Tuberc Respir Dis.
2006 Jul;61(1):41-45.
Difference in Protein Markers According to the Survival of Sepsis Patients using Protein Chips
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Korea. pulmo2@knuh.or.kr
- 2Department of Anesthesia, College of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Korea.
- 3Department of Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Korea.
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Several clinical scoring systems are currently being used to predict the outcome of sepsis, but they all have certain limitations. Therefore, we sought to identify the proteomic biomarkers, with wsing proteomic tools, that differed according to the outcome of sepsis patients.
METHODS
Upon admission to the ICU, blood samples were obtained from the 16 patients with sepsis who were enrolled in this study. Surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (SELDI-TOF MS) was used to identify the markers that could predict the outcome of sepsis.
RESULTS
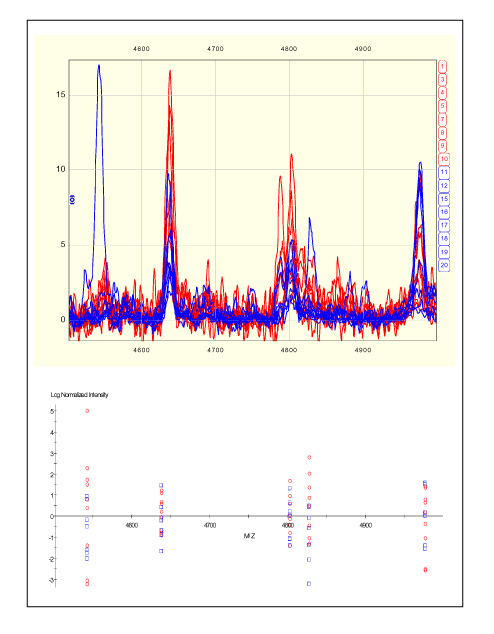
We found six peaks, by using cation and anion chips, that statistically differed between those patients who died and those who survived.
CONCLUSION
The biomarkers we found by using proteomic tools may help predict the prognosis and also plan the treatment of sepsis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Annane D, Bellisant E, Cavaillon JM. Septic shock. Lancet. 2005. 365:63–78.2. Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:138–150.3. Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985. 13:818–829.4. Knaus WA, Wagner DP, Draper EA, Zimmerman JE, Bergner M, Bastos PG, et al. The APACHE III prognostic system: risk prediction of hospital mortality for critically ill hospitalized adults. Chest. 1991. 100:1619–1636.5. le Gall JR, Loirat P, Alperovitch A, Glaser P, Granthil C, Mathieu D, et al. A simplified acute physiology score for ICU patients. Crit Care Med. 1984. 12:975–977.6. Lemeshow S, Teres D, Avrunin JS, Gage RW. Refining intensive care unit outcome prediction by using changing probabilities of mortality. Crit Care Med. 1988. 16:470–477.7. de Rooji SE, Abu-Hanna A, Levi M, de Jonge E. Factors that predict outcome of intensive care treatment in very elderly patients: a review. Crit Care. 2005. 9:R307–R314.8. Livingston BM, MacKirdy FN, Howie JC, Jones R, Norrie JD. Assessment of the performance of five intensive care scoring models within a large Scottish databases. Crit Care Med. 2000. 28:1820–1827.9. Polderman KH, Thijs LG, Girbes AR. Interobserver variability in the use of APACHE II score. Lancet. 1999. 353:380.10. Morales IJ, Peters SG, Afessa B. Hospital mortality rate and length of stay in patients admitted at night to the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2003. 31:858–863.11. Rosenberg AL, Hofer TP, Strachan C, Watts CM, Hayward RA. Accepting critically ill transfer patients: adverse effect on a referral center's outcome and benchmark measures. Ann Intern Med. 2003. 138:882–890.12. Petricoin EF 3rd, Ornstein DK, Paweletz CP, Ardekani A, Hackett PS, Hitt BA, et al. Serum proteomic patterns for detection of prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002. 94:1576–1578.13. Petricoin EF, Ardekani AM, Hitt BA, Levine PJ, Fusaro VA, Steinberg SM, et al. Use of proteomic patterns in serum to identify ovarian cancer. Lancet. 2002. 359:572–577.14. Papadopoulos MC, Abel PM, Agranoff D, Stich A, Tarelli E, Bell BA, et al. A novel and accurate diagnostic test for human African trypanosomiasis. Lancet. 2004. 363:1358–1363.15. Zhu XD, Zhang WH, Li CL, Xu Y, Liang WJ, Tien P. New serum biomarkers for detection of HBV-induced liver cirrhosis using SELDI protein chip technology. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. 10:2327–2329.16. Burchardi H, Schneider H. Economic aspects of severe sepsis: a review of intensive care unit costs, cost of illnessand cost effectiveness of therapy. Pharmacoeconomics. 2004. 22:793–813.17. Ahn WS, Park SP, Bae SM, Lee JM, Namkoong SE, Nam GH, et al. Identification of hemoglobin-α and -β subunits as potential serum biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of ovarian cancer. Cancer Sci. 2005. 96:197–201.18. Ilyin SE, Belkowski SM, Plata-Salaman CR. Biomarker discovery and validation: technologies and integrative approaches. Trends biotechnol. 2004. 22:411–416.19. Rodland KD. Proteomics and cancer diagnosis: the potential of mass spectrometry. Clin Biochem. 2004. 37:579–583.20. Christ-Crain M, Jaccard-Stolz D, Bingisser R, Gencay MM, Huber PR, Tamm M, et al. Effect of procalcitonin-guided treatment on antibiotic use and outcome in lower respiratory tract infections: cluster-randomised, single-blinded intervention trial. Lancet. 2004. 363:600–607.21. Colonna M, Facchetti F. TREM-1: A new player in acute inflammatory responses. JInfect Dis. 2003. 187:S397–S401.22. Scherpereel A, Depontieu F, Grigoriu B, Cavestri B, Tsicopoulos A, Gentina T, et al. Endocan, a new endothelial marker in human sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2006. 34:532–537.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Biomarkers of Sepsis
- Mean cell volumes of neutrophils and monocytes are promising markers of sepsis in elderly patients
- Update on Procalcitonin Measurements
- Unfolded Histidine-Tagged Protein is Immobilized to Nitrilotriacetic Acid-Nickel Beads, But Not the Nickel-Coated Glass Slide
- Clinical Usefulness of Procalcitonin as a Predictive Marker in Accordance with the Severity of Female Patients with Uncomplicated Acute Pyelonephritis