J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2011 Mar;19(1):26-31. 10.4250/jcu.2011.19.1.26.
Correlation between N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Doppler Echocardiographic Parameters of Left Ventricular Filling Pressure in Atrial Fibrillation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical Research Center, Mokdong Hospital, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. pseongh@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2135429
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2011.19.1.26
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia with a population prevalence of about 1%. Natriuretic peptide level is elevated in patients with AF with diastolic dysfunction even with a normal left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction. The N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) level and Doppler echocardiographic parameters for diastolic function have shown correlation with LV filling pressures. We aimed to evaluate the relationship between echocardiographic parameters and serum NT-proBNP in patients with AF with preserved LV ejection fraction.
METHODS
We examined transthoracic echocardiography and NT-proBNP levels in the patients with AF and patients with sinus rhythm. Blood samples were taken for serum NT-proBNP measurements within 24 hours of echocardiographic examination. The group 1 was the patients with sinus rhythm (n = 30, mean age 68 +/- 13 years) and the group 2 was the patients with AF (n = 33, mean age 70 +/- 14 years).
RESULTS
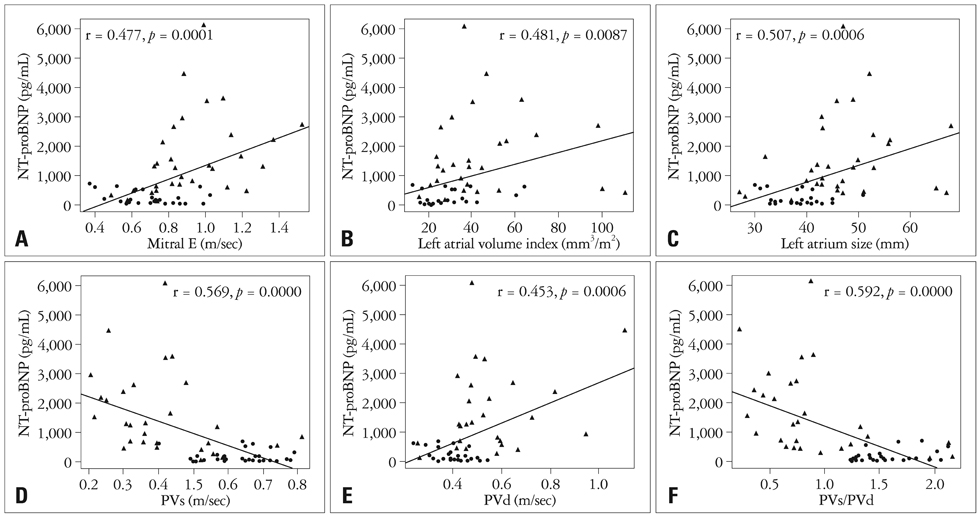
The group 2 patients had significantly higher mitral E, E' (lateral annulus), E/E' (septal annulus), left atrial (LA) volume index, LA size, pulmonary vein diastolic velocity, and NT-proBNP level than those of group 1 patients (p < 0.05). The area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve showed a NT-proBNP had good diagnostic power for E/E' (septal annulus) > 15 in patients with AF at cutoff value of 433 pg/mL.
CONCLUSION
NT-proBNP level is well correlated with Doppler echocardiographic parameters of diastolic function in patients with AF and preserved LV ejection fraction. NT-proBNP level more than 433 pg/mL may suggest elevated LV filling pressure in patients with AF.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Evaluation of the Relationship between Circadian Blood Pressure Variation and Left Atrial Function Using Strain Imaging
Chan Seok Park, Gun-Hee An, Young-Woon Kim, Youn-Jung Park, Mi-Jeong Kim, Eun Joo Cho, Sang-Hyun Ihm, Hae-Ok Jung, Hee-Yeol Kim, Hui-Kyung Jeon, Ho-Joong Youn, Jae-Hyung Kim
J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2011;19(4):183-191. doi: 10.4250/jcu.2011.19.4.183.
Reference
-
1. Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV, Singer DE. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention. The Anticoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA. 2001. 285:2370–2375.
Article2. Bakowski D, Wozakowska-Kaplon B, Opolski G. The influence of left ventricle diastolic function on natriuretic peptides levels in patients with atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2009. 32:745–752.
Article3. Oki T, Tabata T, Yamada H, Wakatsuki T, Fukuda K, Abe M, Onose Y, Iuchi A, Fukuda N, Ito S. Evaluation of left atrial filling using systolic pulmonary venous flow velocity measurements in patients with atrial fibrillation. Clin Cardiol. 1998. 21:169–174.
Article4. Nagueh SF, Mikati I, Kopelen HA, Middleton KJ, Quiñones MA, Zoghbi WA. Doppler estimation of left ventricular filling pressure in sinus tachycardia: A new application of tissue Doppler imaging. Circulation. 1998. 98:1644–1650.
Article5. Seino Y, Ogawa A, Yamashita T, Fukushima M, Ogata K, Fukumoto H, Takano T. Application of NT-proBNP and BNP measurements in cardiac care: a more discerning marker for the detection and evaluation of heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2004. 6:295–300.
Article6. Schiller NB, Shah PM, Crawford M, DeMaria A, Devereux R, Feigenbaum H, Gutgesell H, Reichek N, Sahn D, Schnittger I. American Society of Echocardiography committee on standards. subcommittee on quantitation of two-dimensional echocardiograms. Recommendations for quantitation of the left ventricular by two-dimensional echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1989. 2:358–367.
Article7. Ommen SR, Nishimura RA, Appleton CP, Miller FA, Oh JK, Redfield MM, Tajik AJ. Clinical utility of Doppler echocardiography and tissue Doppler imaing in the estimation of left ventricular filling pressures: A comparative simultaneous Doppler-catheterization study. Circulation. 2000. 102:1788–1794.
Article8. Ulimoen SR, Enger S, Tveit A. Impact of atrial fibrillation on NT-proBNP levels in a 75-year-old population. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2009. 69:579–584.
Article9. Asselbergs FW, van den Berg MP, Bakker SJ, Signorovitch JE, Hillege HL, van Gilst WH, van Veldhuisen . N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide levels predict newly detected atrial fi brillation in a population-based cohort. Neth Heart J. 2008. 16:73–78.
Article10. Hou JL, Gao K, Li M, Ma JY, Shi YK, Wang Y, Zhao YF. Increased N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide level predicts atrial fi brillation after surgery for esophageal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. 14:2582–2585.11. Cardinale D, Colombo A, Sandri MT, Lamantia G, Colombo N, Civelli M, Salvatici M, Veronesi G, Veglia F, Fiorentini C, Spaggiari L, Cipolla CM. Increased perioperative N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels predict atrial fi brillation after thoracic surgery for lung cancer. Circulation. 2007. 115:1339–1344.
Article12. Chung IM, Chung Nk, Choi DH, Shim WH, Cho SY, Kim SS. Morphological Characteristics and Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Lone Atrial Fibrillation. J Korean Soc Echocardiogr. 1994. 2:179–186.
Article13. Hall C. NT-ProBNP: the mechanism behind the marker. J Card Fail. 2005. 11:S81–S83.
Article14. Ren WD, Visentin P, Nicolosi GL, Canterin FA, Dall'Aglio V, Lestuzzi C, Mimo R, Pavan D, Sparacino L, Cervesato E, Zanuttini D. Effect of atrial fibrillation on pulmonary venous flow patterns: Transoesophageal pulsed Doppler echocardiographic study. Eur Heart J. 1993. 14:1320–1327.
Article15. Chen YT, Kan MN, Lee AY, Chen JS, Chiang BN. Pulmonary venous flow: Its relationship to left atrial and mitral valve motion. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1993. 6:387–394.
Article16. Bollmann A. Pulmonary venous flow assessed by Doppler echocardiography in the management of atrial fibrillation. Echocardiography. 2007. 24:430–435.
Article17. Vinereanu D, Florescu N, Sculthorpe N, Tweddel AC, Stephens MR, Fraser AG. Differentiation between pathologic and physiologic left ventricular hypertrophy by tissue Doppler assessment of long-axis function in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or systemic hypertension and in athletes. Am J Cardiol. 2001. 88:53–58.
Article18. Tretjak M, Verovnik F, Benko D, Kozelj M. Tissue Doppler velocities of mitral annulus and NT-proBNP in patients with heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2005. 7:520–524.
Article19. Sohn DW, Song JM, Zo JH, Chai IH, Kim HS, Chun HG, Kim HC. Mitral annulus velocity in the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function in atrial fibrillation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1999. 12:927–931.
Article20. Mak GS, De Maria A, Clopton P, Maisel AS. Utility of B-natriuretic peptide in the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function: Comparison with tissue Doppler imaging recordings. Am Heart J. 2004. 148:895–902.
Article21. Mornos C, Ionac A, Cozma D, Rusinaru D, Maximov D, Petrescu L, Lupu A, Dragulescu SI. The relationship between tissue Doppler imaging and seric NTproBNP levels in sinus rhythm patients: a prospective study. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2008. 24:399–407.
Article22. Wang M, Yip GW, Wang AY, Zhang Y, Ho PY, Tse MK, Lam PK, Sanderson JE. Peak early diastolic mitral annulus velocity by tissue Doppler imaging adds independent and incremental prognostic value. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003. 41:820–826.
Article23. Hwang SJ, Kim BJ, Sung KC, Kim BS, Kang JH, Lee MH, Park JR. Assessment of factors affecting plasma BNP levels in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation and preserved left ventricular systolic function. Korean Circ J. 2005. 35:605–612.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation of N-Terminal Pro-Brain Type Natriuretic Peptide Level and Echocardiographic Parameters
- The Influence of the Left Ventricular Geometry on the Left Atrial Size and Left Ventricular Filling Pressure in Hypertensive Patients, as Assessed by Echocardiography
- A Comparison of Tissue Doppler Echocardiography and B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Estimating Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure
- Bradyarrhythmia Can Increase the Plasma Level of N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide
- Correlation of Right Atrial Appendage Velocity with Left Atrial Appendage Velocity and Brain Natriuretic Peptide