Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2013 Jun;16(2):95-103.
Is It Possible to Predict the Iron Status from an Infant's Diet History?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Inha University Hospital, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. pedkim@inha.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Iron deficiency remains a very common nutritional problem despite the improvement in nutrition and increased understanding of methods for its prevention. Thus, we try to create a new method for screening iron nutrition through infant nutrition history.
METHODS
Among the children who visited Inha University Hospital from March 2006 to July 2012, 181 children with iron deficiency anemia (IDA) and 52 children without IDA ranging from 6 to 36 months of age were reviewed in this study. We used the age when they began to wean food, the type of sort weaning foods, the time required for successful weaning, iron content in weaning foods, and the duration of breastfeeding for scoring infant nutrition history based on a questionnaire.
RESULTS
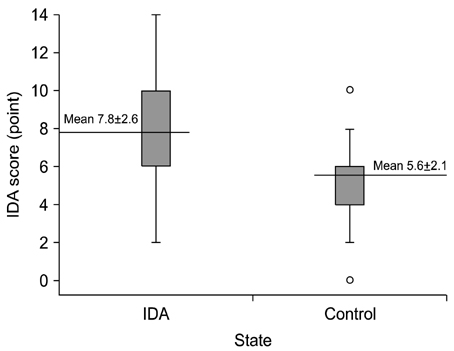
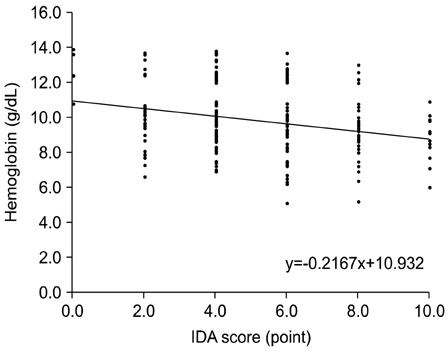
The mean score of the IDA group was 7.8+/-2.6 points, which was significantly higher than that of the control group (5.6+/-2.1) (p=0.000). If we set up the cutoff value at 6 points, this screening has 86.8% sensitivity and 36% specificity. In addition, as the IDA score increased, there was a falling trend of hemoglobin.
CONCLUSION
The IDA score does not have high specificity or high sensitivity. However, this study conveys that those patients who record a high score have low hemoglobin. Therefore, we suggest this score system for screening more IDA patients via nonpainful techniques.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Eden AN, Sandoval C. Iron deficiency in infants and toddlers in the United States. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2012; 29:704–709.
Article2. Yang YJ, Kim SK, Hong YJ, Kim JG, Hyon IY, Hong KS, et al. The prevalence of iron deficiency in preschool children. Korean J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1998; 5:14–20.3. Altuntas N, Beken S, Kulali F, Kazanci E, Unal S, Turan O, et al. Prevalence of iron deficiency at the first age of the infants hospitalized in neonatal period. Transfus Apher Sci. 2012; 47:85–89.
Article4. McLean E, Cogswell M, Egli I, Wojdyla D, de Benoist B. Worldwide prevalence of anaemia, WHO Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System, 1993-2005. Public Health Nutr. 2009; 12:444–454.
Article5. National Health Insurance Corporation. Iron deficiency anemia. accessed 10 Aug 2012. Available from: http://www.nhic.or.kr/portal/site/ida/ida.htm.6. Yoon JH. Is there the value in screening test for anemia in healthy children with capillary blood sampling? Clin Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2012; 19:53–56.7. Choi EH, Jung SH, Jun YH, Lee YJ, Park JY, You JS, et al. Iron deficiency anemia and vitamin D deficiency in breastfed infants. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010; 13:164–171.
Article8. Owen GM. Iron nutrition: growth in infancy. Dietary iron: birth to two years. New York: Raven Health Care Communications;1989. p. 103–113.9. Idjradinata P, Pollitt E. Reversal of developmental delays in iron-deficient anaemic infants treated with iron. Lancet. 1993; 341:1–4.
Article10. Szajewska H, Ruszczynski M, Chmielewska A. Effects of iron supplementation in nonanemic pregnant women, infants, and young children on the mental performance and psychomotor development of children: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010; 91:1684–1690.
Article11. Lozoff B, Jimenez E, Wolf AW. Long-term developmental outcome of infants with iron deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1991; 325:687–694.
Article12. Lozoff B, Jimenez E, Hagen J, Mollen E, Wolf AW. Poorer behavioral and developmental outcome more than 10 years after treatment for iron deficiency in infancy. Pediatrics. 2000; 105:E51.
Article13. Chang JH, Cheong WS, Jun YH, Kim SK, Kim HS, Park SK, et al. Weaning food practice in children with iron deficiency anemia. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:159–166.
Article14. Ahn HS. Pediatrics: Hong Chang Yee. 9th. Seoul: Daehane Textbook Co.;2007. p. 81–85.15. Martınez-Navarrete N, Camacho M, Martınez-Lahuerta J, Martınez-Monzó J, Fito P. Iron deficiency and iron fortified foods-a review. Food Res Int. 2002; 35:225–231.
Article16. Kim YN, Na HJ, Kang HJ. Food sources of vitamin and mineral for Korean people (I)-calcium and iron rich foods-. J Korean Home Econ Educ Assoc. 2000; 12:47–64.17. Kajosaari M, Saarinen UM. Prophylaxis of atopic disease by six months' total solid food elimination. Evaluation of 135 exclusively breast-fed infants of atopic families. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1983; 72:411–414.
Article18. Kang JU, Jin SH, Choi KD, Jang YT. A study on cow's milk and nursing method in relation to iron deficiency. Korean J Pediatr. 2006; 49:144–149.
Article19. Sibeko LN, Dhansay MA, Charlton KE, Johns T, Van Stuijvenberg ME, Gray-Donald K. Full-term, peri-urban South African infants under 6 months of age are at risk for early-onset anaemia. Public Health Nutr. 2004; 7:813–820.
Article20. Noh SJ, Na B, Kim MJ. Iron deficiency and early, low-dose iron supplementation in breast-fed infants. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008; 11:169–178.
Article21. Lozoff B, De Andraca I, Castillo M, Smith JB, Walter T, Pino P. Behavioral and developmental effects of preventing iron-deficiency anemia in healthy full-term infants. Pediatrics. 2003; 112:846–854.
Article22. Lozoff B. Iron deficiency and child development. Food Nutr Bull. 2007; 28:4 Suppl. S560–S571.
Article23. Schoetzau A, Filipiak-Pittroff B, Franke K, Koletzko S, Von Berg A, Gruebl A, et al. German Infant Nutritional Intervention Study Group. Effect of exclusive breast-feeding and early solid food avoidance on the incidence of atopic dermatitis in high-risk infants at 1 year of age. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2002; 13:234–242.
Article24. Fox AT, Du Toit G, Lang A, Lack G. Food allergy as a risk factor for nutritional rickets. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004; 15:566–569.
Article25. Stoltzfus RJ, Dreyfuss ML. Guidelines for the use of iron supplements to prevent and treat iron deficiency anemia. Washington, DC: ILSI Press;1998.26. Ahn SH, Seo WH, Kim SJ, Hwang SJ, Park HY, Han YS, et al. Risk factors of moderate to severe atopic drmatitis in the first 6 months of life. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2005; 15:242–249.27. Boyce JA, Assa'ad A, Burks AW, Jones SM, Sampson HA, Wood RA, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of food allergy in the United States: summary of the NIAID-sponsored expert panel report. Nutr Res. 2011; 31:61–75.
Article28. Ahn HS. Pediatrics: Hong Chang Yee. 9th. Seoul: Daehane Textbook Co.;2007. p. 105–106.29. Sari M, de Pee S, Martini E, Herman S, Sugiatmi , Bloem MW, et al. Estimating the prevalence of anaemia: a comparison of three methods. Bull World Health Organ. 2001; 79:506–511.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Supplementary Diet on Iron Status and Development in Infants
- The relationship between neonatal hypoglycemia and newborn iron status in hypoglycemic large-for-gestational age infants
- Iron Deficiency Anemia in Infants and Young Children
- A study on the incidence of anemia according to feeding patterns and the status of weaning diet
- A Longitudinal Study on Maternal Iron and Folate Status During and After Pregnancy in Korean Women