Tuberc Respir Dis.
2008 Aug;65(2):116-120.
A Case of Henoch-Shonlein Purpura Caused by Rifampin
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pms70@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3The Institute of Chest Diseases, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
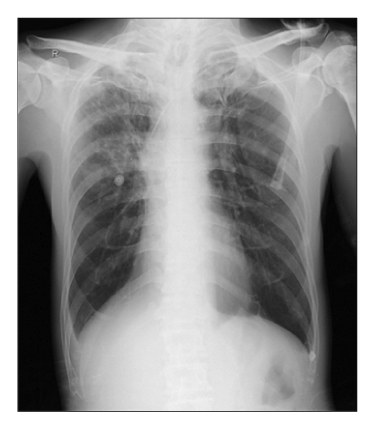
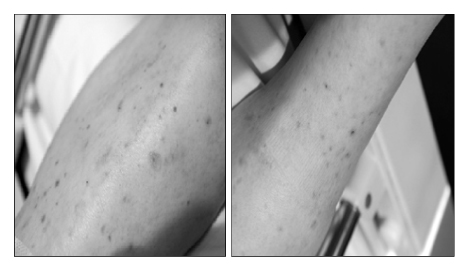
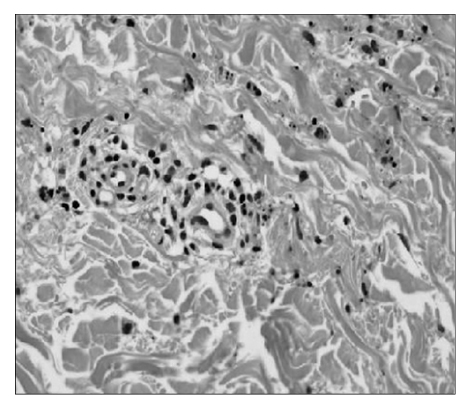
- Rifampin is one of the first line drugs for treating tuberculosis, but it might be associated with serious adverse effects, including renal failure. We report here on a case of a 57-year-old patient who developed Henoch-Shonlein purpura during antituberculosis therapy that included rifampin. The patient converted to negative on the AFB smear for tuberculosis two weeks after the initial administration of antituberculosis medication. After treatment for 60 days, this patient was diagnosed with Henoch-Shonlein purpura by the purpura lesion on the lower legs, the leukocytoclastic vasculitis, the renal impairment and the pathological examination. After stopping rifampin, the skin lesions disappeared in about 10 days and his renal function gradually improved. This case study showed that Henoch-Schonlein purpura can be caused by rifampin during antituberculosis therapy and we recommend that the use of rifampin should be restrained when clinical symptoms of Henoch-Shonlein purpura are observed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yoshioka K, Satake N, Kasamatsu Y, Nakamura Y, Shikata N. Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis due to rifampicin therapy. Nephron. 2002. 90:116–118.2. Gabow PA, Lacher JW, Neff TA. Tubulointerstitial and glomerular nephritis associated with rifampin. Report of a case. JAMA. 1976. 235:2517–2518.3. Massry SG, Glassock RJ. Henoch-Schönlein purpura: clinical feature, etiology, and pathogenesis, laboratory finding, pathology, natural history, management, and transplantation. Massary and Glassock's text book of nephrology. 2001. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Wiliams & Wilkins;804–808.4. Grosset J, Leventis S. Adverse effects of rifampin. Rev Infect Dis. 1983. 5:S440–S450.5. Campese VM, Marzullo F, Schena FP, Coratelli P. Acute renal failure during intermittent rifampicin therapy. Nephron. 1973. 10:256–261.6. Lim CS, Jung YC, Lee SG, Ahn CR, Han JS, Kim SG, et al. Rifampin induced rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Korean J Nephrol. 1998. 17:503–509.7. Covic A, Golea O, Segall L, Meadipudi S, Munteanu L, Nicolicioiu M, et al. A clinical description of rifampicin-induced acute renal failure in 170 consecutive cases. J Indian Med Assoc. 2004. 102:2022–25.8. Prakash J, Kumar NS, Saxena RK, Verma U. Acute renal failure complicating rifampicin therapy. J Assoc Physicians India. 2001. 49:877–880.9. Muthukumar T, Jayakumar M, Fernando EM, Muthusethupathi MA. Acute renal failure due to rifampicin: a study of 25 patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002. 40:690–696.10. Islek I, Muslu A, Totan M, Gok F, Sanic A. Henoch-Shönlein purpura and pulmonary tuberculosis. Pediatr Int. 2002. 44:545–546.11. Chan HS, Pang J. Vasculitis in tuberculous infection. Chest. 1990. 98:511.12. Pacheco A. Henoch-Shönlein vasculitis and tuberculosis. Chest. 1991. 100:293–294.13. Washio M, Nanishi F, Onoyama K, Fujii K, Ohchi N, Fujishima M. Recurrence of Henoch Shönlein purpura nephritis associated with tuberculous pleuritis. Nippon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 1988. 30:1087–1089.14. Kitamura H, Shimizu K, Takeda H, Tai H, Ito Y, Fukunaga M. A case of Henoch-schönlein purpura nephritis in pulmonary tuberculosis. Am J Med Sci. 2007. 333:117–121.15. Chan CH, Chong YW, Sun AJ, Hoheisel GB. Cutaneous vasculitis associated with tuberculosis and its treatment. Tubercle. 1990. 71:297–300.16. Poole G, Stradling P, Worlledge S. Potentially serious side effects of high-dose twice-weekly rifampicin. Br Med J. 1971. 3:343–347.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Henoch-Schonlein Purpura, Allergic Purpura, Anaphylactoid Purpura
- Ileocolonoscopic Diagnosis of Ileal Vasculitis in Henoch - Schonlein Purpura Mimicking Acute Abdomen prior to the Development of Skin Lesions
- Clinical Study on Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
- A Case of Thrombocytopenia and Purpura Induced by Rifamnpin, Pyrazinamide, and Ciprofloxacin
- Clinical analysis and prognostic factors in Henoch-Schonlein purpura