Korean J Urol.
2013 Nov;54(11):797-800.
Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Urinary Bladder Managed by Laparoscopic Partial Cystectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology and Renal Transplantation, Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India. drmrpradhan@yahoo.co.in
- 2Department of Pathology, Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India.
- 3Department of Anaesthesiology, Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India.
Abstract
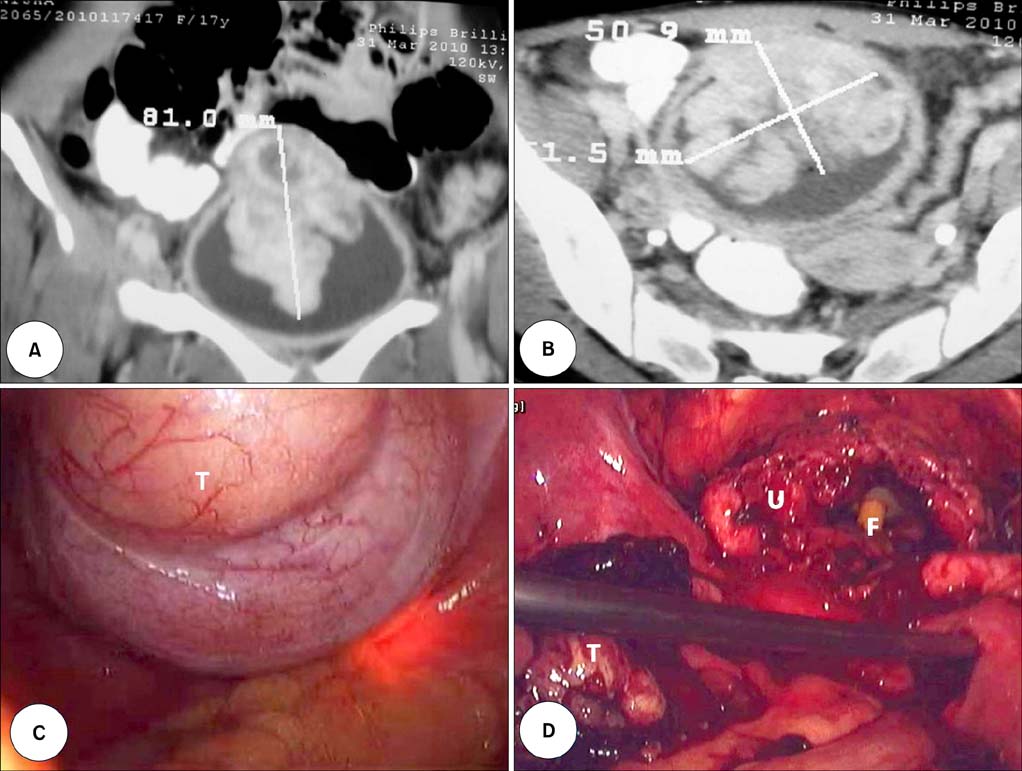
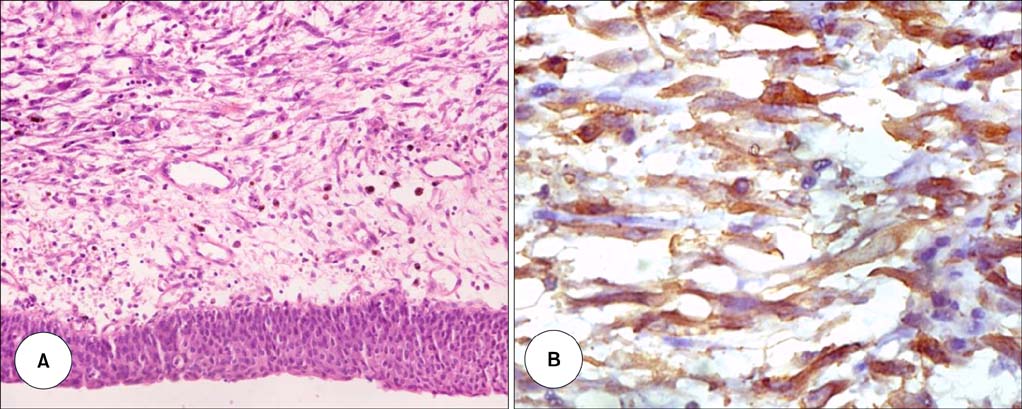
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the urinary bladder is a rare mesenchymal tumor with uncertain malignant potential. It often mimics soft tissue sarcomas both clinically and radiologically. Surgical resection in the form of partial cystectomy or transurethral resection remains the mainstay of treatment. Herein we report the case of an inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in a young girl, which was managed by laparoscopic partial cystectomy. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of laparoscopic management of an inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the urinary bladder.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cheng L, Foster SR, MacLennan GT, Lopez-Beltran A, Zhang S, Montironi R. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors of the genitourinary tract: single entity or continuum. J Urol. 2008; 180:1235–1240.2. Roth JA. Reactive pseudosarcomatous response in urinary bladder. Urology. 1980; 16:635–637.3. Montgomery EA, Shuster DD, Burkart AL, Esteban JM, Sgrignoli A, Elwood L, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors of the urinary tract: a clinicopathologic study of 46 cases, including a malignant example inflammatory fibrosarcoma and a subset associated with high-grade urothelial carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006; 30:1502–1512.4. Coffin CM, Humphrey PA, Dehner LP. Extrapulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: a clinical and pathological survey. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1998; 15:85–101.5. Watanabe K, Baba K, Saito A, Hoshi N, Suzuki T. Pseudosarcomatous myofibroblastic tumor and myosarcoma of the urogenital tract. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2001; 125:1070–1073.6. Emerson RE, Cheng L. Immunohistochemical markers in the evaluation of tumors of the urinary bladder: a review. Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 2005; 27:301–316.7. Iczkowski KA, Shanks JH, Gadaleanu V, Cheng L, Jones EC, Neumann R, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor and sarcoma of urinary bladder: differential diagnosis and outcome in thirty-eight spindle cell neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 2001; 14:1043–1051.8. Watanabe K, Kusakabe T, Hoshi N, Saito A, Suzuki T. h-Caldesmon in leiomyosarcoma and tumors with smooth muscle cell-like differentiation: its specific expression in the smooth muscle cell tumor. Hum Pathol. 1999; 30:392–396.9. Harik LR, Merino C, Coindre JM, Amin MB, Pedeutour F, Weiss SW. Pseudosarcomatous myofibroblastic proliferations of the bladder: a clinicopathologic study of 42 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006; 30:787–794.10. Nezhat CR, Nezhat FR. Laparoscopic segmental bladder resection for endometriosis: a report of two cases. Obstet Gynecol. 1993; 81:882–884.