim KC, Lee SC, Jung TH, Park JY, et al. The clinical characteristics and prognosis of elderly patient with lung cancer diagnosed in Daegu and Gyeongsangbukdo. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2008; 65:15–22.10. Hsu CL, Chen KY, Shih JY, Ho CC, Yang CH, Yu CJ, et al. Advanced non-small cell lung cancer in patients aged 45 years or younger: outcomes and prognostic factors. BMC Cancer. 2012; 12:241.11. Jang TW, Kim YC, Kwon YS, Oh IJ, Kim KS, Kim SY, et al. Female lung cancer: re-analysis of national survey of lung cancer in Korea, 2005. J Lung Cancer. 2010; 9:57–63.12. Berghmans T, Paesmans M, Sculier JP. Prognostic factors in stage III non-small cell lung cancer: a review of conventional, metabolic and new biological variables. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2011; 3:127–138.13. Rivera MP, Stover DE. Gender and lung cancer. Clin Chest Med. 2004; 25:391–400.14. Brown JS, Eraut D, Trask C, Davison AG. Age and the treatment of lung cancer. Thorax. 1996; 51:564–568.15. Montella M, Gridelli C, Crispo A, Scognamiglio F, Ruffolo P, Gatani T, et al. Has lung cancer in the elderly different characteristics at presentation? Oncol Rep. 2002; 9:1093–1096.16. Van Cutsem E, Arends J. The causes and consequences of cancer-associated malnutrition. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2005; 9:Suppl 2. S51–S63.17. Yang R, Cheung MC, Pedroso FE, Byrne MM, Koniaris LG, Zimmers TA. Obesity and weight loss at presentation of lung cancer are associated with opposite effects on survival. J Surg Res. 2011; 170:e75–e83.18. Luo J, Chen YJ, Narsavage GL, Ducatman A. Predictors of survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2012; 39:609–616.19. Langer CJ. Clinical evidence on the undertreatment of older and poor performance patients who have advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: is there a role for targeted therapy in these cohorts? Clin Lung Cancer. 2011; 12:272–279.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgery for Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Relationship between DNA ploidy and Survival Time in Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Management of Locally Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Molecularly Targeted Therapy for Lung Cancer : Recent Topics
- The Relationship between (the) Loss of Blood Group Antigen A in Cancer Tissue and Survival Time in the Antigen A Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer