Nat Prod Sci.
2016 Mar;22(1):20-24. 10.20307/nps.2016.22.1.20.
Biological Activities and Stability of a Standardized Pentacyclic Triterpene Enriched Centella asiatica Extract
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacognosy and Pharmaceutical Botany, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Prince of Songkla University, Hat-Yai, Songkhla 90112, Thailand. pharkphoom.p@psu.ac.th
- 2Phytomedicine and Pharmaceutical Biotechnology Excellence Center, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Prince of Songkla University, Hat-Yai, Songkhla 90112, Thailand.
- 3Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Department of Pharmacognosy, University of Graz, Universitaetsplatz 4/I, A-8010 Graz, Austria.
- KMID: 2312916
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2016.22.1.20
Abstract
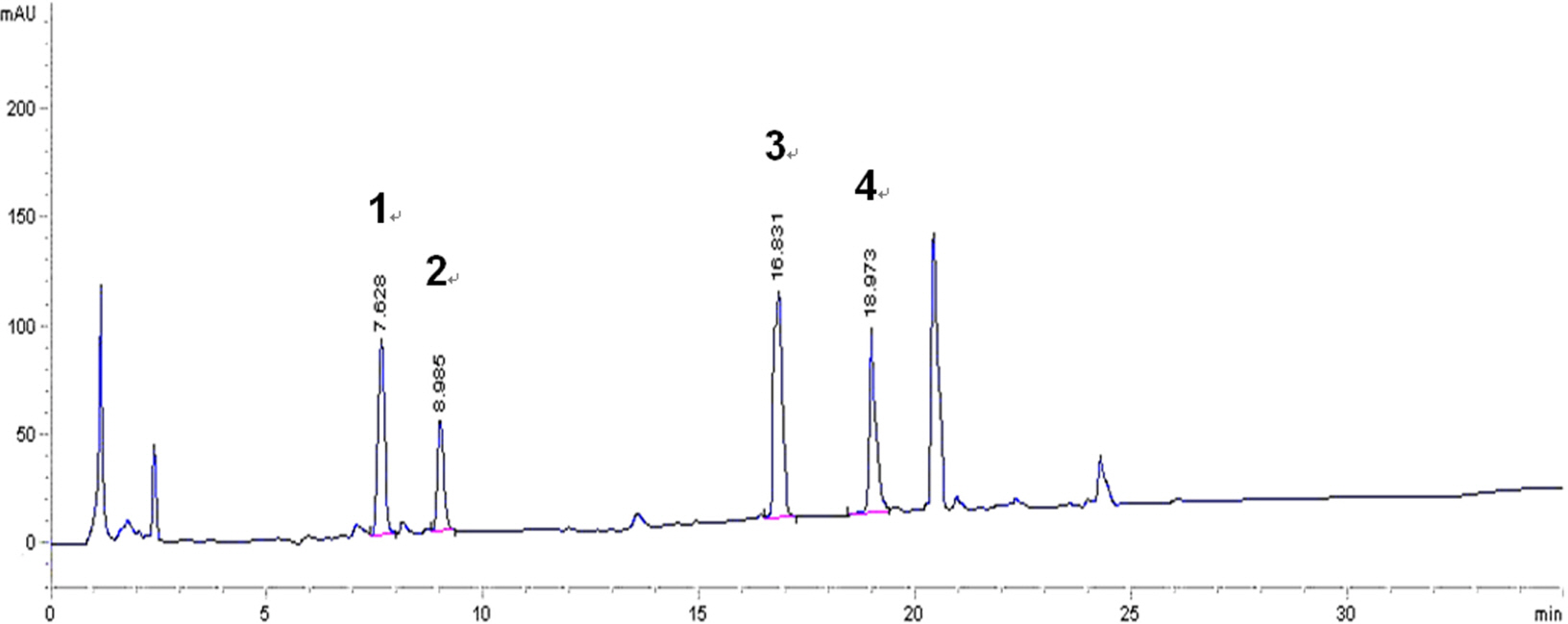
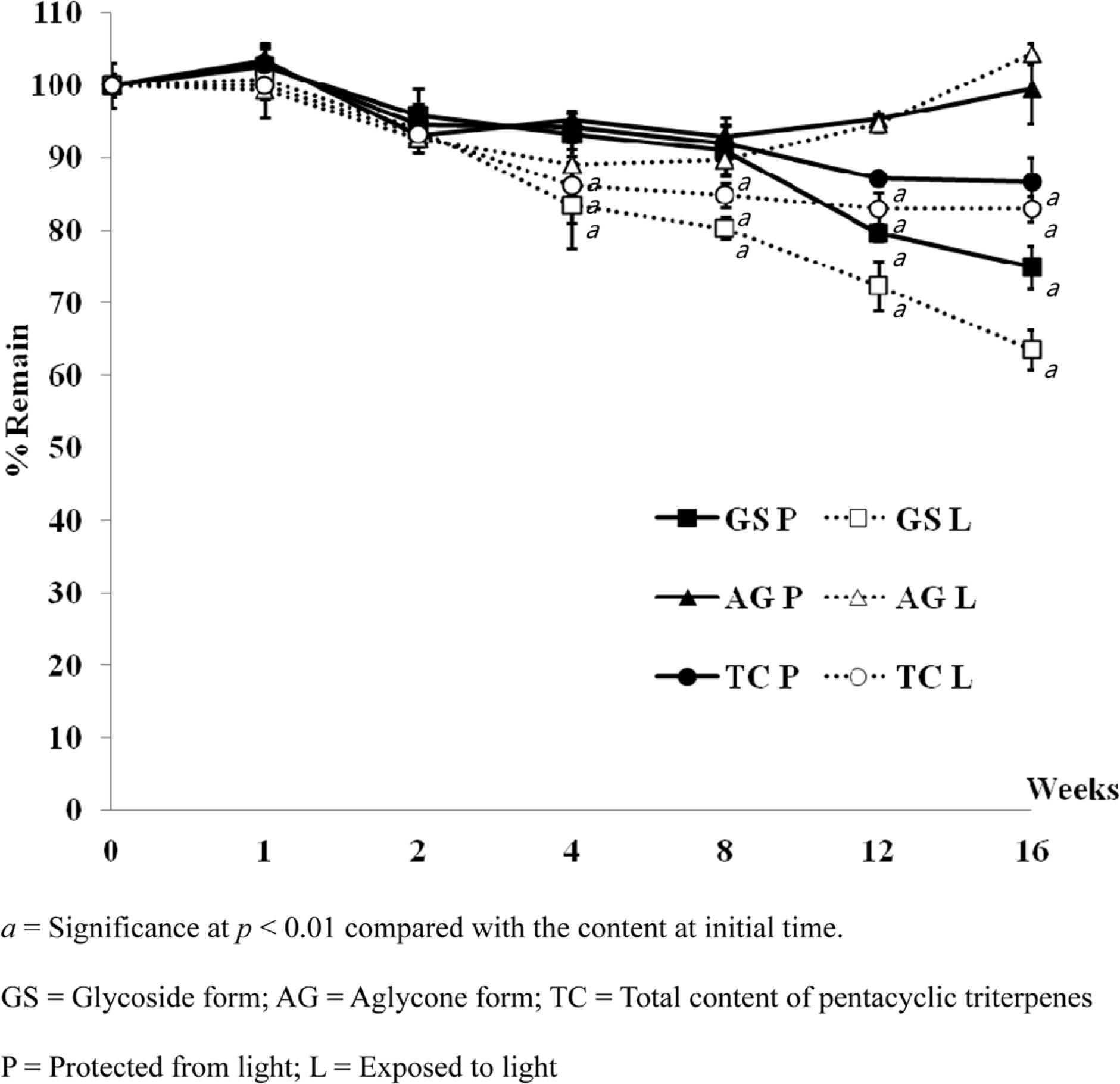
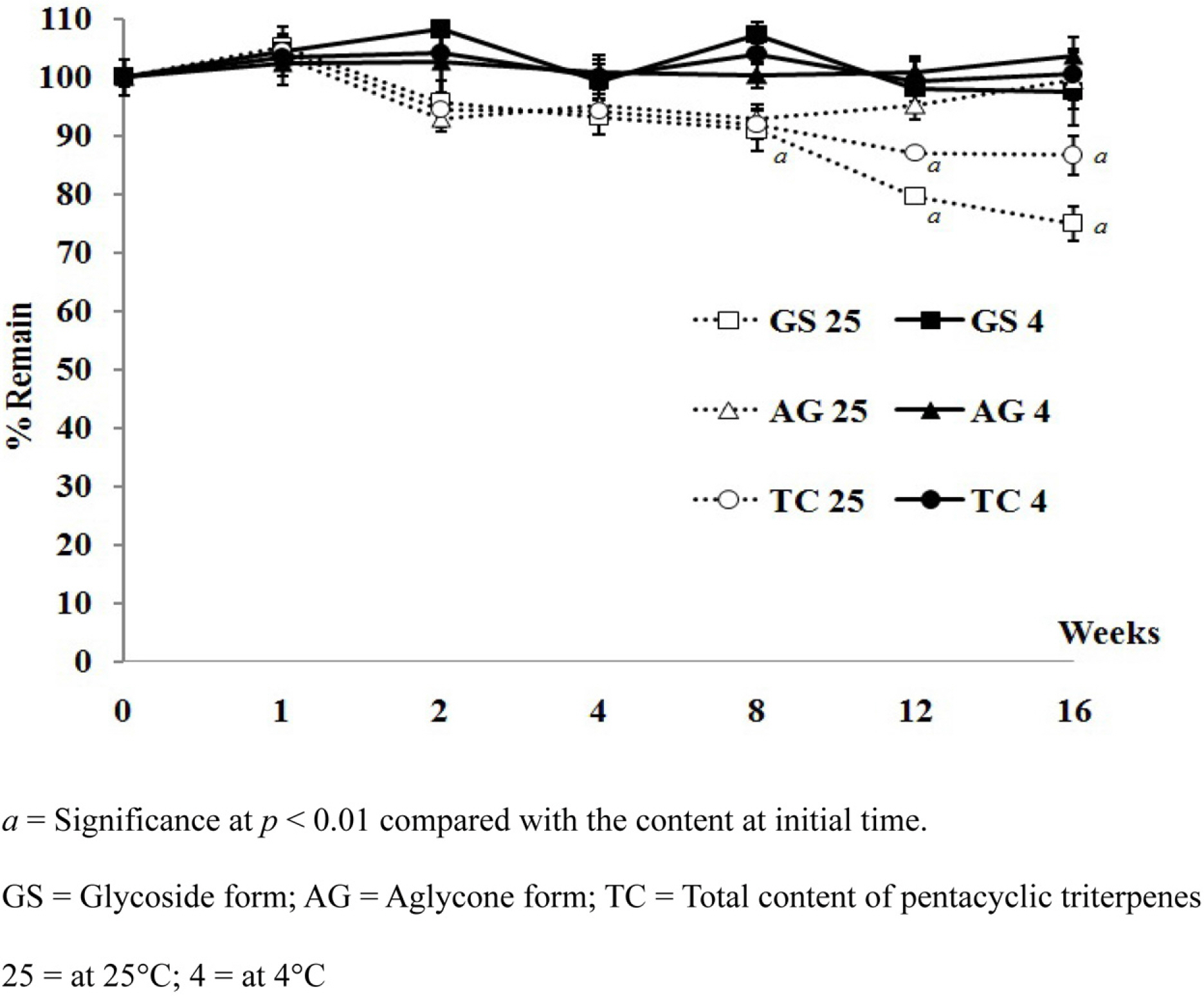
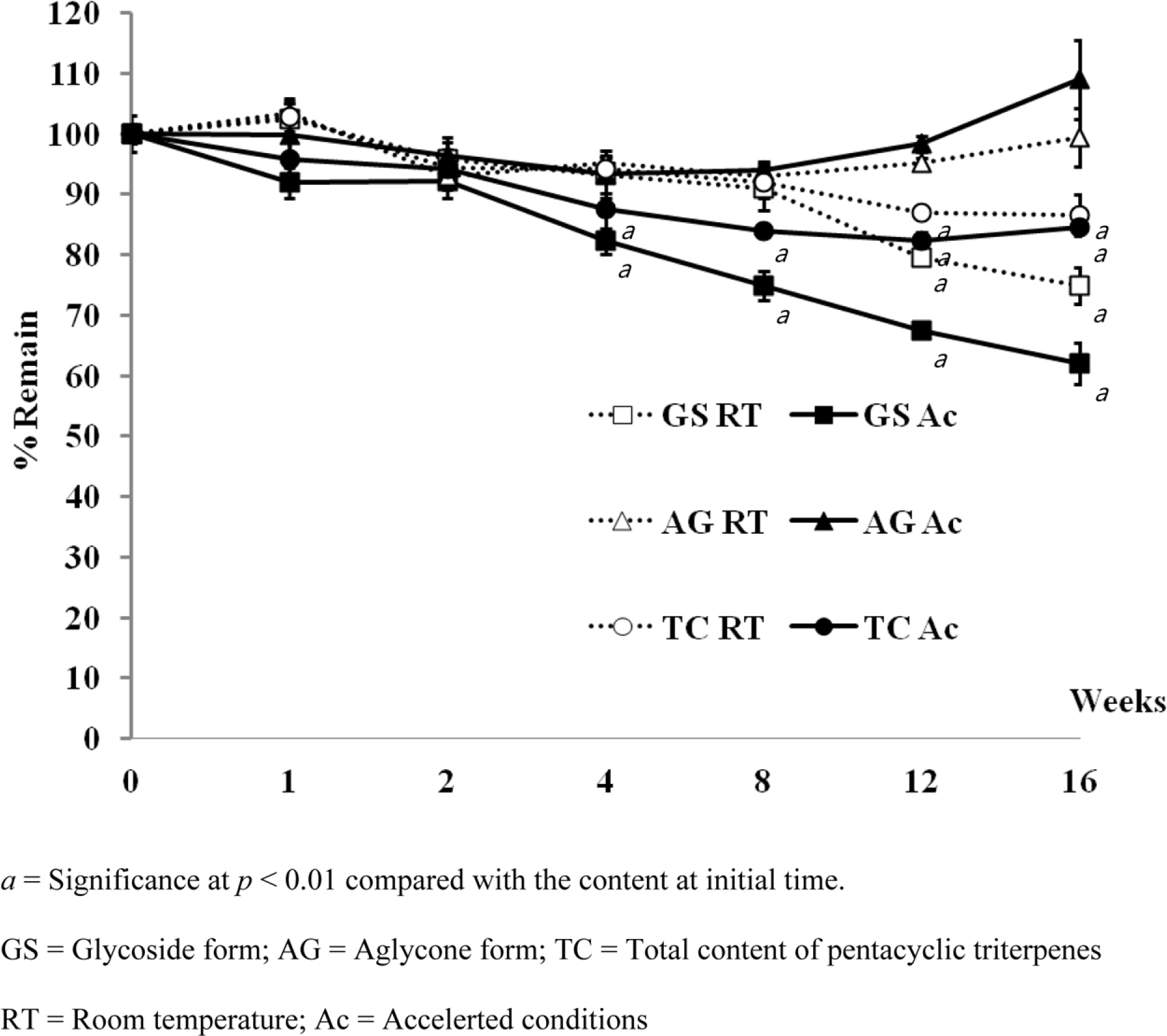
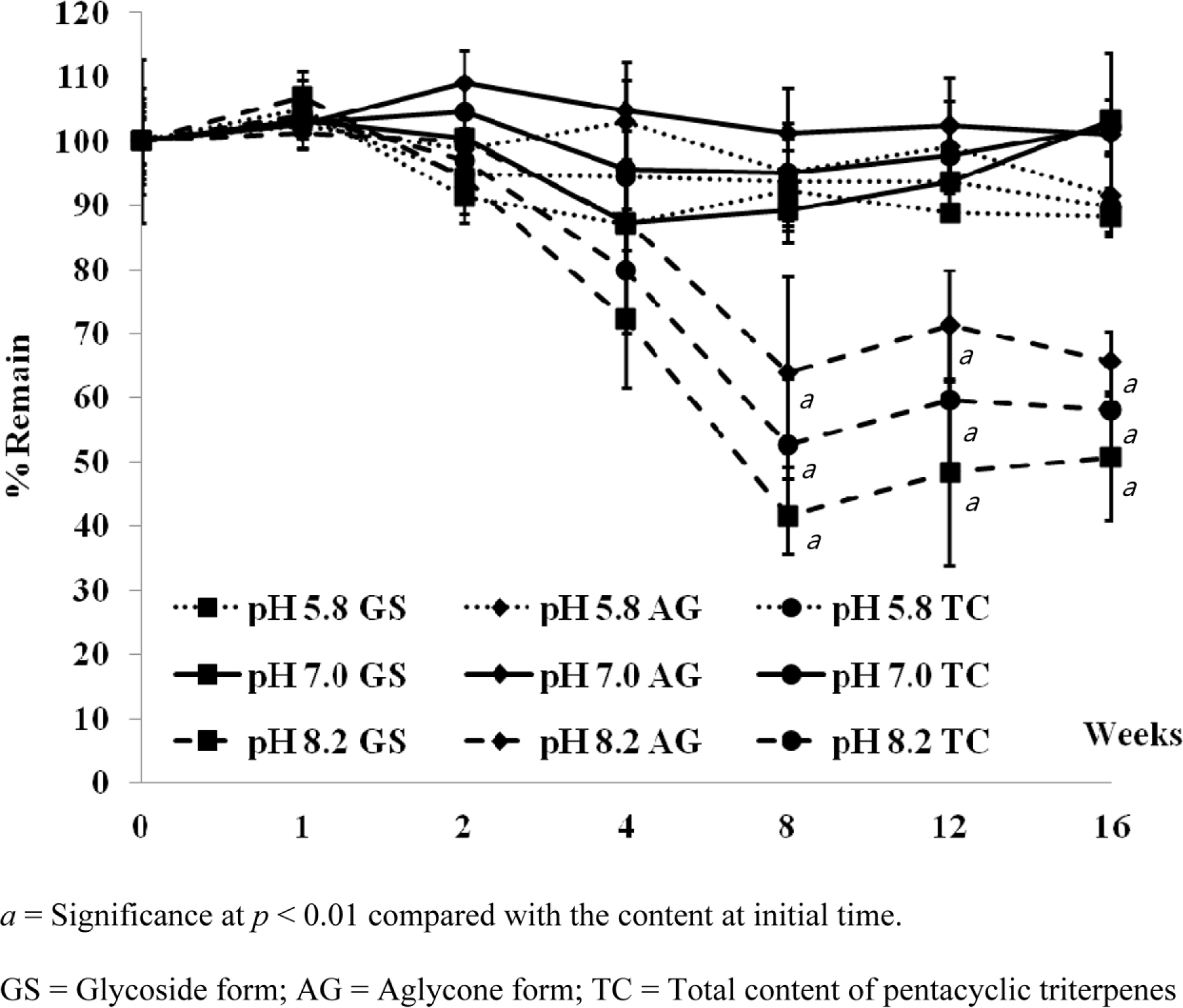
- Pentacyclic triterpenes, mainly, asiatic acid, madecassic acid, asiaticoside, and madecassoside are the active constituents of Centella asiatica. A pentacyclic triterpene enriched C. asiatica extract (PRE) was prepared and standardized to contain a total pentacyclic triterpenes not less than 65% w/w. This work was focused on determination of antiinflammatory, antioxidant, and tyrosinase inhibitory activities of PRE and its stability. The PRE exhibited a satisfactory nitric oxide inhibitory effect, with an IC50 value of 64.6 µg/mL. In addition, the PRE inhibited tyrosinase enzyme activity with an IC50 value of 104.8 µg/mL. In contrast, the PRE possessed only weak antioxidant activity. The PRE was stable over a period of four months when stored as a dried powder but only in a well-closed container protected from light at 4 °C. An aqueous alcoholic solution of the PRE was stable at pH values of 5.8 and 7.0, but was not stable at a pH of 8.2. Preparations of the PRE in an aqueous solution should be performed in acidic or neutral conditions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
(1). Bonte F., Dumas M., Chaudagne C., Meybeck A.Planta Med. 1994; 60:133–135.(2). Maquart F. X., Bellon G., Gillery P., Wegrowski Y., Borel J. P.Connect. Tissue Res. 1990; 24:107–120.(3). Yun K. J., Kim J. Y., Kim J. B., Lee K. W., Jeong S. Y., Park H. J., Jung H. J., Cho Y. W., Yun K., Lee K. T.Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008; 8:431–441.(4). Won J. H., Shin J. S., Park H. J., Jung H. J., Koh D. J., Jo B. G., Lee J. Y., Yun K., Lee K. T.Planta Med. 2010; 76:251–257.(5). Cheng C. L., Guo J. S., Luk J., Koo M. W. L.Life Sci. 2004; 74:2237–2249.(6). Puttarak P., Panichayupakaranant P.Nat. Prod. Res. 2013; 27:684–686.(7). Park B. C., Bosire K. O., Lee E. S., Lee Y. S., Kim J. A.Cancer Lett. 2005; 218:81–90.(8). Kaewchoothong A., Tewtrakul S., Panichayupakaranant P.Phytother. Res. 2012; 26:1789–1792.(9). Panichayupakaranant P., Itsuriya A., Sirikatitham A.Pharm. Biol. 2010; 48:201–205.(10). Burits M., Bucar F.Phytother. Res. 2000; 14:323–328.(11). Rangkadilok N., Sitthimonchai S., Worasuttayangkurn L., Mahidol C., Ruchirawat M., Satayavivad J.Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007; 45:328–336.(12). Puttarak P., Charoonratana T., Panichayupakaranant P.Phytomedicine. 2010; 17:323–327.(13). Pittella F., Dutra R. C., Junior D. D., Lopes M. T., Barbosa N. R.Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009; 10:3713–3721.(14). Ariffin F., Chew S. H., Bhupinder K., Karim A. A., Huda N. J.Sci. Food Agric. 2011; 91:2731–2739.(15). Subban R., Veerakumar A., Manimaran R., Hashim K. M., Balachandran I. J.Nat. Med. 2008; 62:369–373.(16). Kubo I., Kinst-Hori I., Chaudhuri S.K., Kubo Y, Sánchez Y, Ogura T.Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2000; 8:1749–1755.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- First Report of Septoria centellae Associated with Leaf Spot of Centella asiatica in Korea
- Antifungal Activity of Methanolic of Centella asiatica and Andrographis panicuiata
- Centella asiatica enhances neurogenesis and protects neuronal cells against H2O2-induced oxidative injury
- The Potential of Centella asiatica (Linn.) Urban as an Anti-Microbial and Immunomodulator Agent: A Review
- A split-face study of moisturizer containing Centella asiatica extract after ablative fractional carbon dioxide laser resurfacing