Korean J Urol.
2010 Sep;51(9):642-646.
Is a 22 cm Ureteric Stent Appropriate for Korean Patients Smaller than 175 cm in Height?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drsilent@kuh.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Determining the ideal length of a ureteric stent is important to avoid complications associated with stent placement. Clinically, most urologists usually choose the length of a ureteric stent according to the patient's height. On the basis of a Chinese population study, a 22 cm ureteric stent has been recommended for patients smaller than 175 cm. We evaluated the appropriateness of this recommendation in Korean patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
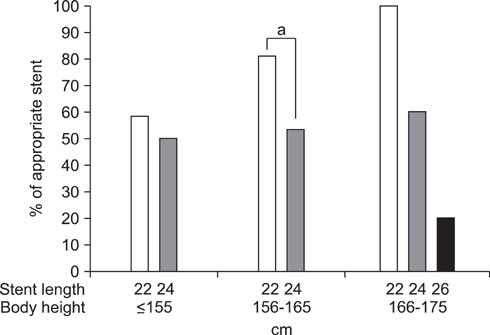
A total of 70 patients who were smaller than 175 cm and who underwent ureteroscopic lithotripsy and ureteric stent insertion were studied. The appropriateness of the stent length was determined on the basis of plain film findings. Patient discomfort was measured by use of a visual analogue scale (VAS) before the removal of the ureteric stent.
RESULTS
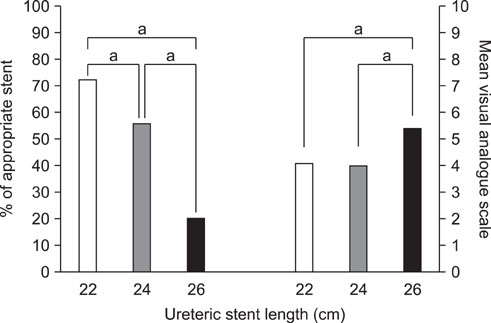
In 29 patients with a 22 cm ureteric stent, 21 patients (72.4%) had an appropriate ureteric stent length and the mean VAS was 4.1. In 36 patients with a 24 cm ureteric stent, 20 patients (55.6%) had an appropriate ureteric stent length and the mean VAS was 4.0. Among 5 patients with a 26 cm ureteric stent, 1 patient (20%) had an appropriate ureteric stent length and the mean VAS was 5.4.
CONCLUSIONS
In Korean patients smaller than 175 cm in height, a 22 cm ureteric stent was an appropriate length.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pollard SG, Macfarlane R. Symptoms arising from Double-J ureteral stents. J Urol. 1988. 139:37–38.2. Joshi HB, Okeke A, Newns N, Keeley FX Jr, Timoney AG. Characterization of urinary symptoms in patients with ureteral stents. Urology. 2002. 59:511–516.3. Lee JW, Park SC, Seo IY. The clinical characteristics of malignant ureteral obstruction secondary to non-genitourinary malignancy. Korean J Urol. 2008. 49:49–54.4. Han CH, Ha US, Park DJ, Kim SH, Lee YS, Kang SH. Change of symptom characteristics with time in patients with indwelling double-J ureteral stents. Korean J Urol. 2005. 46:1137–1140.5. Rane A, Saleemi A, Cahill D, Sriprasad S, Shrotri N, Tiptaft R. Have stent-related symptoms anything to do with placement technique? J Endourol. 2001. 15:741–745.6. Slaton JW, Kropp KA. Proximal ureteral stent migration: an avoidable complication? J Urol. 1996. 155:58–61.7. Breau RH, Norman RW. Optimal prevention and management of proximal ureteral stent migration and remigration. J Urol. 2001. 166:890–893.8. Wills MI, Gilbert HW, Chadwick DJ, Harrison SC. Which ureteric stent length? Br J Urol. 1991. 68:440.9. Pilcher JM, Patel U. . Clin Radiol. 2002. 57:59–62.10. Bhudhikanok GS, Wang MC, Eckert K, Matkin C, Marcus R, Bachrach LK. Differences in bone mineral in young Asian and Caucasian Americans may reflect differences in bone size. J Bone Miner Res. 1996. 11:1545–1556.11. Ho CH, Huang KH, Chen SC, Pu YS, Liu SP, Yu HJ. Choosing the ideal length of a double-pigtail ureteral stent according to body height: study based on a Chinese population. Urol Int. 2009. 83:70–74.12. Jeon SS, Choi YS, Hong JH. Determination of ideal stent length for endourologic surgery. J Endourol. 2007. 21:906–910.13. Shah J, Kulkarni RP. Height does not predict ureteric length. Clin Radiol. 2005. 60:812–814.14. Paick SH, Park HK, Byun SS, Oh SJ, Kim HH. Direct ureteric length measurement from intravenous pyelography: Does height represent ureteric length? Urol Res. 2005. 33:199–202.15. Hruby GW, Ames CD, Yan Y, Monga M, Landman J. Correlation of ureteric length with anthropometric variables of surface body habitus. BJU Int. 2007. 99:1119–1122.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Direct Ureteric Length Measurement Using Intravenous Pyelography
- Association of height loss with falls and sarcopenia in communitydwelling older women
- The Use of Extension Tube in Sono-guide FNAC
- Estrogen-mediated Height Control in Girls with Marfan Syndrome
- Growth Hormone Therapy in Girls with Turner Syndrome; Results of the Korean Turner Study Group