Nutr Res Pract.
2011 Feb;5(1):40-45.
Effectiveness of zinc protoporphyrin/heme ratio for screening iron deficiency in preschool-aged children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hotel Culinary Arts, Ulsan College, 101 Bongsu-ro, Dong-gu, Ulsan 682-715, Korea. khyu@uc.ac.kr
Abstract
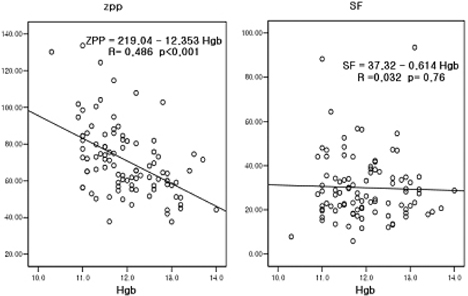
- Hemoglobin and zinc protoporphyrin (ZPP) tests are commonly used to screen for iron deficiency, but little research has been done to systematically evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of these two tests. The goal of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of zinc protoporphyrin/heme (ZPP/H) ratio as a point-of-service screening test for iron deficiency among preschool-aged children by comparing the sensitivity and specificity of hemoglobin, ZPP/H ratio, and serum ferritin (SF). Also completed were assessments for the prevalence of anemia, iron deficiency (ID), and iron deficiency anemia (IDA) with indicators of ferritin models. This study was carried out with 95 children ages 3 to 6 y. Anthropometric measurements were assessed, and blood samples were analyzed for hemoglobin, SF, transferrin saturation (TS), and ZPP. Anemia was common and the prevalences of anemia, ID, and IDA were 14.7%, 12.6%, and 5.2%, respectively. The ZPP/H ratio was strongly and significantly correlated with hemoglobin. And ZPP/H ratio was a more sensitive test for ID than hemoglobin or SF measurement, correctly identifying more than twice as many iron-deficient children (sensitivity of 91.7%, compared to 41.7% for hemoglobin and SF). However, ZPP/H ratio had lower specificity (60.2%, compared to 89.1% for hemoglobin or 96.4% for SF) and resulted in the false identification of more subjects who actually were not iron deficient than did hemoglobin or SF. Low hemoglobin concentration is a late-stage indicator of ID, but ZPP/H ratio can detect ID at early stages and can be performed easily at a relatively low cost. Therefore, ZPP/H ratio can serve as a potential screening test for pre-anemic iron deficiency in community pediatric practices.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Crowell R, Ferris AM, Wood RJ, Joyce P, Slivka H. Comparative effectiveness of zinc protoporphyrin and hemoglobin concentrations in identifying iron deficiency in a group of low-income, preschool-aged children: practical implications of recent illness. Pediatrics. 2006. 118:224–232.
Article2. Cook JD, Skikne BS, Baynes RD. Iron deficiency: the global perspective. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1994. 356:219–228.
Article3. Halterman JS, Kaczorowski JM, Aligne A, Auinger P, Szilagyi PG. Iron deficiency and cognitive achievement among school-aged children and adolescents in the United States. Pediatrics. 2001. 107:1381–1386.
Article4. Yehuda S, Youdim MB. Brain iron: a lesson for animal models. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989. 50:618–629.5. Lozoff B, Jimenez E, Wolf AW. Long-term developmental outcome of infants with iron deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1991. 325:687–694.
Article6. Looker AC, Dallman PR, Carroll MD, Gunter EW, Johnson CL. Prevalence of iron deficiency in the United States. JAMA. 1997. 277:973–976.
Article7. Rettmer RL, Carlson TH, Origenes ML, Jack RM, Labb RF. Zinc protoporphyrin/heme ratio for diagnosis of preanemic iron deficiency. Pediatrics. 1999. 104:e37.
Article8. Labbé RF, Vreman HJ, Stevenson DK. Zinc protoporphyrin: a metabolite with a mission. Clin Chem. 1999. 45:2060–2072.
Article9. Yip R, Schwartz S, Deinard AS. Screening for iron deficiency with the erythrocyte protoporphyrin test. Pediatrics. 1983. 72:214–219.
Article10. Mei Z, Parvanta I, Cogswell ME, Gunter EW, Grummer-Strawn LM. Erythrocyte protoporphyrin or hemoglobin: which is a better screening test for iron deficiency in children and women? Am J Clin Nutr. 2003. 77:1229–1233.
Article11. Soldin OP, Miller M, Soldin SJ. Pediatric reference ranges for zinc protoporphyrin. Clin Biochem. 2003. 36:21–25.
Article12. Siegel RM, LaGrone DH. The use of zinc protoporphyrin in screening young children for iron deficiency. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1994. 33:473–479.
Article13. Zimmermann MB, Molinari L, Staubli-Asobayire F, Hess SY, Chaouki N, Adou P, Hurrell RF. Serum transferrin receptor and zinc protoporphyrin as indicators of iron status in African children. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005. 81:615–623.
Article14. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendations to prevent and control iron deficiency in the United States. MMWR Recomm Rep. 1998. 47:1–29.15. Hastka J, Lasserre JJ, Schwarzbeck A, Reiter A, Hehlmann R. Laboratory tests of iron status: correlation or common sense? Clin Chem. 1996. 42:718–724.
Article16. Schneider JM, Fujii ML, Lamp CL, Lönnerdal B, Dewey KG, Zidenberg-Cherr S. Anemia, iron deficiency, and iron deficiency anemia in 12-36-mo-old children from low-income families. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005. 82:1269–1275.
Article17. Gibson RS. Principles of nutritional assessment. 1990. New York: Oxford University Press.18. Stanton NV, Gunter EW, Parsons PJ, Field PH. Empirically determined lead- poisoning screening cutoff for the Protofluor-Z hematofluorometer. Clin Chem. 1989. 35:2104–2107.
Article19. Expert Scientific Working Group. Summary of a report on assessment of the iron nutritional status of the United States population. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985. 42:1318–1330.20. Cogswell ME, Looker AC, Pfeiffer CM, Cook JD, Lacher DA, Beard JL, Lynch SR, Grummer-Strawn LM. Assessment of iron deficiency in US preschool children and nonpregnant females of childbearing age: National Health and nutrition Examination Survey 2003-2006. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009. 89:1334–1342.
Article21. WHO. UNICEF. UNU. Iron deficiency anemia: assessment, prevention, and control. A guide for program managers. 2001. Geneva: World Health Organization;1–114.22. Deinard AS, Schwartz S, Yip R. Developmental changes in serum ferritin and erythrocyte protoporphyrin in normal (nonanemic) children. Am J Clin Nutr. 1983. 38:71–76.
Article23. American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Nutrition. Kleinman RE, editor. Iron deficiency. Pediatric Nutrition Handbook. 2003. 5th ed. ELK Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics;299–311.24. Hastka J, Lasserre JJ, Schwarzbeck A, Strauch M, Hehlmann R. Washing erythrocytes to remove interferents in measurements of zinc protoporphyrin by front-face hematofluorometry. Clin Chem. 1992. 38:2184–2189.
Article25. Öhlund I, Lind T, Hörnell A, Hernell O. Predictors of iron status in well-nourished 4-y-old children. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008. 87:839–845.
Article26. Gunnarsson BS, Thorsdottir I, Palsson G. Iron status in 6-y-old children: associations with growth and earlier iron status. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2005. 59:761–767.
Article27. Karr M, Alperstein G, Causer J, Mira M, Lammi A, Fett MJ. Iron status and anaemia in preschool children in Sydney. Aust N Z J Public Health. 1996. 20:618–622.
Article28. Serdar MA, Sarici SÜ, Kurt I, Alpay F, Okutan V, Kurnaz L, Kutluay T. The role of erythrocyte protoporphyrin in the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia of children. J Trop Pediatr. 2000. 46:323–326.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on the Iron Nutritional Status with Biochemical Parameters in Preschool Children
- The Prevalence of Iron Deficiency in Preschool Children
- Assessment of Iron Parameters in Children with Acute Infectious Disease
- Therapeutic Iron and Zinc Supplementation in Children
- Iron Contents in Rice Food Derived from the Iron Pot, and In Vitro Study Regarding Heme Oxygenase-1 Activity