Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2012 Jun;15(2):111-116.
A Pediatric Case of Toxic Hepatitis Induced by Hovenia Dulcis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Sungkyunkwan University School of medicine, Seoul, Korea. hl.jung@samsung.com
Abstract
- Toxic hepatitis is a rare but devastating disease in children. Herbs are widely used in oriental medicine to treat various symptoms in Korea, however, several herbs have been reported to induce liver injury. We report a case of toxic hepatitis induced by Hovenia dulcis in a 3-year-old boy. He complained of nausea, abdominal discomfort, and jaundice. The patient had consumed water boiled with hovenia dulcis for about 1 year prior to presentation. A diagnosis of toxic hepatitis was made based on his history, laboratory data, viral markers, ultrasonography, and biopsied liver tissue. We administered supportive management for acute fulminant hepatitis but his symptoms and liver function progressed. He was transferred to another hospital for further evaluation and consideration for liver transplantation. Because acute liver failure due to herbs or dietary supplement taken for a long time is often fetal, it is important to make early diagnosis and stop taking the drug as soon as drug induced liver injury is suspected.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
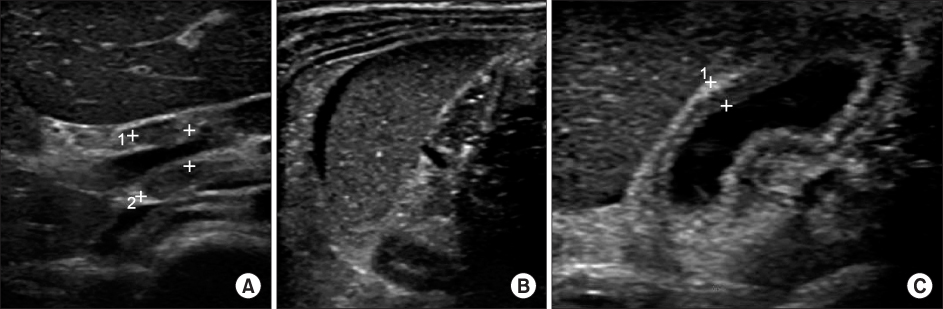
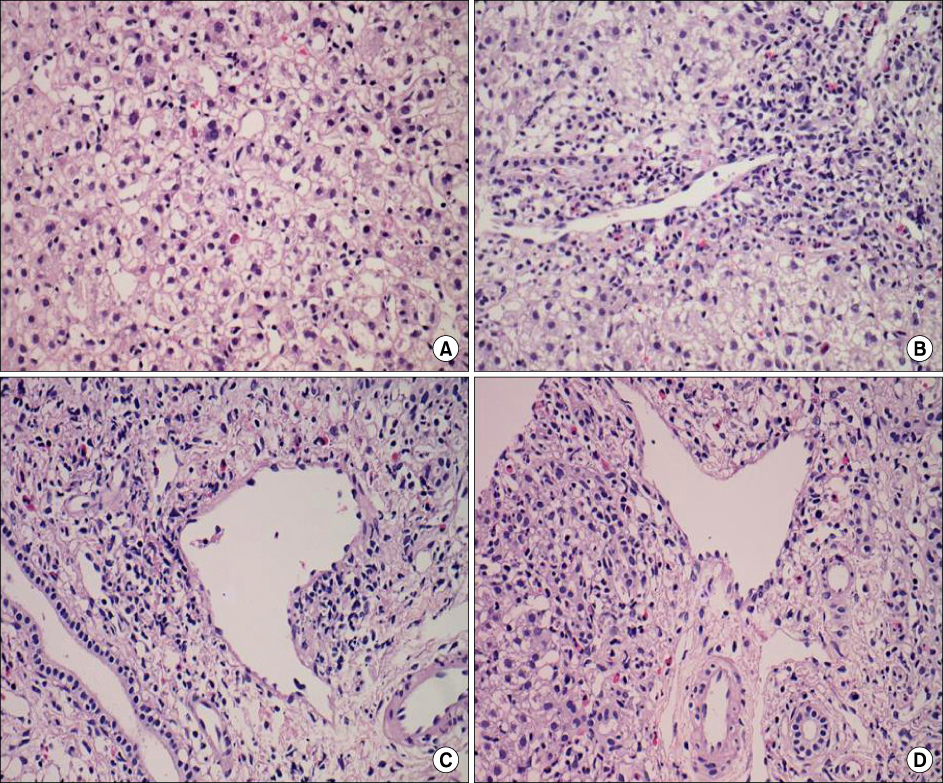
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kang HS, Choi HS, Yun TJ, Lee KG, Seo YS, Yeon JE, et al. A case of acute cholestatic hepatitis induced by Corydalis spediosa Max. The Korean Journal of Hepatology. 2009. 15:517–523.2. Larrey D. Drug-induced liver diseases. J Hepatol. 2000. 32:77–88.
Article3. Kang SH, Kim JI, Jeong KH, Ko KH, Ko PG, Hwang SW, et al. Clinical characteristics of 159 cases of acute toxic hepatitis. The Korean Journal of Hepatology. 2008. 14:483–492.
Article4. Kim KM. Acute liver failure in children. Korean Journal of Pediatrics. 2007. 50:841–847.
Article5. Fang HL, Lin HY, Chan MC, Lin WL. Treatment of chronic liver injuries in mice by oral administration of ethanolic extract of the fruit of Hovenia dulcis. Am J Chin Med. 2007. 35:693–703.
Article6. Sohn CH, Cha MI, Oh BJ, Yeo WH, Lee JH, Kim W, et al. Liver transplantation for acute toxic hepatitis due to Herbal medicines and preparations. Journal of the Korean Society of Clinical Toxicology. 2008. 6:110–116.7. Kim DJ. The assessment of toxic liver injury. The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology. 2009. 53:5–14.8. Bae SH, Kim DH, Bae YS, Lee KJ, Kim DW, Yoon JH, et al. Toxic hepatitis associated with Polygonimultiflori. The Korean Journal of Hepatology. 2010. 16:182–186.9. Bénichou C. Criteria of drug-induced liver disorders. Report of an international meeting. J Hepatol. 1990. 11:272–276.10. Larrey D. Hepatotoxicity of herbal remedies. J Hepatol. 1997. 26:47–51.
Article11. Hyun TK, Eom SH, Yu CY, Roitsch T. Hoveniadulcis-an Asian traditional herb. Planta Med. 2010. 76:943–949.12. An SY, Cheong JY, Kim SS, Lee DM, Seok JY, Kim YB, et al. One case of fulminant hepatic failure related to Dictamnusdasycarpus. Korean Journal of Medicine. 2010. 78:490–494.13. Fontana RJ, Watkins PB, Bonkovsky HL, Chalasani N, Davern T, Serrano J, et al. Drug-induced liver injury network (DILIN) prospective study: rationale, design and conduct. Drug Safety. 2009. 32:55–68.
Article14. Bissell DM, Gores GJ, Laskin DL, Hoofnagle JH. Drug-induced liver injury:mechanisms and test systems. Hepatology. 2001. 33:1009–1013.
Article15. Seeff LB. Herbal hepatotoxicity. Clin Liver Dis. 2007. 11:577–596.
Article16. Shim JO. Diagnosis and management of acute liver failure in children. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. 11:Suppl 2. 50–58.17. Berardinis V, Moulis C, Maurice M, Beaune P, Pessaryre D, Prmpon D, et al. Human microsomal epoxide hydrolase is the target of germander-induced autoantibodies on the surface of human hepatocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 2000. 58:542–551.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Liver Transplantation for Acute Toxic Hepatitis due to Herbal Medicines and Preparations
- Acute Toxic Hepatitis: RUCAM Application to Drug-induced Liver Injury and Its Limitations
- A Case of Toxic Erythema, Toxic Hepatitis and Exfoliative Deratitis due to Trichloroethylene
- A case report of toxic hepatitis caused by chloroform in automotive parts manufacturer coating process
- Amanita virosa induced toxic hepatitis: report of three cases