Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Jan;74(1):23-27.
A Case of Multicentric Castleman's Disease Presenting with Follicular Bronchiolitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. sicha@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
Abstract
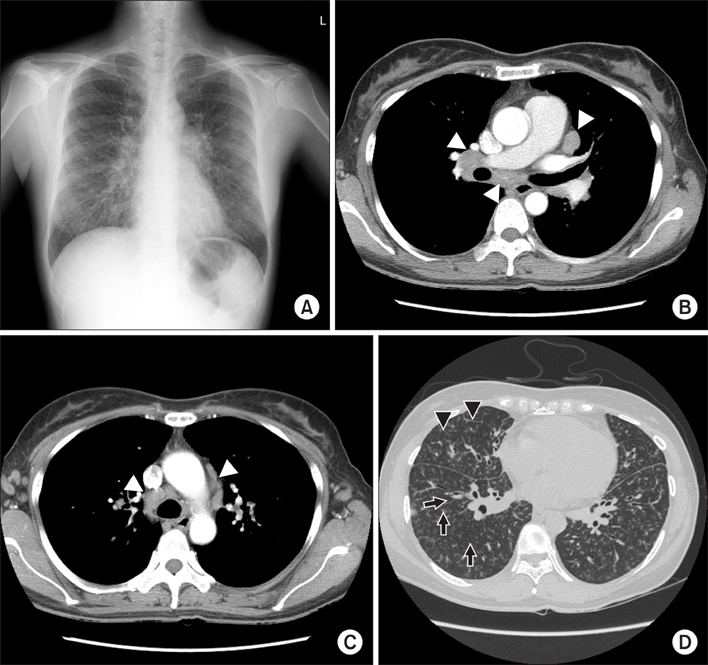
- Multicentric Castleman's disease (CD) is a rare atypical lymphoproliferative disorder, which is characterized by various systemic manifestations. Some patients with multicentric CD may have concomitant lung parenchymal lesions, for which lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP) is known to be the most common pathologic finding. Follicular bronchiolitis and LIP are considered to be on the same spectrum of the disease. We describe a case of multicentric CD with pulmonary involvement, which was pathologically proven as follicular bronchiolitis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ko SF, Hsieh MJ, Ng SH, Lin JW, Wan YL, Lee TY, et al. Imaging spectrum of Castleman's disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 182:769–775.2. Keller AR, Hochholzer L, Castleman B. Hyaline-vascular and plasma-cell types of giant lymph node hyperplasia of the mediastinum and other locations. Cancer. 1972. 29:670–683.3. Castleman B, Iverson L, Menendez VP. Localized mediastinal lymphnode hyperplasia resembling thymoma. Cancer. 1956. 9:822–830.4. Johkoh T, Muller NL, Ichikado K, Nishimoto N, Yoshizaki K, Honda O, et al. Intrathoracic multicentric Castleman disease: CT findings in 12 patients. Radiology. 1998. 209:477–481.5. Casper C. The aetiology and management of Castleman disease at 50 years: translating pathophysiology to patient care. Br J Haematol. 2005. 129:3–17.6. Peterson BA, Frizzera G. Multicentric Castleman's disease. Semin Oncol. 1993. 20:636–647.7. Nishimoto N, Kanakura Y, Aozasa K, Johkoh T, Nakamura M, Nakano S, et al. Humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody treatment of multicentric Castleman disease. Blood. 2005. 106:2627–2632.8. Weisenburger DD, Nathwani BN, Winberg CD, Rappaport H. Multicentric angiofollicular lymph node hyperplasia: a clinicopathologic study of 16 cases. Hum Pathol. 1985. 16:162–172.9. Frizzera G, Peterson BA, Bayrd ED, Goldman A. A systemic lymphoproliferative disorder with morphologic features of Castleman's disease: clinical findings and clinicopathologic correlations in 15 patients. J Clin Oncol. 1985. 3:1202–1216.10. Iyonaga K, Ichikado K, Muranaka H, Fujii K, Yamaguchi T, Suga M. Multicentric Castleman's disease manifesting in the lung: clinical, radiographic, and pathologic findings and successful treatment with corticosteroid and cyclophosphamide. Intern Med. 2003. 42:182–186.11. Higuchi T, Nakanishi T, Takada K, Matsumoto M, Okada M, Horikoshi H, et al. A case of multicentric Castleman's disease having lung lesion successfully treated with humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab. J Korean Med Sci. 2010. 25:1364–1367.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Human Herpesvirus-8 Positive Multicentric Castleman’s Disease with Complete Response after Rituximab Monotherapy: A Case Report
- A Case of Kaposi's Sarcoma Associated with Castleman's Disease
- General anesthesia in a patient with multicentric Castleman's disease: a case report
- A Case of Glomeruloid Hemangioma in a Patient with Multicentric Castleman's Disease
- A Case of Localized Castleman's Disease in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis