Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2012 Jun;15(2):122-126.
Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis with a Single Heterozygote Mutation in the ATP8B1 Gene
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. i101016@skku.edu
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine & Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis (BRIC) is a rare autosomal recessive inherited disorder characterized by multiple recurrent episodes of severe cholestatic jaundice without obstruction of extrahepatic bile duct. We present the case of a 7-year-old boy with BRIC confirmed by mutation analysis in the ATP8B1 gene and typical clinical manifestation. Despite inheritance of BRIC, we detected a mutation on only one allele. To our knowledge, this is the first report of BRIC with a confirmed single heterozygote novel mutation in the ATP8B1 gene in Korea.
MeSH Terms
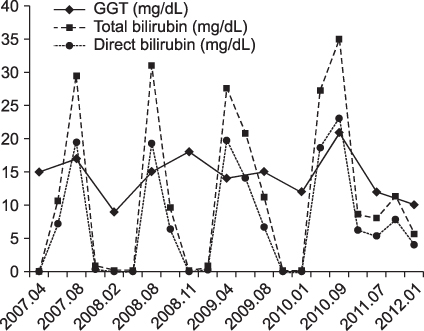
Figure
Reference
-
1. Folvik G, Hilde O, Helge GO. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis: review and long-term follow-up of five cases. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2012. 47:482–488.
Article2. Kim OY, Sung BY, Kowg GD, Yoon HS, Shin YM, Oh HT, et al. A case of nonfamilial benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Korean J Hepatol. 1998. 4:188–193.3. Ko JS, Seo JK. The etiologies of neonatal cholestasis. Korean J Pediatr. 2007. 50:835–840.
Article4. Klomp LW, Vargas JC, van Mil SW, Pawlikowska L, Strautnieks SS, van Eijk MJ, et al. Characterization of mutations in ATP8B1 associated with hereditary cholestasis. Hepatology. 2004. 40:27–38.
Article5. van der Woerd WL, van Mil SW, Stapelbroek JM, Klomp LW, van de Graaf SF, Houwen RH. Familial cholestasis: progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis, benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010. 24:541–553.
Article6. Lykavieris P, van Mil S, Cresteil D, Fabre M, Hadchouel M, Klomp L, et al. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 1 and extrahepatic features: no catch-up of stature growth, exacerbation of diarrhea, and appearance of liver steatosis after liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 2003. 39:447–452.
Article7. Summerskill WH, Walshe JM. Benign recurrent intrahepatic "obstructive" jaundice. Lancet. 1959. 2:686–690.8. Tygstrup N, Jensen B. Intermittent intrahepatic cholestasis of unknown etiology in five young males from the Faroe Islands. Acta Med Scand. 1969. 185:523–530.
Article9. Houwen RH, Baharloo S, Blankenship K, Raeymaekers P, Juyn J, Sandkuijl LA, et al. Genome screening by searching for shared segments: mapping a gene for benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Nat Genet. 1994. 8:380–386.
Article10. Bull LN, van Eijk MJ, Pawlikowska L, DeYoung JA, Juijn JA, Liao M, et al. A gene encoding a P-type ATPase mutated in two forms of hereditary cholestasis. Nat Genet. 1998. 18:219–224.
Article11. Stapelbroek JM, van Erpecum KJ, Klomp LW, Houwen RH. Liver disease associated with canalicular transport defects: current and future therapies. J Hepatol. 2010. 52:258–271.
Article12. Davit-Spraul A, Gonzales E, Baussan C, Jacquemin E. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009. 4:1.
Article13. Liu LY, Wang XH, Wang ZL, Zhu QR, Wang JS. Characterization of ATP8B1 gene mutations and a hot-linked mutation found in Chinese children with progressive intrahepatic cholestasis and low GGT. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010. 50:179–183.
Article14. Bull LN, Juijn JA, Liao M, van Eijk MJ, Sinke RJ, Stricker NL, et al. Fine-resolution mapping by haplotype evaluation: the examples of PFIC1 and BRIC. Hum Genet. 1999. 104:241–248.
Article15. Tygstrup N, Steig BA, Juijn JA, Bull LN, Houwen RH. Recurrent familial intrahepatic cholestasis in the Faeroe Islands. Phenotypic heterogeneity but genetic homogeneity. Hepatology. 1999. 29:506–508.
Article16. Mezey E, Burns C, Burdick JF, Braine HG. A case of severe benign intrahepatic cholestasis treated with liver transplantation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002. 97:475–477.
Article17. van Mil SW, Klomp LW, Bull LN, Houwen RH. FIC1 disease: a spectrum of intrahepatic cholestatic disorders. Semin Liver Dis. 2001. 21:535–544.
Article18. van Ooteghem NA, Klomp LW, van Berge-Henegouwen GP, Houwen RH. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis progressing to progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis: low GGT cholestasis is a clinical continuum. J Hepatol. 2002. 36:439–443.
Article19. van Mil SW, van der Woerd WL, van der Brugge G, Sturm E, Jansen PL, Bull LN, et al. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis type 2 is caused by mutations in ABCB11. Gastroenterology. 2004. 127:379–384.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis
- Novel ATP8B1 Gene Mutations in a Child with Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 1
- Familial Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis
- A Case of Nonfamilial Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis
- Phenotypic and Molecular Characteristics of Children with Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis in South China