Tuberc Respir Dis.
2007 Oct;63(4):346-352.
Correlation Between NT-proBNP and Pulmonary Arterial Pressure in COPD Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University, College of Medicine, Lung Institute of Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Korea. jhlee7@snubh.org
- 2Medicine and Respiratory Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension is one of the cardiovascular complications of in COPD. However, a diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension requires an invasive test, such as right heart catheterization. NT-proBNP is a cardiac hormone that is elevated when a cardiac volume or pressure overload is present. It was hypothesized that NT-proBNP might play a role in detecting of pulmonary hypertension in COPD patients.
METHOD: The 31 COPD patients, who underwent all of NT-proBNP, echocardiography, and spirometry in Seoul National University Bundang Hospital during the period from November 2003 to July 2005, were retrospectively analyzed.
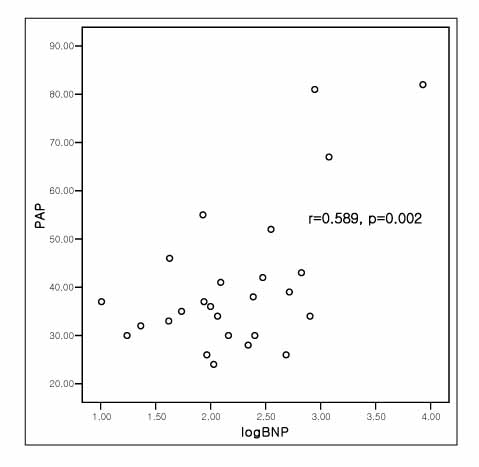
RESULT: Of the 31 COPD patients, 9 patients had pulmonary hypertension. A significant positive correlation was observed between the NT-proBNP and pulmonary arterial pressure (r=0.589, p=0.002). However, there was no significant correlation observed between the FEV(1) and NT-proBNP and FEV(1) and pulmonary arterial pressure.
CONCLUSION
NT-proBNP might indicate the presence of pulmonary hypertension in COPD patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and World Health Organization. Global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease: global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health. [revised 2006]. Bethesda, MD, USA: Available from: http://www.goldcopd.com.2. Kim DS, Kim YS, Jung K-S, Chang JH, Lim CM, Lee JH, et al. Prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Korea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005. 172:842–847.3. Agusti AG, Noguera A, Sauleda J, Sala E, Pons J, Busquets X. Systemic effects of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 2003. 21:347–360.4. Higenbottam T. Pulmonary hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a case for treatment. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005. 2:12–19.5. Naeije R. Pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005. 2:20–22.6. Barbera JA, Peinado VI, Santos S. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 2003. 21:892–905.7. Naeije R, Barbera JA. Pulmonary hypertension associated with COPD. Crit Care. 2001. 5:286–289.8. Weitzenblum E, Chaouat A. Severe pulmonary hypertension in COPD: is it a distinct disease? Chest. 2005. 127:1480–1482.9. Lee-Chiong TL Jr, Matthay RA. Pulmonary hypertension and cor pulmonale in COPD. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2003. 24:263–272.10. Arcasoy SM, Christie JD, Ferrari VA, Sutton MS, Zisman DA, Blumenthal NP, et al. Echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary hypertension in patients with advanced lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003. 167:735–740.11. Kessler R, Faller M, Weitzenblum E, Chaouat A, Aykut A, Ducolone A, et al. "Natural history" of pulmonary hypertension in a series of 131 patients with chronic obstructive lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001. 164:219–224.12. Bossone E, Bodini BD, Mazza A, Allegra L. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: the key role of echocardiography. Chest. 2005. 127:1836–1843.13. Kim NH. Diagnosis and evaluation of patient with pulmonary hypertension. Cardiol Clin. 2004. 22:367–373.14. Yap LB, Mukerjee D, Timms PM, Ashrafian H, Coghlan JG. Natriuretic peptides, respiratory disease, and right heart. Chest. 2004. 126:1330–1336.15. Ruskoaho H. Caridac hormones as diagnostic tools in heart failure. Endocr Rev. 2003. 24:341–356.16. Clerico A, Emdin M. Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic relavance of measurement of cardiac natriuretic peptides: a review. Clin Chem. 2004. 50:33–50.17. McQuillan BM, Picard MH, Leavitt M, Weyman AE. Clinical correlates and reference intervals for pulmonary arterial systolic pressure among echocardiographically normal subjects. Circulation. 2001. 104:2797–2802.18. Barst RJ, McGoon M, Torbicki A, Sitbon O, Krowka MJ, Olschewski H, et al. Diagnosis and differential assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004. 43:40S–47S.19. Voelkel NF, Cool CD. Pulmonary vascular involvement in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J Suppl. 2003. 46:28S–32S.20. Chaouat A, Bugnet A, Kadaoui N, Schott R, Enache I, Ducolone A, et al. Severe pulmoanry hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005. 172:189–194.21. Scharf SM, Iqbal M, Keller C, Criner G, Lee S, Fessler HE. National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) Research Group. Hemodynamic characterization of patients with severe emphysema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002. 166:314–322.22. Mitchell RS, Vincent TN, Ryan S, Filley GF. Chronic obstructive bronchopulmonary disease, IV: The clinical and physiological difference of chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Am J Med Sci. 1964. 247:513–517.23. Renzetti AD Jr, McClement JH, Litt BD. The Veterans Administration cooperative study of pulmonary function, 3. Mortality in relation to respiratory function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Med. 1966. 41:115–129.24. Nagaya N, Nishikimi T, Uematsu M, Satoh T, Kyotani S, Sakamaki F, et al. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide as a prognostic indicator in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2000. 102:865–870.25. Bando M, Ishii Y, Sugiyama Y, Kitamura S. Elevated plasma brain natriuretic peptide levels in chronic respiratory failure with cor pulmonale. Respir Med. 1999. 93:507–514.26. Ishii J, Nomura M, Ito M, Naruse H, Mori Y, Wang JH, et al. Plasma concentration of brain natriuretic peptide as a biochemical marker for evaluation of right ventricular overload and mortality in chronic respiratory disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2000. 301:19–30.27. Nagaya N, Nishikimi T, Okano Y, Uematsu M, Satoh T, Kyotani S, et al. Plasma brain natiruretic peptide levels increase in proportion to extent of right ventricular dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998. 31:202–208.28. Ueda R, Yokouchi M, Suzuki T, Otomo E, Katagiri T. Prognostic value of high plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentrations in very elderly persons. Am J Med. 2003. 114:266–270.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Utility of Measurement of Plasma N-terminal Pro-brain Natriuretic Peptide in Diagnosis of Pulmonary Hypertension
- Correlation between N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Doppler Echocardiographic Parameters of Left Ventricular Filling Pressure in Atrial Fibrillation
- Diagnosis of Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Acute Pulmonary Embolism with N-terminal Probrain Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP)
- Combined Serum N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Level and Ejection Fraction for Risk Prediction in Patients With Chronic Total Occlusion Who Underwent Successful Interventions
- Comparatives Study of Pulmonary Artery and Pulmonary Venous Wedge Pressure in Congenital Heart Disease