Korean J Urol.
2011 Feb;52(2):90-95.
The Relationship between B7-H4 Expression and Clinicopathological Characteristics in Clinical Stage T1 Conventional Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea. lsd@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The diagnosis of clinically early-stage (T1) renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has increased. The present study evaluated the association of B7-H4 expression on the pathological outcome and recurrence of carcinoma in the T1 stage of RCC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
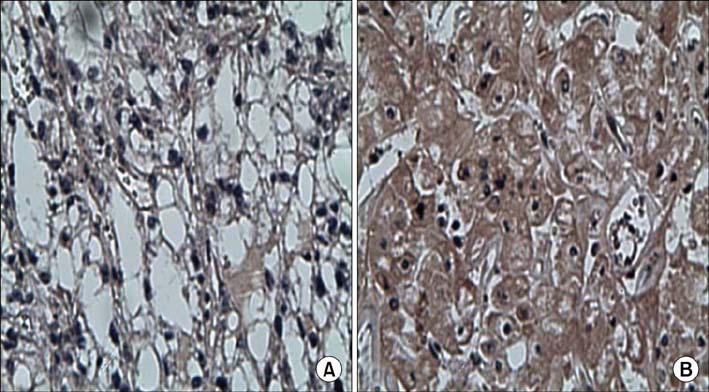
Among patients who underwent partial or radical nephrectomy after diagnosis of T1 stage RCC during the period of January 2000 to March 2007, 102 pathologically confirmed cases of clear cell carcinoma were included in this study. The patients' medical records were reviewed retrospectively. For the immunohistochemical staining tests, the B7-H4 antibody (Abbiotec 1:500) was used, and clinicopathological characteristics were analyzed.
RESULTS
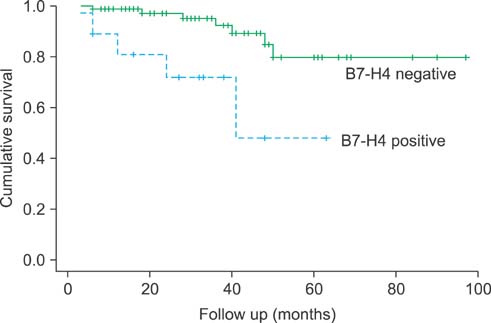
The mean age of the patients (39 males: 38.2%, 63 females: 61.8%) was 53.0+/-12.0 years (range, 31-74 years), and the mean follow-up time was 33.4+/-21.0 months (range, 6-84 months). B7-H4 expression was positive in 18 cases and negative in 84 cases. Recurrence during the follow-up period occurred in 5 cases in the group with positive B7-H4 expression and in 7 cases in the group with negative B7-H4 expression, respectively (p=0.035). In the univariate analysis, a statistically significant relationship was observed only for the presence of B7-H4 expression (p=0.0019). In the multivariate analysis, other than the expression of B7-H4, cancer size and TNM stage had effects on the recurrence of cancer.
CONCLUSIONS
For clear cell RCC, B7-H4 expression had a critical impact on the prognosis of the patients, particularly on the recurrence of the carcinoma in patients with clinical stage T1 RCC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lam JS, Pantuck AJ, Belldegrun AS, Figlin RA. Protein expression profiles in renal cell carcinoma: staging, prognosis, and patient selection for clinical trials. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. 13:703s–708s.2. Kattan MW, Reuter V, Motzer RJ, Katz J, Russo P. A postoperative prognostic nomogram for renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2001. 166:63–67.3. Frank I, Blute ML, Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Weaver AL, Zincke H. An outcome prediction model for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with radical nephrectomy based on tumor stage, size, grade and necrosis: the SSIGN score. J Urol. 2002. 168:2395–2400.4. Lam JS, Leppert JT, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. Role of molecular markers in the diagnosis and therapy of renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 2005. 66:5 Suppl. 1–9.5. Krambeck AE, Thompson RH, Dong H, Lohse CM, Park ES, Kuntz SM, et al. B7-H4 expression in renal cell carcinoma and tumor vasculature: associations with cancer progression and survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. 103:10391–10396.6. Zang X, Loke P, Kim J, Murphy K, Waitz R, Allison JP. B7x: a widely expressed B7 family member that inhibits T cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. 100:10388–10392.7. Prasad DV, Richards S, Mai XM, Dong C. B7S1, a novel B7 family member that negatively regulates T cell activation. Immunity. 2003. 18:863–873.8. Sica GL, Choi IH, Zhu G, Tamada K, Wang SD, Tamura H, et al. B7-H4, a molecule of the B7 family, negatively regulates T cell immunity. Immunity. 2003. 18:849–861.9. Choi IH, Zhu G, Sica GL, Strome SE, Cheville JC, Lau JS, et al. Genomic organization and expression analysis of B7-H4, an immune inhibitory molecule of the B7 family. J Immunol. 2003. 171:4650–4654.10. Fyfe G, Fisher RI, Rosenberg SA, Sznol M, Parkinson DR, Louie AC. Results of treatment of 255 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1995. 13:688–696.11. Thompson RH, Gillett MD, Cheville JC, Lohse DM, Dong H, Webster WS, et al. Costimulatory B7-H1 in renal cell carcinoma patients: indicator of tumor aggressiveness and potential therapeutic target. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. 101:17174–17179.12. Bui MH, Seligson D, Han KR, Pantuck AJ, Dorey FJ, Huang Y, et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX is an independent predictor of survival in advanced renal clear cell carcinoma: implications for prognosis and therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. 9:802–811.13. Leibovich BC, Sheinin Y, Lohse CM, Thompson RH, Cheville JC, Zavada J, et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX is not an independent predictor of outcome for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:4757–4764.14. Zheng W, Yi X, Fadare O, Liang SX, Martel M, Schwartz PE, et al. The oncofetal protein IMP3: a novel biomarker for endometrial serous carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008. 32:304–315.15. Hoffmann NE, Sheinin Y, Lohse CM, Parker AS, Leibovich BC, Jiang Z, et al. External validation of IMP3 expression as an independent prognostic marker for metastatic progression and death for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2008. 112:1471–1479.16. Parker AS, Kosari F, Lohse CM, Houston Thompson R, Kwon ED, Murphy L, et al. High expression levels of survivin protein independently predict a poor outcome for patients who undergo surgery for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2006. 107:37–45.17. Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, Chen L. B7-H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med. 1999. 5:1365–1369.18. Krambeck AE, Dong H, Thompson RH, Kuntz SM, Lohse CM, Leibovich BC, et al. Survivin and b7-h1 are collaborative predictors of survival and represent potential therapeutic targets for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. 13:1749–1756.19. Pantuck AJ, Zisman A, Belldegrun AS. The changing natural history of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2001. 166:1611–1623.20. Salceda S, Tang T, Kmet M, Munteanu A, Ghosh M, Macina R, et al. The immunomodulatory protein B7-H4 is overexpressed in breast and ovarian cancers and promotes epithelial cell transformation. Exp Cell Res. 2005. 306:128–141.21. Watanabe N, Gavrieli M, Sedy JR, Yang J, Fallarino F, Loftin SK, et al. BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1. Nat Immunol. 2003. 4:670–679.22. Tringler B, Liu W, Corral L, Torkko KC, Enomoto T, Davidson S, et al. B7-H4 overexpression in ovarian tumors. Gynecol Oncol. 2006. 100:44–52.23. Bander NH, Finstad CL, Cordon-Cardo C, Ramsawak RD, Vaughan ED Jr, Whitmore WF Jr, et al. Analysis of a mouse monoclonal antibody that reacts with a specific region of the human proximal tubule and subsets renal cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1989. 49:6774–6780.24. van den Berg E, van der Hout AH, Oosterhuis JW, Störkel S, Dijkhuizen T, Dam A, et al. Cytogenetic analysis of epithelial renal-cell tumors: relationship with a new histopathological classification. Int J Cancer. 1993. 55:223–227.25. Webster WS, Lohse CM, Thompson RH, Dong H, Frigola X, Dicks DL, et al. Mononuclear cell infiltration in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma independently predicts patient survival. Cancer. 2006. 107:46–53.26. Leppert JT, Pantuck AJ, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. The role of molecular markers in the staging of renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2007. 99:1208–1211.27. Gonzalgo ML, Eisenberger CF, Lee SM, Trock BJ, Marshall FF, Hortopan S, et al. Prognostic significance of preoperative molecular serum analysis in renal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. 8:1878–1881.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship between Clinicopathological Characteristics and Telomerase Activity of Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Cilnicopathological Significance of E-Cadherin Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Cyclooxygenase-2 and p53 Expression as Prognostic Indicators in Conventional Renal Cell Carcinoma
- The Relationship of Clusterin Expression with Ki-67 Expression and Clinicopathological Factors in Human Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Correlation of Clinical Stage and Presumptive Prognostic Factors in Renal Cell Carcinoma