Tuberc Respir Dis.
2012 May;72(5):409-415.
Increasing Trend of Isolation of Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria in a Tertiary University Hospital in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shimts@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The isolation of non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) has been increasing in South Korea. To date, however, the cause of this increase has not been determined, and it remains unclear whether the use of liquid media has contributed to this increase. The aim of this study was to evaluate the factors associated with NTM isolation and the impact of liquid media on NTM culture.
METHODS
Mycobacterial smear/culture results of respiratory specimens (sputum and bronchial aspirates), obtained during the years 2002, 2005, and 2010, were retrieved and analyzed retrospectively.
RESULTS
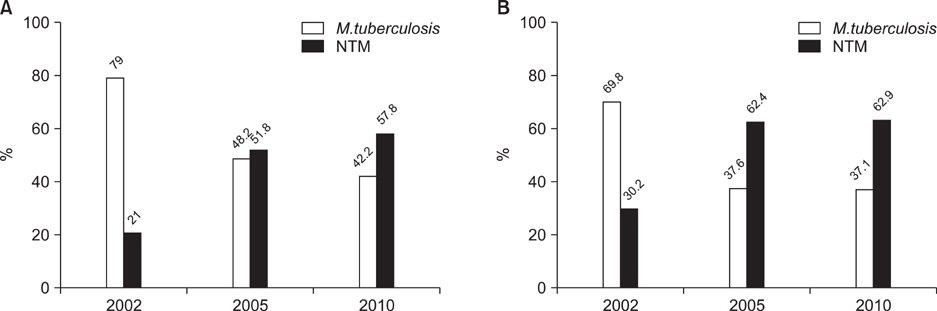
During the years 2002, 2005, and 2010, 83,096 sputum specimens were collected from 31,104 patients, and were cultured for mycobacteria, using solid media only in the 2002 and 2005 specimens and both solid and liquid media in the 2010. Of these, 3,516 (4.2%) specimens were smear-positive for acid-fast bacilli (AFB). The annual rate of NTM among positive culture specimens increased from 21% in 2002 to 57.8% in 2010 (p<0.001), as did the proportion of NTM, among AFB smear- and culture-positive specimens, from 12.2% in 2002 to 45.2% in 2010 (p<0.001). In 2010, the NTM culture rate was higher in the liquid than in the solid media (13.9% vs. 8.4%, p<0.001). The NTM rate among AFB-positive specimens was higher in patients aged >50 than < or =50 years.
CONCLUSION
The rate of NTM isolation has steadily been increasing at the hospital in South Korea, likely due in part to the use of liquid media for the culture.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Marras TK, Chedore P, Ying AM, Jamieson F. Isolation prevalence of pulmonary non-tuberculous mycobacteria in Ontario, 1997-2003. Thorax. 2007. 62:661–666.2. van Ingen J, Bendien SA, de Lange WC, Hoefsloot W, Dekhuijzen PN, Boeree MJ, et al. Clinical relevance of non-tuberculous mycobacteria isolated in the Nijmegen-Arnhem region, The Netherlands. Thorax. 2009. 64:502–506.3. Hosker HS, Lam CW, Ng TK, Ma HK, Chan SL. The prevalence and clinical significance of pulmonary infection due to non-tuberculous mycobacteria in Hong Kong. Respir Med. 1995. 89:3–8.4. Lai CC, Tan CK, Chou CH, Hsu HL, Liao CH, Huang YT, et al. Increasing incidence of nontuberculous mycobacteria, Taiwan, 2000-2008. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010. 16:294–296.5. Tsukamura M, Kita N, Shimoide H, Arakawa H, Kuze A. Studies on the epidemiology of nontuberculous mycobacteriosis in Japan. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988. 137:1280–1284.6. Andréjak C, Thomsen VØ, Johansen IS, Riis A, Benfield TL, Duhaut P, et al. Nontuberculous pulmonary mycobacteriosis in Denmark: incidence and prognostic factors. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010. 181:514–521.7. Jeon K, Koh WJ, Kwon OJ, Suh GY, Chung MP, Kim H, et al. Recovery rate of NTM from AFB smear-positive sputum specimens at a medical centre in South Korea. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2005. 9:1046–1051.8. Park YS, Lee CH, Lee SM, Yang SC, Yoo CG, Kim YW, et al. Rapid increase of non-tuberculous mycobacterial lung diseases at a tertiary referral hospital in South Korea. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2010. 14:1069–1071.9. Chien HP, Yu MC, Wu MH, Lin TP, Luh KT. Comparison of the BACTEC MGIT 960 with Löwenstein-Jensen medium for recovery of mycobacteria from clinical specimens. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2000. 4:866–870.10. Bae E, Im JH, Kim SW, Yoon NS, Sung H, Kim MN, et al. Evaluation of combination of BACTEC mycobacteria growth indicator tube 960 system and Ogawa media for mycobacterial culture. Korean J Lab Med. 2008. 28:299–306.11. Devallois A, Goh KS, Rastogi N. Rapid identification of mycobacteria to species level by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the hsp65 gene and proposition of an algorithm to differentiate 34 mycobacterial species. J Clin Microbiol. 1997. 35:2969–2973.12. Diagnostic Standards and Classification of Tuberculosis in Adults and Children. This official statement of the American Thoracic Society and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention was adopted by the ATS Board of Directors, July 1999. This statement was endorsed by the Council of the Infectious Disease Society of America, September 1999. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 161(4 Pt 1):1376–1395.13. Glassroth J. Pulmonary disease due to nontuberculous mycobacteria. Chest. 2008. 133:243–251.14. Daley CL, Griffith DE. Pulmonary non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2010. 14:665–671.15. Yoo KH, Kim YS, Sheen SS, Park JH, Hwang YI, Kim SH, et al. Prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Korea: the fourth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2008. Respirology. 2011. 16:659–665.16. Bird BR, Denniston MM, Huebner RE, Good RC. Changing practices in mycobacteriology: a follow-up survey of state and territorial public health laboratories. J Clin Microbiol. 1996. 34:554–559.17. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Updated guidelines for the use of nucleic acid amplification tests in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009. 58:7–10.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recovery Rates of Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria from Clinical Specimens Are Increasing in Korean Tertiary-Care Hospitals
- Continued Upward Trend in Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria Isolation over 13 Years in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Korea
- Isolation and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria in a Tertiary Hospital in Korea, 2016 to 2020
- Increasing Recovery of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria from Respiratory Specimens over a 10-Year Period in a Tertiary Referral Hospital in South Korea
- Immunopathogenesis of Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria Lung Disease