J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2012 Mar;20(1):37-41. 10.4250/jcu.2012.20.1.37.
Correlation of Right Atrial Appendage Velocity with Left Atrial Appendage Velocity and Brain Natriuretic Peptide
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. chatjn@hananet.net
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Ulsan Hospital, Ulsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2177339
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2012.20.1.37
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
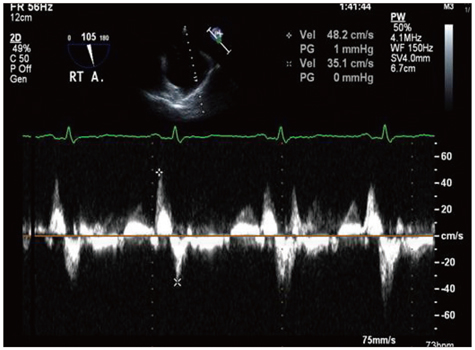
Left atrial appendage (LAA) anatomy and function have been well characterized both in healthy and diseased people, whereas relatively little attention has been focused on the right atrial appendage (RAA). We sought to evaluate RAA flow velocity and to compare these parameters with LAA indices and with a study of biomarkers, such as brain natriuretic peptide, among patients with sinus rhythm (SR) and atrial fibrillation (AF).
METHODS
In a series of 79 consecutive patients referred for transesophageal echocardiography, 43 patients (23 with AF and 20 controls) were evaluated.
RESULTS
AF was associated with a decrease in flow velocity for both LAA and RAA [LAA velocity-SR vs. AF: 61 +/- 22 vs. 29 +/- 18 m/sec (p < 0.01), RAA velocity-SR vs. AF: 46 +/- 20 vs. 19 +/- 8 m/sec (p < 0.01)]. Based on simple linear regression analysis, LAA velocity and RAA velocity were positively correlated, and RAA velocity was inversely correlated with brain natriuretic peptide (BNP).
CONCLUSION
AF was associated with decreased RAA and LAA flow velocities. RAA velocity was found to be positively correlated with LAA velocity and negatively correlated with BNP. The plasma BNP concentration may serve as a determinant of LAA and RAA functions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Petersen P. Thromboembolic complications in atrial fibrillation. Stroke. 1990. 21:4–13.
Article2. Caplan LR, D'Cruz I, Hier DB, Reddy H, Shah S. Atrial size, atrial fibrillation, and stroke. Ann Neurol. 1986. 19:158–161.
Article3. Igarashi Y, Kashimura K, Makiyama Y, Sato T, Ojima K, Aizawa Y. Left atrial appendage dysfunction in chronic nonvalvular atrial fibrillation is significantly associated with an elevated level of brain natriuretic peptide and a prothrombotic state. Jpn Circ J. 2001. 65:788–792.
Article4. Fatkin D, Kelly RP, Feneley MP. Relations between left atrial appendage blood flow velocity, spontaneous echocardiographic contrast and thromboembolic risk in vivo. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994. 23:961–969.
Article5. Grimm RA, Stewart WJ, Maloney JD, Cohen GI, Pearce GL, Salcedo EE, Klein AL. Impact of electrical cardioversion for atrial fibrillation on left atrial appendage function and spontaneous echo contrast: characterization by simultaneous transesophageal echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993. 22:1359–1366.
Article6. Zeppellini R, Schön F, Gheno G, Drozdz J, Balzereit A, Cucchini F, Erbel R. Left atrial appendage systolic forward flow. Am J Cardiol. 1995. 75:204–206.
Article7. Klein AL, Grimm RA, Jasper SE, Murray RD, Apperson-Hansen C, Lieber EA, Black IW, Davidoff R, Erbel R, Halperin JL, Orsinelli DA, Porter TR, Stoddard MF. ACUTE Steering and Publications Committee for the ACUTE Investigators. Efficacy of transesophageal echocardiography-guided cardioversion of patients with atrial fibrillation at 6 months: a randomized controlled trial. Am Heart J. 2006. 151:380–389.
Article8. Manning WJ, Silverman DI, Gordon SP, Krumholz HM, Douglas PS. Cardioversion from atrial fibrillation without prolonged anticoagulation with use of transesophageal echocardiography to exclude the presence of atrial thrombi. N Engl J Med. 1993. 328:750–755.
Article9. Manning WJ, Silverman DI, Keighley CS, Oettgen P, Douglas PS. Transesophageal echocardiographically facilitated early cardioversion from atrial fibrillation using short-term anticoagulation: final results of a prospective 4.5-year study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995. 25:1354–1361.
Article10. Stoddard MF, Dawkins PR, Prince CR, Longaker RA. Transesophageal echocardiographic guidance of cardioversion in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am Heart J. 1995. 129:1204–1215.
Article11. Omran H, Jung W, MacCarter D, Schimpf R, Rabahieh R, Schumacher B, Wolpert C, Becher H, Lüderitz B. Right atrial thrombi and depressed right atrial appendage function after cardioversion of atrial fibrillation. Echocardiography. 1999. 16:245–251.
Article12. Bilge M, Eryonucu B, Güler N, Erkoç R. Right atrial appendage function in patients with chronic nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Jpn Heart J. 2000. 41:451–462.
Article13. Henry WL, DeMaria A, Gramiak R, King DL, Kisslo JA, Popp RL, Sahn DJ, Schiller NB, Tajik A, Teichholz LE, Weyman AE. Report of the American Society of Echocardiography Committee on Nomenclature and Standards in Two-dimensional Echocardiography. Circulation. 1980. 62:212–217.
Article14. Yock PG, Popp RL. Noninvasive estimation of right ventricular systolic pressure by Doppler ultrasound in patients with tricuspid regurgitation. Circulation. 1984. 70:657–662.
Article15. Seward JB, Khandheria BK, Freeman WK, Oh JK, Enriquez-Sarano M, Miller FA, Edwards WD, Tajik AJ. Multiplane transesophageal echocardiography: image orientation, examination technique, anatomic correlations, and clinical applications. Mayo Clin Proc. 1993. 68:523–551.
Article16. Donal E, Yamada H, Leclercq C, Herpin D. The left atrial appendage, a small, blind-ended structure: a review of its echocardiographic evaluation and its clinical role. Chest. 2005. 128:1853–1862.
Article17. Mikael Kortz RA, Delemarre BJ, van Dantzig JM, Bot H, Kamp O, Visser CA. Left atrial appendage blood flow determined by transesophageal echocardiography in healthy subjects. Am J Cardiol. 1993. 71:976–981.
Article18. Titcomb CP Jr. LVH: consequences associated with cardiac remodeling. J Insur Med. 2004. 36:42–46.19. Bilge M, Eryonucu B, Güler N, Aşker M. Evaluation of right atrial appendage blood flow by transesophageal echocardiography in subjects with a normal heart. Jpn Heart J. 1999. 40:599–607.
Article20. de Divitiis M, Omran H, Rabahieh R, Rang B, Illien S, Schimpf R, MacCarter D, Jung W, Becher H, Lüderitz B. Right atrial appendage thrombosis in atrial fibrillation: its frequency and its clinical predictors. Am J Cardiol. 1999. 84:1023–1028.
Article21. Subramaniam B, Riley MF, Panzica PJ, Manning WJ. Transesophageal echocardiographic assessment of right atrial appendage anatomy and function: comparison with the left atrial appendage and implications for local thrombus formation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2006. 19:429–433.
Article22. Tabata T, Oki T, Yamada H, Abe M, Onose Y, Thomas JD. Relationship between left atrial appendage function and plasma concentration of atrial natriuretic peptide. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2000. 1:130–137.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Underdevelopment of Left Atrial Appendage
- The Influence of Electrical Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation on Left Atrial Appendage Function: A Transesophageal Echocardiography Study
- A Case of the Thrombi in Left Atrial Appendage Confirmed by Transesophageal Echocardiography(TEE) in A Patient with Acute Myocardial Infarction Accompanied by Cerebral Infarction
- Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Related to a Congenital Pericardial Defect and Left Atrial Appendage Herniation
- A Left Atrial Appendage Phantom Structure