Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2012 Dec;15(4):197-209.
Diagnosis of Wilson Disease in Young Children: Molecular Genetic Testing and a Paradigm Shift from the Laboratory Diagnosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. jkseo@snu.ac.kr
Abstract
- Wilson disease (WD) is an autosomal recessive disorder of copper metabolism that results in accumulation of copper primarily in the liver, brain and cornea. Mutations in the WD gene, ATP7B, cause failure of copper excretion from hepatocyte into bile and a defective synthesis of ceruloplasmin. More than 500 mutations are now recognized, scattered throughout the ATP7B gene. Since WD has protean clinical presentations, awareness of WD in clinical practice is important for the early diagnosis and prevention of accumulated copper toxicity. Molecular genetic testing is playing an increasingly important role in the diagnosis of WD in uncertain cases and family screening. Siblings should be screened for WD once an index case has been diagnosed. Discrimination of heterozygotes from asymptomatic patients is essential to avoid inappropriate lifelong therapy for heterozygotes. Genetic testing, either by haplotype analysis or by mutation analysis, is the only definite solution for differentiating heterozygote carriers from affected asymptomatic patients. Routine genetic testing, because of the multitude of documented mutations, has been thought to be impractical until recently. However, genetic testing is now being more actively applied to the diagnosis of WD, particularly in young children in whom conventional biochemical diagnosis has much limitation and only genetic testing is able to confirm WD. Because advancement of modern biochemical technology now allows more rapid, easier, and less expensive mutation detection, direct DNA sequencing could be actively considered as the primary mode of diagnostic investigation rather than a supplementary test to the conventional biochemical tests. This review will focus on the recent advancement of molecular genetics and genetic diagnosis of WD in very young children on the basis of research data of the Seoul National University Children's Hospital and recent literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Seo JK, Kim YS, Hahn CJ, Baik SK. A nationwide survey for prevalence and clinical characteristics of Wilson disease in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2004. 10:Suppl. 5–15.2. Seo JK. Wilson disease: an update. Korean J Hepatol. 2006. 12:333–363.3. Wilson SAK. Progressive lenticular degeneration: a familial nervous disease associated with cirrhosis of the liver. Brain. 1912. 34:295–507.
Article4. Bull PC, Thomas GR, Rommens JM, Forbes JR, Cox DW. The Wilson disease gene is a putative copper transporting P-type ATPase similar to the Menkes gene. Nat Genet. 1993. 5:327–337.
Article5. Chelly J, Monaco AP. Cloning the Wilson disease gene. Nat Genet. 1993. 5:317–318.
Article6. Petrukhin K, Fischer SG, Pirastu M, Tanzi RE, Chernov I, Devoto M, et al. Mapping, cloning and genetic characterization of the region containing the Wilson disease gene. Nat Genet. 1993. 5:338–343.
Article7. Tanzi RE, Petrukhin K, Chernov I, Pellequer JL, Wasco W, Ross B, et al. The Wilson disease gene is a copper transporting ATPase with homology to the Menkes disease gene. Nat Genet. 1993. 5:344–350.
Article8. Yamaguchi Y, Heiny ME, Gitlin JD. Isolation and characterization of a human liver cDNA as a candidate gene for Wilson disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993. 197:271–277.
Article9. Petrukhin K, Lutsenko S, Chernov I, Ross BM, Kaplan JH, Gilliam TC. Characterization of the Wilson disease gene encoding a P-type copper transporting ATPase: genomic organization, alternative splicing, and structure/function predictions. Hum Mol Genet. 1994. 3:1647–1656.
Article10. Cox DW, Moore SD. Copper transporting P-type ATPases and human disease. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2002. 34:333–338.11. Kim ST, Park YH, Lee KU, Kum SJ, Youn YK, Seo JK, et al. An experience of first liver transplantation in Korea. J Korean Soc Transplant. 1988. 2:27.12. Moon JS, Ko JS, Seo JK. Long-term clinical follow-up of Korean children with Wilson disease; twenty years' experience. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2001. 44:127–138.13. Seo JK, Moon HR. Hepatitis in childhood as a manifestation of treatable Wilson's disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1983. 15:55–64.14. Thomas GR, Forbes JR, Roberts EA, Walshe JM, Cox DW. The Wilson disease gene: spectrum of mutations and their consequences. Nat Genet. 1995. 9:210–217.
Article15. Lutsenko S, Barnes NL, Bartee MY, Dmitriev OY. Function and regulation of human copper-transporting ATPases. Physiol Rev. 2007. 87:1011–1046.
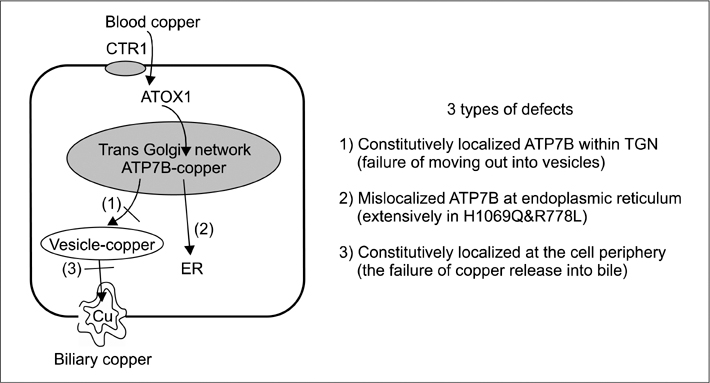
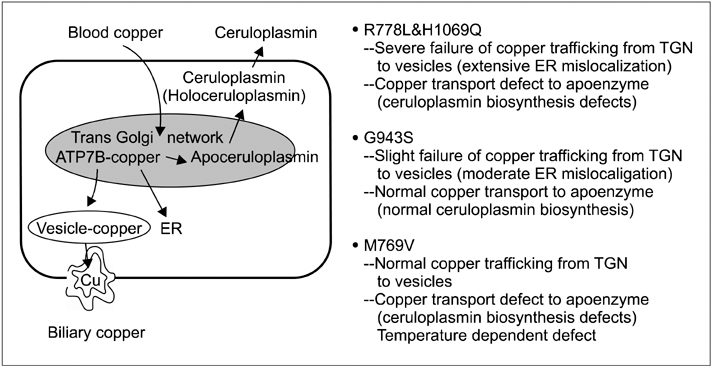
Article16. Schaefer M, Hopkins RG, Failla ML, Gitlin JD. Hepatocyte-specific localization and copper-dependent trafficking of the Wilson's disease protein in the liver. Am J Physiol. 1999. 276:G639–G646.17. Forbes JR, Cox DW. Copper-dependent trafficking of Wilson disease mutant ATP7B proteins. Hum Mol Genet. 2000. 9:1927–1935.
Article18. de Bie P, Muller P, Wijmenga C, Klomp LW. Molecular pathogenesis of Wilson and Menkes disease: correlation of mutations with molecular defects and disease phenotypes. J Med Genet. 2007. 44:673–688.
Article19. Ambrosini L, Mercer JF. Defective copper-induced trafficking and localization of the Menkes protein in patients with mild and copper-treated classical Menkes disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1999. 8:1547–1555.
Article20. Cater MA, La Fontaine S, Shield K, Deal Y, Mercer JF. ATP7B mediates vesicular sequestration of copper: insight into biliary copper excretion. Gastroenterology. 2006. 130:493–506.
Article21. Meusser B, Hirsch C, Jarosch E, Sommer T. ERAD: the long road to destruction. Nat Cell Biol. 2005. 7:766–772.
Article22. Forbes JR, Hsi G, Cox DW. Role of the copper-binding domain in the copper transport function of ATP7B, the P-type ATPase defective in Wilson disease. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:12408–12413.
Article23. DiDonato M, Hsu HF, Narindrasorasak S, Que L Jr, Sarkar B. Copper-induced conformational changes in the N-terminal domain of the Wilson disease copper-transporting ATPase. Biochemistry. 2000. 39:1890–1896.
Article24. Seo JK. Molecular genetic testing and diagnosis of Wilson disease. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. 11:Suppl. 72S–82S.25. Seo JK, Kim JW. Mutation analysis of Wilson disease Gene: Arg778Leu mutation in Korean Children. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999. 2:164–168.
Article26. Yoo HW. Identification of novel mutations and the three most common mutations in the human ATP7B gene of Korean patients with Wilson disease. Genet Med. 2002. 4:6 Suppl. 43S–48S.
Article27. Bae SH, Kim JW, Seo JK. Haplotype analysis and possible founder effect at the R778L mutation of the ATP7B gene in Korean patients with Wilson disease. Korean J Hepatol. 2009. 15:309–319.
Article28. Tsai CH, Tsai FJ, Wu JY, Chang JG, Lee CC, Lin SP, et al. Mutation analysis of Wilson disease in Taiwan and description of six new mutations. Hum Mutat. 1998. 12:370–376.
Article29. Wan L, Tsai CH, Tsai Y, Hsu CM, Lee CC, Tsai FJ. Mutation analysis of Taiwanese Wilson disease patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. 345:734–738.
Article30. Xu Y, Fan Y, Yu L, Jiang Y, Yang R, Han Y, et al. Identification of a mutation hotspot in exon 8 of Wilson's disease gene by cycle sequencing. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 1998. 15:284–287.31. Nanji MS, Nguyen VT, Kawasoe JH, Inui K, Endo F, Nakajima T, et al. Haplotype and mutation analysis in Japanese patients with Wilson disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1997. 60:1423–1429.
Article32. Czlonkowska A, Rodo M, Gajda J, Ploos van Amstel HK, Juyn J, Houwen RH. Very high frequency of the His1069Gln mutation in Polish Wilson disease patients. J Neurol. 1997. 244:591–592.
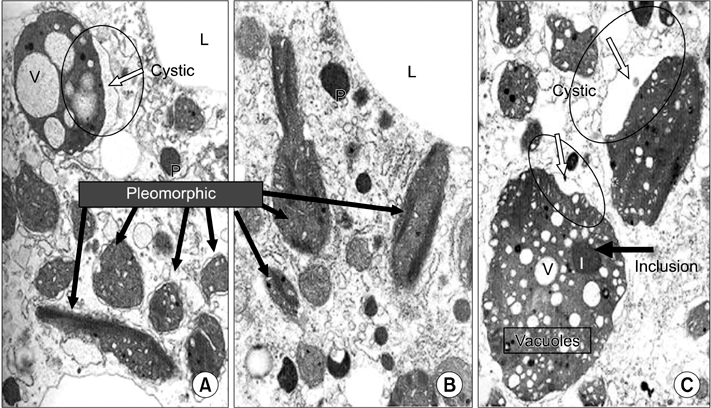
Article33. Sternlieb I. Fraternal concordance of types of abnormal hepatocellular mitochondria in Wilson's disease. Hepatology. 1992. 16:728–732.
Article34. Cheon JE, Kim IO, Seo JK, Ko JS, Lee JM, Shin CI, et al. Clinical application of liver MR imaging in Wilson's disease. Korean J Radiol. 2010. 11:665–672.
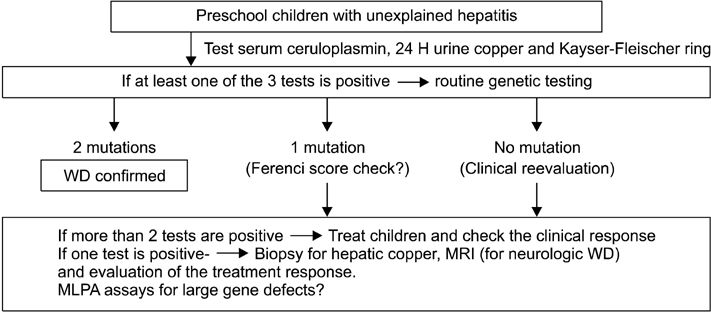
Article35. Kim TJ, Kim IO, Kim WS, Cheon JE, Moon SG, Kwon JW, et al. MR imaging of the brain in Wilson disease of childhood: findings before and after treatment with clinical correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006. 27:1373–1378.36. Ferenci P, Caca K, Loudianos G, Mieli-Vergani G, Tanner S, Sternlieb I, et al. Diagnosis and phenotypic classification of Wilson disease. Liver Int. 2003. 23:139–142.37. Gow PJ, Smallwood RA, Angus PW, Smith AL, Wall AJ, Sewell RB. Diagnosis of Wilson's disease: an experience over three decades. Gut. 2000. 46:415–419.
Article38. Iorio R, D'Ambrosi M, Mazzarella G, Varrella F, Vecchione R, Vegnente A. Early occurrence of hypertransaminasemia in a 13-month-old child with Wilson disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2003. 36:637–638.
Article39. Beyersdorff A, Findeisen A. Morbus Wilson: case report of a two-year-old child as first manifestation. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2006. 41:496–497.
Article40. Wilson DC, Phillips MJ, Cox DW, Roberts EA. Severe hepatic Wilson's disease in preschool-aged children. J Pediatr. 2000. 137:719–722.
Article41. Caprai S, Loudianos G, Massei F, Gori L, Lovicu M, Maggiore G. Direct diagnosis of Wilson disease by molecular genetics. J Pediatr. 2006. 148:138–140.
Article42. Kim JH, Kim JH, Seo KS, Ko JS, Chang JY, Yang HR, et al. Genetically confirmed Wilson disease in a 9 month-old boy with elevation of aminotransferase. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. [being in press].43. Stewart EA, White A, Tomfohrde J, Osborne-Lawrence S, Prestridge L, Bonne-Tamir B, et al. Polymorphic microsatellites and Wilson disease (WD). Am J Hum Genet. 1993. 53:864–873.44. Kim JW, Kim SI, Seo JK. A genetic linkage study of Wilson disease in Korean families. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1993. 36:1596–1612.45. Thomas GR, Roberts EA, Walshe JM, Cox DW. Haplotypes and mutations in Wilson disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1995. 56:1315–1319.46. Luoma LM, Deeb TM, Macintyre G, Cox DW. Functional analysis of mutations in the ATP loop of the Wilson disease copper transporter, ATP7B. Hum Mutat. 2010. 31:569–577.
Article47. Forbes JR, Cox DW. Functional characterization of missense mutations in ATP7B: Wilson disease mutation or normal variant? Am J Hum Genet. 1998. 63:1663–1674.
Article48. Yang HR, Ko JS, Seo JK. Germlinemutation analysis of STK11 gene using direct sequencing and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification assay in Korean children with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2010. 55:3458–3465.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Molecular Genetic Diagnosis of Genetic Endocrine Diseases
- Integrated diagnostic approach of pediatric neuromuscular disorders
- Presentation of Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 3 Mimicking Wilson Disease: Molecular Genetic Diagnosis and Response to Treatment
- The Study of the Initial Presentations of Wilson Disease at Diagonosis
- Infantile nystagmus syndrome: Promise and pitfalls of genetic testing