Tuberc Respir Dis.
2012 Jun;72(6):467-474.
Validity and Reliability of CAT and Dyspnea-12 in Bronchiectasis and Tuberculous Destroyed Lung
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ymoh55@amc.seoul.kr
- 3Asthma Center, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Clinical Reserch Center for Chronic Obstructive Airway Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Division of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea. hyicyk@hallym.or.kr
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The objective of this study was to assess the validity and reliability of the Korean version of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease assessment test (CAT) and Dyspnea-12 Questionnaire for patients with bronchiectasis or tuberculous destroyed lung.
METHODS
For 62 bronchiectasis patients and 37 tuberculous destroyed lung patients, 3 questionnaires including St. George's Respiratory Questionnaires (SGRQ), CAT, and Dyspnea-12 were obtained, in addition to spirometric measurements. To assess the validity of CAT and Dyspnea-12, correlation with SGRQ was evaluated. To assess the reliability of CAT and Dyspnea-12, Cronbach's alpha coefficient was calculated.
RESULTS
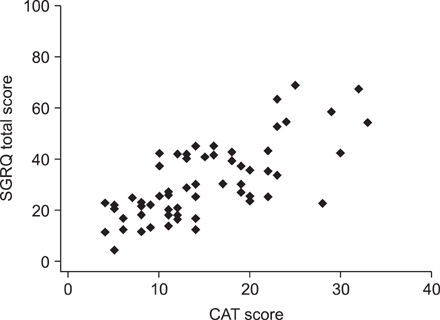
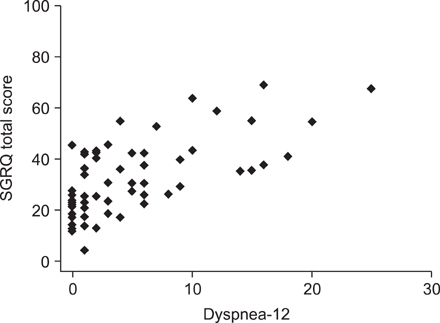
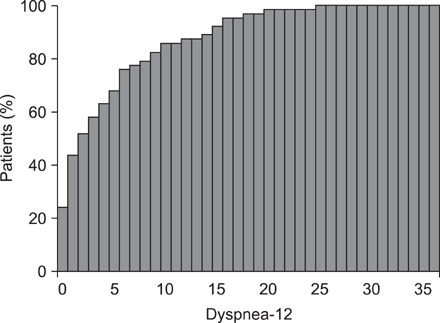
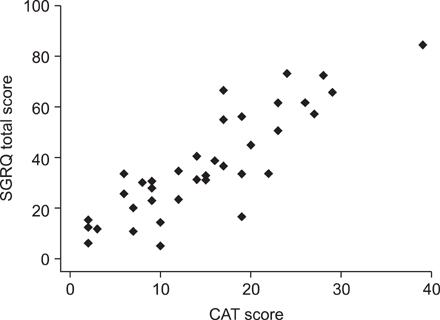
The mean ages of the patients were 60.7+/-8.3 years in bronchiectasis and 64.4+/-9.3 years in tuberculous destroyed lung. 46.8% and 54.1% were male, respectively. The SGRQ score was correlated with the score of the Korean version of CAT (r=0.72, p<0.0001) and Dyspnea-12 (r=0.67, p<0.0001) in bronchiectasis patients. The SGRQ score was correlated with the score of CAT (r=0.86, p<0.0001) and Dyspnea-12 (r=0.80, p<0.0001) in tuberculous destroyed lung patients. The Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the CAT and Dyspnea-12 were 0.84 and 0.90 in bronchiectasis, and 0.88 and 0.94 in tuberculous destroyed lung, respectively.
CONCLUSION
We found that Korean version of CAT and Dyspnea-12 are valid and reliable in patients with tuberculous destroyed lung and bronchiectasis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Guyatt GH, Feeny DH, Patrick DL. Measuring health-related quality of life. Ann Intern Med. 1993. 118:622–629.2. Curtis JR, Martin DP, Martin TR. Patient-assessed health outcomes in chronic lung disease: what are they, how do they help us, and where do we go from here? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997. 156(4 Pt 1):1032–1039.3. Jones PW, Bosh TK. Quality of life changes in COPD patients treated with salmeterol. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997. 155:1283–1289.4. Jones PW, Quirk FH, Baveystock CM. The St George's Respiratory Questionnaire. Respir Med. 1991. 85:Suppl B. 25–31.5. Kim YS, Byun MK, Jung WY, Jeong JH, Choi SB, Kang SM, et al. Validation of the Korean version of the St. George's respiratory questionnaire for patients with chronic respiratory disease. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2006. 61:121–128.6. Pasipanodya JG, Miller TL, Vecino M, Munguia G, Bae S, Drewyer G, et al. Using the St. George respiratory questionnaire to ascertain health quality in persons with treated pulmonary tuberculosis. Chest. 2007. 132:1591–1598.7. Wilson CB, Jones PW, O'Leary CJ, Cole PJ, Wilson R. Validation of the St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire in bronchiectasis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997. 156(2 Pt 1):536–541.8. Lee BH, Kim YS, Lee KD, Lee JH, Kim SH. Health-related quality of life measurement with St. George's respiratory questionnaire in post-tuberculous destroyed lung. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2008. 65:183–190.9. Jones PW, Harding G, Berry P, Wiklund I, Chen WH, Kline Leidy N. Development and first validation of the COPD Assessment Test. Eur Respir J. 2009. 34:648–654.10. Lee S, Lee JS, Song JW, Choi CM, Shim TS, Kim TB, et al. Validation of the Korean version of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease assessment test (CAT) and Dyspnea-12 questionnaire. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2010. 69:171–176.11. Stoller JK, Ferranti R, Feinstein AR. Further specification and evaluation of a new clinical index for dyspnea. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986. 134:1129–1134.12. Yorke J, Moosavi SH, Shuldham C, Jones PW. Quantification of dyspnoea using descriptors: development and initial testing of the Dyspnoea-12. Thorax. 2010. 65:21–26.13. Lee JH, Chang JH. Lung function in patients with chronic airflow obstruction due to tuberculous destroyed lung. Respir Med. 2003. 97:1237–1242.14. Choi JK, Paek D, Lee JO. Normal predictive values of spirometry in Korean population. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005. 58:230–242.15. World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis control: WHO report 2011. 2011. Geneva: World Health Organization.16. Pasipanodya JG, Miller TL, Vecino M, Munguia G, Garmon R, Bae S, et al. Pulmonary impairment after tuberculosis. Chest. 2007. 131:1817–1824.17. Barker AF. Bronchiectasis. N Engl J Med. 2002. 346:1383–1393.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- CT Radiologic Findings in Patients with Tuberculous Destroyed Lung and Correlation with Lung Function
- Prognostic Factors Affecting Postoperative Morbidity and Mortality in Destroyed Lung
- Validation of the Korean Version of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Assessment Test (CAT) and Dyspnea-12 Questionnaire
- Validation of the Korean Version of the Bronchiectasis Health Questionnaire
- Health-related Quality of Life Measurement with St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire in Post-tuberculous Destroyed Lung