Tuberc Respir Dis.
2012 Jun;72(6):507-510.
Intralobar Pulmonary Sequestration Showing Increased Serum CA19-9
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Plus Internal Medicine Clinic, Suncheon, Korea. spikeahn@naver.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Plus Internal Medicine Clinic, Suncheon, Korea.
Abstract
- Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) is a specific tumor marker of the biliary, pancreatic and gastrointestinal tracts. CA19-9 is occasionally elevated in serum in patiens with benign pulmonary diseases such as bronchiectasis, idiopathic interstitial pneumonia or collagen disease-associated pulmonary fibrosis. Intralobar pulmonary sequestration is an uncommon congenital lung anomaly. It is dissociated from the normal tracheobronchial tree and is supplied by an anomalous systemic artery. There have been some reports of elevation of CA19-9 in this lesion. We report a case of intralobar pulmonary sequestration with elevated serum CA19-9 in a 29-year-old man who was diagnosed with bronchiectasia of left lower lung field on general check up. He had no evidence of any malignant disease in pancreatobiliary or gastrointestinal tracts. Elevated serum CA19-9 level might be encountered with benign pulmonary disease such as pulmonary sequestration.
MeSH Terms
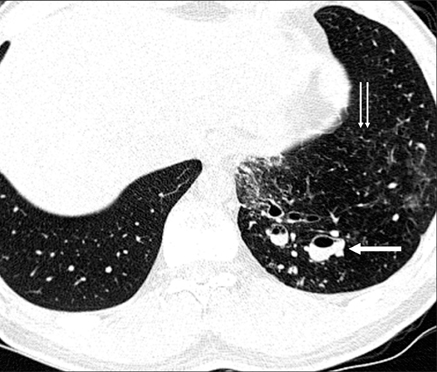
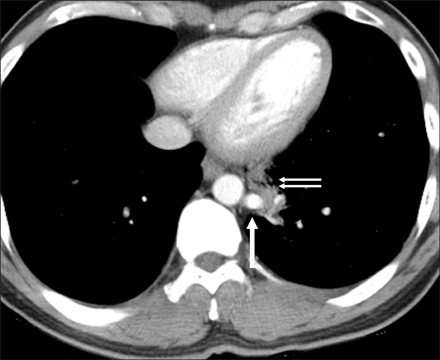
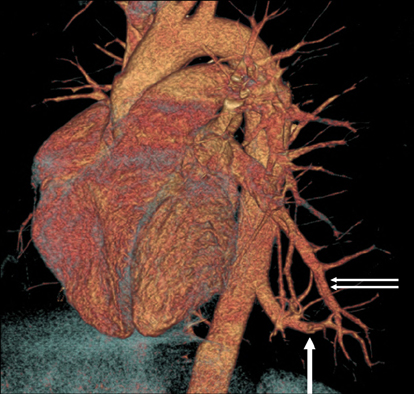
Figure
Reference
-
1. Savic B, Birtel FJ, Tholen W, Funke HD, Knoche R. Lung sequestration: report of seven cases and review of 540 published cases. Thorax. 1979. 34:96–101.2. Cho HM, Shin DH, Kim KD, Lee S, Chung KY. Clinicopathological correlation of intralobar pulmonary sequestration. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003. 36:356–362.3. Gupta MK, Arciaga R, Bocci L, Tubbs R, Bukowski R, Deodhar SD. Measurement of a monoclonal-antibody-defined antigen (CA19-9) in the sera of patients with malignant and nonmalignant diseases: comparison with carcinoembryonic antigen. Cancer. 1985. 56:277–283.4. Kodama T, Satoh H, Ishikawa H, Ohtsuka M. Serum levels of CA19-9 in patients with nonmalignant respiratory diseases. J Clin Lab Anal. 2007. 21:103–106.5. Ambiru S, Nakamura S, Fukasawa M, Mishima O, Kuwahara T, Takeshi A. Intralobar pulmonary sequestration associated with marked elevation of serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009. 88:2010–2011.6. Yagyu H, Adachi H, Furukawa K, Nakamura H, Sudoh A, Oh-ishi S, et al. Intralobar pulmonary sequestration presenting increased serum CA19-9 and CA125. Intern Med. 2002. 41:875–878.7. Uyama T, Monden Y, Harada K, Tsuzuki H, Hashioka K, Nobuhara K, et al. A case of intralobar pulmonary sequestration with calcification and elevated serum values of carcinoembryonic antigen and carbohydrate antigen 19-9. J Thorac Imaging. 1989. 4:74–76.8. Armbruster C, Kriwanek S, Feichtinger H, Armbruster C. Intra-abdominal sequestration of the lung and elevated serum levels of CA 19-9: a diagnostic pitfall. HPB (Oxford). 2004. 6:45–48.9. Matsuoka Y, Endo K, Kawamura Y, Yoshida T, Saga T, Watanabe Y, et al. Normal bronchial mucus contains high levels of cancer-associated antigens, CA125, CA19-9, and carcinoembryonic antigen. Cancer. 1990. 65:506–510.10. Nagaoka H, Taniguchi T, Iesato H, Inoue T, Watanuki A, Yokomori T, et al. Pulmonary sequestration with the elevated serum value of CA19-9: a case report. J Jpn Pract Surg Soc. 1996. 57:571–574.11. Ishiura Y, Fujimura M, Minami S, Ueda A, Iwata M, Watanabe K, et al. Increased CA19-9 level in serum and brochoalveolar lavage fluid from a patient with pulmonary tuberculosis. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1996. 34:477–481.12. Park JM, Oh BS. Intralobar pulmonary sequestration with hemoptysis and hemothorax. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007. 40:708–710.13. Nakamura H, Makihara K, Taniguchi Y, Ishiguro K, Ohgi S. Thoracoscopic surgery for intralobar pulmonary sequestration. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1999. 5:405–407.14. Huh JH, Lee SM, Koo TH, Shin BC, Um SJ, Yang DK, et al. A case of bronchiectasis with high serum CA19-9. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2008. 64:383–386.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Roentgenogram of the Issue : A Case of Pneumonic Consolidation with Multiple Cavitary Lesion
- Aspergillosis within an Intralobar Sequestration: A Case Report
- Ultrasound and computed tomographic findings of pulmonary sequestration
- Endovascular Treatment of Intralobar Pulmonary Sequestration with Vascular Plug: A Case Report
- Intralobar Pulmonary Sequestration, Supplied from Left Gastric Artery: A Case Report