Korean J Urol.
2013 Nov;54(11):750-755.
Impact of Treatment With Statins on Prostate-Specific Antigen and Prostate Volume in Patients With Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Kangbuk Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hjae.park@samsung.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We investigated the impact on prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and prostate volume (PV) of statin medication for 1 year in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively investigated 791 patients in whom BPH was diagnosed. For analysis, the patients were divided into four groups according to their medications: group A, alpha-blocker; group B, alpha-blocker+statin; group C, alpha-blocker+dutasteride; group D, alpha-blockers+statin+dutasteride. To investigate changes in serum PSA, PV, and total cholesterol, we analyzed the data at the time of initial treatment and after 1 year of medication.
RESULTS
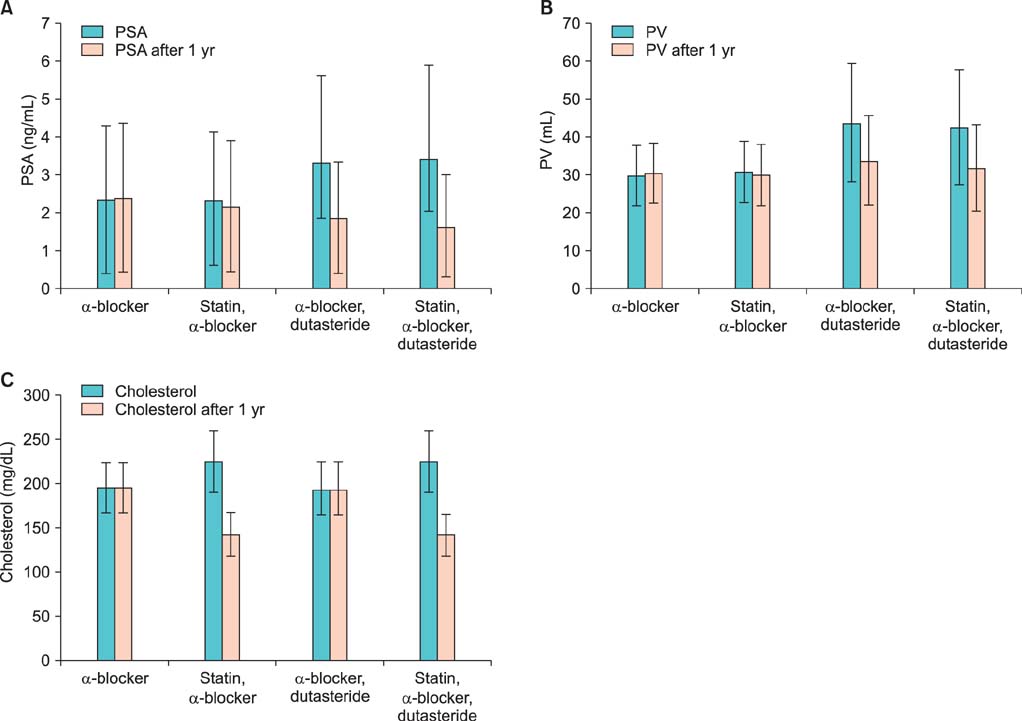
After 1 year, group A showed a 1.3% increase in PSA and a 1.0% increase in PV. Group B showed a 4.3% decrease in PSA and a 1.8% decrease in PV. The difference in PV reduction between groups A and B was statistically significant (p<0.001). Group C showed a 49.1% reduction in PSA and a 22.9% reduction in PV. Group D showed a 51.6% reduction in PSA and a 24.5% reduction in PV. The difference in PV reduction between groups C and D was not statistically significant (p=0.762). By use of a multivariate logistic regression model, we found that the probability of PV reduction after 1 year was more than 14.8 times in statin users than in statin nonusers (95% confidence interval, 5.8% to 37.6%; p<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Statin administration reduced PSA and PV in BPH patients. This finding may imply the improvement of lower urinary tract symptoms and prevention of cardiovascular disease and chemoprevention of prostate cancer with statin treatment.
MeSH Terms
-
Azasteroids
Cardiovascular Diseases
Chemoprevention
Cholesterol
Humans
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors*
Logistic Models
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
Morinda
Prostate*
Prostate-Specific Antigen*
Prostatic Hyperplasia*
Prostatic Neoplasms
Retrospective Studies
Dutasteride
Azasteroids
Cholesterol
Prostate-Specific Antigen
Figure
Reference
-
1. AUA Practice Guidelines Committee. AUA guideline on management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (2003). Chapter 1: Diagnosis and treatment recommendations. J Urol. 2003; 170(2 Pt 1):530–547.2. Bruchovsky N, Rennie PS, Batzold FH, Goldenberg SL, Fletcher T, McLoughlin MG. Kinetic parameters of 5 alpha-reductase activity in stroma and epithelium of normal, hyperplastic, and carcinomatous human prostates. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988; 67:806–816.3. Marihart S, Harik M, Djavan B. Dutasteride: a review of current data on a novel dual inhibitor of 5alpha reductase. Rev Urol. 2005; 7:203–210.4. Choi YH, Cho SY, Cho IR. The different reduction rate of prostate-specific antigen in dutasteride and finasteride. Korean J Urol. 2010; 51:704–708.5. Cannon CP, Braunwald E, McCabe CH, Rader DJ, Rouleau JL, Belder R, et al. Intensive versus moderate lipid lowering with statins after acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:1495–1504.6. Baigent C, Keech A, Kearney PM, Blackwell L, Buck G, Pollicino C, et al. Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: prospective meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet. 2005; 366:1267–1278.7. Ray KK, Cannon CP. Atorvastatin and cardiovascular protection: a review and comparison of recent clinical trials. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005; 6:915–927.8. Ndrepepa G, Fusaro M, King L, Cassese S, Tada T, Schomig A, et al. Statin pretreatment and presentation patterns in patients with coronary artery disease. Cardiol J. 2013; 20:52–58.9. Rees RW, Foxwell NA, Ralph DJ, Kell PD, Moncada S, Cellek S. Y-27632, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, inhibits proliferation and adrenergic contraction of prostatic smooth muscle cells. J Urol. 2003; 170(6 Pt 1):2517–2522.10. Watts KL, Spiteri MA. Connective tissue growth factor expression and induction by transforming growth factor-beta is abrogated by simvastatin via a Rho signaling mechanism. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004; 287:L1323–L1332.11. Padayatty SJ, Marcelli M, Shao TC, Cunningham GR. Lovastatin-induced apoptosis in prostate stromal cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997; 82:1434–1439.12. Sivaprasad U, Abbas T, Dutta A. Differential efficacy of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase inhibitors on the cell cycle of prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006; 5:2310–2316.13. Ploumidou K, Kyroudi-Voulgari A, Perea D, Anastasiou I, Mitropoulos D. Effect of a hypercholesterolemic diet on serum lipid profile, plasma sex steroid levels, and prostate structure in rats. Urology. 2010; 76:1517e.1–1517e.5.14. Weng TC, Yang YH, Lin SJ, Tai SH. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the therapeutic equivalence of statins. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2010; 35:139–151.15. Muller R, Gerber L, Moreira D, Andriole G, Parsons JK, Fleshner N, et al. 1249 Statins slow prostate growth: Results from the reduction by dutasteride of cancer events (REDUCE) trial [abstract]. J Urol. 2012; 187:4 Suppl. e505. Abstract no. 1249.16. Hamilton RJ, Goldberg KC, Platz EA, Freedland SJ. The influence of statin medications on prostate-specific antigen levels. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008; 100:1511–1518.17. Kim BS, Yoon YE, Lee SB, Park SY, Son YW, Kim YT, et al. The change of prostate-specific antigen and prostate-specific antigen density in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia after dutasteride treatment. Korean J Urol. 2008; 49:893–898.18. Schaffner CP. Prostatic cholesterol metabolism: regulation and alteration. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981; 75A:279–324.19. Hager MH, Solomon KR, Freeman MR. The role of cholesterol in prostate cancer. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2006; 9:379–385.20. Zhuang L, Kim J, Adam RM, Solomon KR, Freeman MR. Cholesterol targeting alters lipid raft composition and cell survival in prostate cancer cells and xenografts. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115:959–968.21. Pelton K, Freeman MR, Solomon KR. Cholesterol and prostate cancer. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2012; 12:751–759.22. Biasucci LM, Biasillo G, Stefanelli A. Inflammatory markers, cholesterol and statins: pathophysiological role and clinical importance. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2010; 48:1685–1691.23. Weis M, Heeschen C, Glassford AJ, Cooke JP. Statins have biphasic effects on angiogenesis. Circulation. 2002; 105:739–745.24. Kusama T, Mukai M, Iwasaki T, Tatsuta M, Matsumoto Y, Akedo H, et al. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor-induced RhoA translocation and invasion of human pancreatic cancer cells by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2001; 61:4885–4891.25. Rao S, Porter DC, Chen X, Herliczek T, Lowe M, Keyomarsi K. Lovastatin-mediated G1 arrest is through inhibition of the proteasome, independent of hydroxymethyl glutaryl-CoA reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:7797–7802.26. Parikh A, Childress C, Deitrick K, Lin Q, Rukstalis D, Yang W. Statin-induced autophagy by inhibition of geranylgeranyl biosynthesis in prostate cancer PC3 cells. Prostate. 2010; 70:971–981.27. Tan N, Klein EA, Li J, Moussa AS, Jones JS. Statin use and risk of prostate cancer in a population of men who underwent biopsy. J Urol. 2011; 186:86–90.28. Guess HA, Gormley GJ, Stoner E, Oesterling JE. The effect of finasteride on prostate specific antigen: review of available data. J Urol. 1996; 155:3–9.29. Debruyne F, Barkin J, van Erps P, Reis M, Tammela TL, Roehrborn C, et al. Efficacy and safety of long-term treatment with the dual 5 alpha-reductase inhibitor dutasteride in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 2004; 46:488–494.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prostate-Specific Antigen as an Estimator of Prostate Volume in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Decade of Life
- The Correlation between Metabolic Syndrome and the Prostate Volume
- The role of serum prostate specific antigen in prostatic cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia
- The effect of prazosin as a first-line therapy for the symptomatic benign prostatichypertrophy
- The relationship among PSA levels, prostatic volume and resected prostate weight