Korean J Urol.
2009 Nov;50(11):1037-1047.
Management of BCG Failures in Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology and Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sjhong346@yuhs.ac
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) intravesical therapy is the standard treatment in high-risk patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer, but a significant number of patients experience recurrence after BCG therapy. Although several treatment options are available for recurrence after BCG therapy, the optimal treatment strategy is still controversial. We reviewed current and promising treatment options after BCG failure.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
search of published literature using PubMed and meeting abstracts was performed.
RESULTS
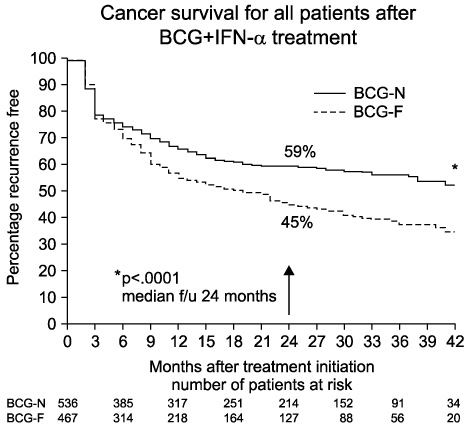
BCG failures are further subdefined as BCG refractory, BCG resistant, BCG relapsing, and BCG intolerance. Several predictors for BCG response have been studied, but prediction or stratification before therapy seems to be difficult in clinical practice. Novel biomarkers associated with immunologic mechanisms appear to be promising to predict BCG failure. Radical cystectomy is the standard treatment for BCG-refractory disease, but the timing of cystectomy is controversial. BCG maintenance or combination with interferon-alpha is a promising therapy for BCG resistance or relapse. Some salvage therapies or device-assisted instillations have been also promising, but the efficacy and safety of these novel therapies should be confirmed by large prospective studies before their clinical use in BCG failure.
CONCLUSIONS
Patients with BCG failure are not a homogeneous group and need to be stratified. Radical cystectomy should be performed without delay in patients with BCG-refractory status, but salvage intravesical therapies may be an alternative in cases without true refractory status. Although BCG and interferon intravesical therapy is promising, more efficient salvage therapy after BCG failure is required.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brandau S, Suttmann H. Thirty years of BCG immunotherapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: a success story with room for improvement. Biomed Pharmacother. 2007. 61:299–305.2. Morales A, Eidinger D, Bruce AW. Intracavitary bacillus Calmette-Guérin in the treatment of superficial bladder tumors. J Urol. 1976. 116:180–183.3. Shelley MD, Kynaston H, Court J, Wilt TJ, Coles B, Burgon K, et al. A systematic review of intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin plus transurethral resection vs transurethral resection alone in Ta and T1 bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2001. 88:209–216.4. Han RF, Pan JG. Can intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin reduce recurrence in patients with superficial bladder cancer? A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Urology. 2006. 67:1216–1223.5. Böhle A, Jocham D, Bock PR. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin versus mitomycin C for superficial bladder cancer: a formal meta-analysis of comparative studies on recurrence and toxicity. J Urol. 2003. 169:90–95.6. Hong SJ, Choi HY, Ahn HJ, Kim CS, Yang WJ. Effect of intravesical high dose epirubicin versus bacillus Calmette-Guerin instillation on the recurrence and progression of superficial bladder cancer: a prospective, multicenter study. Korean J Urol. 2005. 46:677–682.7. Park JW, Park CH, Kim CI. Superficial bladder carcinoma treated with Bacillus Calmette-Guerin: minimum 5-year follow up results. Korean J Urol. 2003. 44:573–578.8. Park JO, Kim DS, Yoon DK, Cho JH. A long term effects of single 6-week intravesical bcg therapy for the recurrence and progression of stage T1 bladder cancer. Korean J Urol. 2000. 41:1–7.9. Palou Redorta J. Management of BCG "Failures". Eur Urol. 2006. 49:779–780.10. Martin FM, Kamat AM. Definition and management of patients with bladder cancer who fail BCG therapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2009. 9:815–820.11. Klein EA, Rogatko A, Herr HW. Management of local bacillus Calmette-Guerin failures in superficial bladder cancer. J Urol. 1992. 147:601–605.12. Glashan RW. A randomized controlled study of intravesical alpha-2b-interferon in carcinoma in situ of the bladder. J Urol. 1990. 144:658–661.13. Sarosdy MF, Manyak MJ, Sagalowsky AI, Belldegrun A, Benson MC, Bihrle W, et al. Oral bropirimine immunotherapy of bladder carcinoma in situ after prior intravesical bacille Calmette-Guerin. Urology. 1998. 51:226–231.14. O'Donnell MA, Boehle A. Treatment options for BCG failures. World J Urol. 2006. 24:481–487.15. Herr HW, Dalbagni G. Defining bacillus Calmette-Guerin refractory superficial bladder tumors. J Urol. 2003. 169:1706–1708.16. Sengupta S, Blute ML. The management of superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urology. 2006. 67:3 Suppl 1. 48–54.17. Lamma D, Colombel M, Persad R, Soloway M, Böhle A, Palou J, et al. Clinical practice recommendations for the management of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2008. 7:Suppl. 651–666.18. Saint F, Salomon L, Quintela R, Cicco A, Hoznek A, Abbou CC, et al. Do prognostic parameters of remission versus relapse after Bacillus Calmette-Géurin (BCG) immunotherapy exist?. analysis of a quarter century of literature. Eur Urol. 2003. 43:351–360.19. Fernandez-Gomez J, Solsona E, Unda M, Martinez-Piñeiro L, Gonzalez M, Hernandez R, et al. Prognostic factors in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer treated with bacillus Calmette-Guérin: multivariate analysis of data from four randomized CUETO trials. Eur Urol. 2008. 53:992–1001.20. Kondylis FI, Demirci S, Ladaga L, Kolm P, Schellhammer PF. Outcomes after intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin are not affected by substaging of high grade T1 transitional cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2000. 163:1120–1123.21. Orsola A, Trias I, Raventós CX, Español I, Cecchini L, Búcar S, et al. Initial high-grade T1 urothelial cell carcinoma: feasibility and prognostic significance of lamina propria invasion microstaging (T1a/b/c) in BCG-treated and BCG-non-treated patients. Eur Urol. 2005. 48:231–238.22. Orsola A, Cecchini L, Raventós CX, Trilla E, Planas J, Landolfi S, et al. Risk factors for positive findings in patients with high-grade T1 bladder cancer treated with transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TUR) and bacille Calmette-Guérin therapy and the decision for a repeat TUR. BJU Int. 2009. Epub ahead of print.23. Saint F, Le Frere Belda MA, Quintela R, Hoznek A, Patard JJ, Bellot J, et al. Pretreatment p53 nuclear overexpression as a prognostic marker in superficial bladder cancer treated with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG). Eur Urol. 2004. 45:475–482.24. Lebret T, Becette V, Hervé JM, Molinié V, Barré P, Lugagne PM, et al. Prognostic value of MIB-1 antibody labeling index to predict response to Bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy in a high-risk selected population of patients with stage T1 grade G3 bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2000. 37:654–659.25. Lacombe L, Dalbagni G, Zhang ZF, Cordon-Cardo C, Fair WR, Herr HW, et al. Overexpression of p53 protein in a high-risk population of patients with superficial bladder cancer before and after bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy: correlation to clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol. 1996. 14:2646–2652.26. Lebret T, Becette V, Barbagelatta M, Hervé JM, Gaudez F, Barré P, et al. Correlation between p53 over expression and response to bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy in a high risk select population of patients with T1G3 bladder cancer. J Urol. 1998. 159:788–791.27. Zlotta AR, Noel JC, Fayt I, Drowart A, Van Vooren JP, Huygen K, et al. Correlation and prognostic significance of p53, p21WAF1/CIP1 and Ki-67 expression in patients with superficial bladder tumors treated with bacillus Calmette-Guerin intravesical therapy. J Urol. 1999. 161:792–798.28. Esuvaranathan K, Chiong E, Thamboo TP, Chan YH, Kamaraj R, Mahendran R, et al. Predictive value of p53 and pRb expression in superficial bladder cancer patients treated with BCG and interferon-alpha. Cancer. 2007. 109:1097–1105.29. Palou J, Algaba F, Vera I, Rodriguez O, Villavicencio H, Sanchez-Carbayo M. Protein expression patterns of ezrin are predictors of progression in T1G3 bladder tumours treated with nonmaintenance Bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Eur Urol. 2008. Epub ahead of print.30. Thalmann GN, Dewald B, Baggiolini M, Studer UE. Interleukin-8 expression in the urine after bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy: a potential prognostic factor of tumor recurrence and progression. J Urol. 1997. 158:1340–1344.31. Thalmann GN, Sermier A, Rentsch C, Möhrle K, Cecchini MG, Studer UE. Urinary interleukin-8 and 18 predict the response of superficial bladder cancer to intravesical therapy with bacillus Calmette-Guerin. J Urol. 2000. 164:2129–2133.32. Saint F, Kurth N, Maille P, Vordos D, Hoznek A, Soyeux P, et al. Urinary IL-2 assay for monitoring intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin response of superficial bladder cancer during induction course and maintenance therapy. Int J Cancer. 2003. 107:434–440.33. Saint F, Patard JJ, Maille P, Soyeux P, Hoznek A, Salomon L, et al. Prognostic value of a T helper 1 urinary cytokine response after intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin treatment for superficial bladder cancer. J Urol. 2002. 167:364–367.34. Saint F, Patard JJ, Maille P, Soyeux P, Hoznek A, Salomon L, et al. T helper 1/2 lymphocyte urinary cytokine profiles in responding and nonresponding patients after 1 and 2 courses of bacillus Calmette-Guerin for superficial bladder cancer. J Urol. 2001. 166:2142–2147.35. Kumar A, Dubey D, Bansal P, Mandhani A, Naik S. Urinary interleukin-8 predicts the response of standard and low dose intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin (modified Danish 1331 strain) for superficial bladder cancer. J Urol. 2002. 168:2232–2235.36. Takayama H, Nishimura K, Tsujimura A, Nakai Y, Nakayama M, Aozasa K, et al. Increased infiltration of tumor associated macrophages is associated with poor prognosis of bladder carcinoma in situ after intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin instillation. J Urol. 2009. 181:1894–1900.37. Ayari C, LaRue H, Hovington H, Decobert M, Harel F, Bergeron A, et al. Bladder tumor infiltrating mature dendritic cells and macrophages as predictors of response to bacillus Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy. Eur Urol. 2009. 55:1386–1395.38. Metwalli AR, Kamat AM. Controversial issues and optimal management of stage T1G3 bladder cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2006. 6:1283–1294.39. Gallagher BL, Joudi FN, Maymí JL, O'Donnell MA. Impact of previous bacille Calmette-Guérin failure pattern on subsequent response to bacille Calmette-Guérin plus interferon intravesical therapy. Urology. 2008. 71:297–301.40. Raj GV, Herr H, Serio AM, Donat SM, Bochner BH, Vickers AJ, et al. Treatment paradigm shift may improve survival of patients with high risk superficial bladder cancer. J Urol. 2007. 177:1283–1286.41. Grossman HB, O'Donnell MA, Cookson MS, Greenberg RE, Keane TE. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin failures and beyond: contemporary management of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Rev Urol. 2008. 10:281–289.42. Herr HW, Sogani PC. Does early cystectomy improve the survival of patients with high risk superficial bladder tumors? J Urol. 2001. 166:1296–1299.43. Mahmud SM, Fong B, Fahmy N, Tanguay S, Aprikian AG. Effect of preoperative delay on survival in patients with bladder cancer undergoing cystectomy in Quebec: a population based study. J Urol. 2006. 175:78–83.44. Lamm D. Improving patient outcomes: optimal BCG treatment regimen to prevent progression in superficial bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2006. 5:Suppl. 654–659.45. Bui TT, Schellhammer PF. Additional bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy for recurrent transitional cell carcinoma after an initial complete response. Urology. 1997. 49:687–690.46. Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Lamm DL. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin reduces the risk of progression in patients with superficial bladder cancer: a meta-analysis of the published results of randomized clinical trials. J Urol. 2002. 168:1964–1970.47. Böhle A, Bock PR. Intravesical bacille Calmette-Guérin versus mitomycin C in superficial bladder cancer: formal meta-analysis of comparative studies on tumor progression. Urology. 2004. 63:682–686.48. Herr HW. Is maintenance bacillus Calmette-Guérin really necessary? Eur Urol. 2008. 54:971–973.49. Belldegrun AS, Franklin JR, O'Donnell MA, Gomella LG, Klein E, Neri R, et al. Superficial bladder cancer: the role of interferon-alpha. J Urol. 1998. 159:1793–1801.50. Portillo J, Martin B, Hernandez R, Correas M, Gutierrez J, Del Valle J, et al. 2: Results at 43 months' follow-up of a double-blind, randomized, prospective clinical trial using intravesical interferon alpha-2b in the prophylaxis of stage pT1 transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urology. 1997. 49:187–190.51. Joudi FN, Smith BJ, O'Donnell MA. Final results from a national multicenter phase II trial of combination bacillus Calmette-Guérin plus interferon alpha-2B for reducing recurrence of superficial bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. 2006. 24:344–348.52. Bouffioux C, Denis L, Oosterlinck W, Viggiano G, Vergison B, Keuppens F, et al. The European Organization for Research on Treatment of Cancer Genitourinary Group. Adjuvant chemotherapy of recurrent superficial transitional cell carcinoma: results of a European organization for research on treatment of cancer randomized trial comparing intravesical instillation of thiotepa, doxorubicin and cisplatin. J Urol. 1992. 148:297–301.53. Malmström PU, Wijkström H, Lundholm C, Wester K, Busch C, Norlén BJ. Swedish-Norwegian Bladder Cancer Study Group. 5-year followup of a randomized prospective study comparing mitomycin C and bacillus Calmette-Guerin in patients with superficial bladder carcinoma. J Urol. 1999. 161:1124–1127.54. Witjes JA. Management of BCG failures in superficial bladder cancer: a review. Eur Urol. 2006. 49:790–797.55. Steinberg G, Bahnson R, Brosman S, Middleton R, Wajsman Z, Wehle M. The Valrubicin Study Group. Efficacy and safety of valrubicin for the treatment of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin refractory carcinoma in situ of the bladder. J Urol. 2000. 163:761–767.56. Morabito F, Rossi R, Graziano ME, Ferrando U, Lancini V, Cretarola E, et al. Multicenter study on the use of gemcitabine to prevent recurrence of multiple-recurring superficial bladder tumors following intravesical antiblastic agents and/or BCG: evaluation of tolerance. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2006. 78:1–4.57. Dalbagni G, Russo P, Sheinfeld J, Mazumdar M, Tong W, Rabbani F, et al. Phase I trial of intravesical gemcitabine in bacillus Calmette-Guérin-refractory transitional-cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Clin Oncol. 2002. 20:3193–3198.58. Gontero P, Casetta G, Maso G, Sogni F, Pretti G, Zitella A, et al. Phase II study to investigate the ablative efficacy of intravesical administration of gemcitabine in intermediate-risk superficial bladder cancer (SBC). Eur Urol. 2004. 46:339–343.59. Bartoletti R, Cai T, Gacci M, Giubilei G, Viggiani F, Santelli G, et al. Intravesical gemcitabine therapy for superficial transitional cell carcinoma: results of a Phase II prospective multicenter study. Urology. 2005. 66:726–731.60. Bassi P, De Marco V, Tavolini IM, Longo F, Pinto F, Zucchetti M, et al. Pharmacokinetic study of intravesical gemcitabine in carcinoma in situ of the bladder refractory to bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy. Urol Int. 2005. 75:309–313.61. Gacci M, Bartoletti R, Cai T, Nerozzi S, Pinzi N, Repetti F, et al. Intravesical gemcitabine in BCG-refractory T1G3 transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: a pilot study. Urol Int. 2006. 76:106–111.62. Dalbagni G, Russo P, Bochner B, Ben-Porat L, Sheinfeld J, Sogani P, et al. Phase II trial of intravesical gemcitabine in bacille Calmette-Guérin-refractory transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:2729–2734.63. McKiernan JM, Masson P, Murphy AM, Goetzl M, Olsson CA, Petrylak DP, et al. Phase I trial of intravesical docetaxel in the management of superficial bladder cancer refractory to standard intravesical therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:3075–3080.64. Barlow L, McKiernan J, Sawczuk I, Benson M. A single-institution experience with induction and maintenance intravesical docetaxel in the management of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer refractory to bacille Calmette-Guérin therapy. BJU Int. 2009. 104:1098–1102.65. Maymi JL, Saltsgaver N, O'Donell MA. Intravesical sequential gemcitabine-mitomycin chemotherapy as salvage treatment for patients with refractory superficial bladder cancer. J Urol. 2006. 175:271. abstract 840.66. Colombo R, Brausi M, Da Pozzo L, Salonia A, Montorsi F, Scattoni V, et al. Thermo-chemotherapy and electromotive drug administration of mitomycin C in superficial bladder cancer eradication. a pilot study on marker lesion. Eur Urol. 2001. 39:95–100.67. Di Stasi SM, Giannantoni A, Giurioli A, Valenti M, Zampa G, Storti L, et al. Sequential BCG and electromotive mitomycin versus BCG alone for high-risk superficial bladder cancer: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006. 7:43–51.68. Gofrit ON, Shapiro A, Pode D, Sidi A, Nativ O, Leib Z, et al. Combined local bladder hyperthermia and intravesical chemotherapy for the treatment of high-grade superficial bladder cancer. Urology. 2004. 63:466–471.69. van der Heijden AG, Kiemeney LA, Gofrit ON, Nativ O, Sidi A, Leib Z, et al. Preliminary European results of local microwave hyperthermia and chemotherapy treatment in intermediate or high risk superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol. 2004. 46:65–71.70. Alfred Witjes J, Hendricksen K, Gofrit O, Risi O, Nativ O. Intravesical hyperthermia and mitomycin-C for carcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder: experience of the European Synergo working party. World J Urol. 2009. 27:319–324.71. Juarranz A, Jaén P, Sanz-Rodríguez F, Cuevas J, González S. Photodynamic therapy of cancer. Basic principles and applications. Clin Transl Oncol. 2008. 10:148–154.72. Zuluaga MF, Lange N. Combination of photodynamic therapy with anti-cancer agents. Curr Med Chem. 2008. 15:1655–1673.73. Waidelich R, Stepp H, Baumgartner R, Weninger E, Hofstetter A, Kriegmair M. Clinical experience with 5-aminolevulinic acid and photodynamic therapy for refractory superficial bladder cancer. J Urol. 2001. 165:1904–1907.74. Berger AP, Steiner H, Stenzl A, Akkad T, Bartsch G, Holtl L. Photodynamic therapy with intravesical instillation of 5-aminolevulinic acid for patients with recurrent superficial bladder cancer: a single-center study. Urology. 2003. 61:338–341.75. Wo JY, Shipley WU, Dahl DM, Coen JJ, Heney NM, Kaufman DS, et al. The results of concurrent chemoradiotherapy for recurrence after treatment with bacillus Calmette-Guérin for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: is immediate cystectomy always necessary? BJU Int. 2009. 104:179–183.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Optimal Management of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin–Refractory Non–Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer in 2023
- Recombinant Bacille Calmette–Guérin for Immunotherapy in Nonmuscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
- Emerging treatments for bacillus Calmette– Guérin-unresponsive non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer
- The effect of immediate neoadjuvant electromotive instillation of mitomycin C with Bacillus Calmette–Guérin versus BCG alone in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A randomized controlled trial
- Efficacy of intravesical gemcitabine instillation compared with intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin instillation for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer