Lab Med Online.
2013 Oct;3(4):221-226.
Performance Evaluation of the CAPILLARYS 2 FLEX Piercing Analyzer for HbA1c Determination
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. songjhcp@snu.ac.kr
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level is widely used to monitor glycemic control in diabetes mellitus patients, and various methods are used for its determination. The CAPILLARYS 2 FLEX Piercing (Sebia) is a fully automated, high-throughput glycohemoglobin (HbA1c) analyzer based on capillary electrophoresis.
METHODS
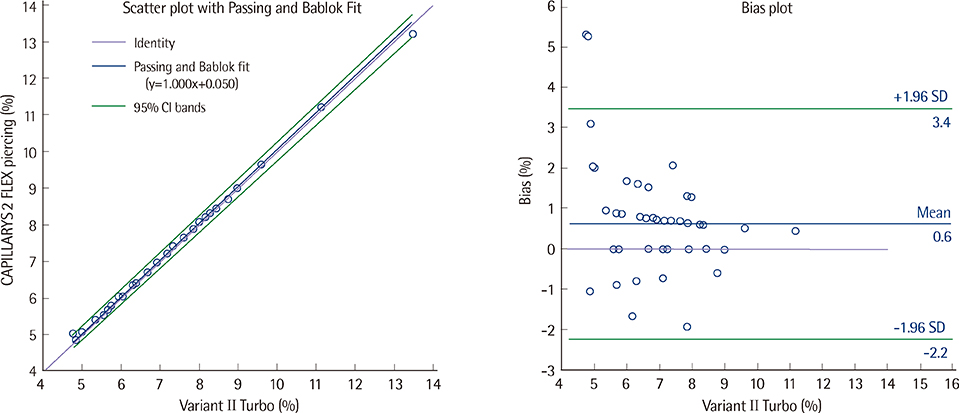
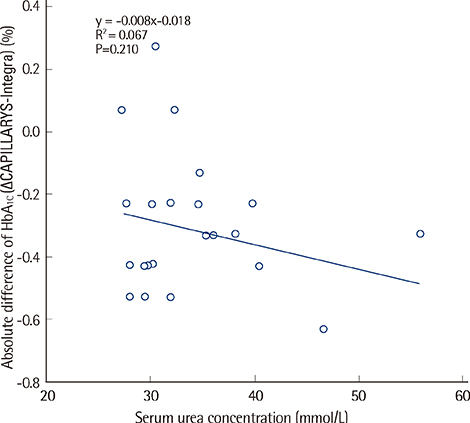
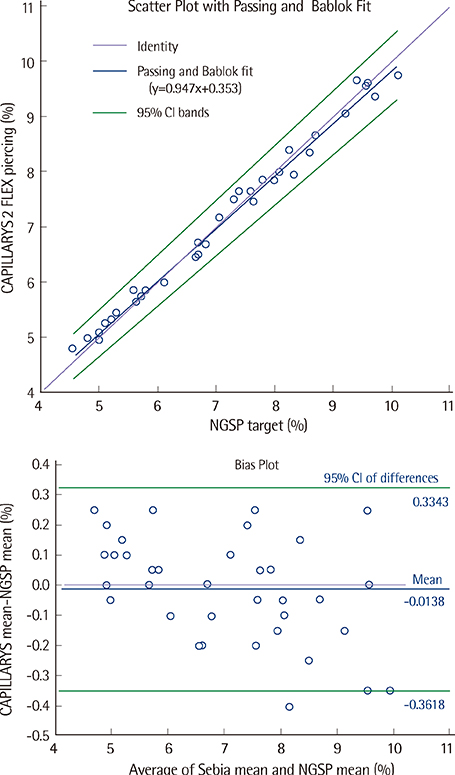
The analytical performance of the CAPILLARYS 2 FLEX Piercing analyzer was evaluated for its precision, linearity, correlation with the Variant II Turbo (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) analyzer, and its vulnerability to interference by carbamylated hemoglobin. We also investigated its agreement with National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program (NGSP) targets. All evaluations were performed according to CLSI guidelines EP05, EP06, and EP09.
RESULTS
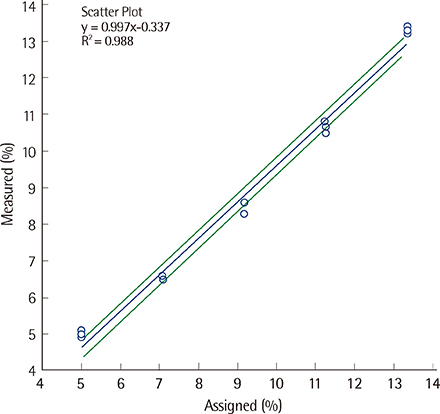
The coefficients of variation (CVs) for within-run and total imprecision were 1.7% and 1.8% at low concentrations and 1.2% and 1.3% at high concentrations, respectively. Linearity was excellent, with R2=0.9882 in the range of 5.13-13.83%; these results highly correlated with those produced by Variant II Turbo (R2=0.9978). The 95% confidence interval (for differences from the NGSP target) was -0.3618-0.3343%. No significant interference of carbamylated hemoglobin was noted.
CONCLUSIONS
The CAPILLARYS 2 FLEX Piercing analyzer showed excellent precision and linearity. Its results correlated with those obtained by the Variant II Turbo analyzer, and were agreement with the NGSP target. Therefore, its analytical performance is satisfactory for diabetes diagnosis and treatment monitoring.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia. Report of a WHO/IDF consultation. Geneva: WHO;2006.2. Korea Health Statistics 2009: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.3. Bunn HF, Gabbay KH, Gallop PM. The glycosylation of hemoglobin: relevance to diabetes mellitus. Science. 1978; 200:21–27.
Article4. Treviño G. Consensus statement on the Worldwide Standardization of the Hemoglobin A1c Measurement: the American Diabetes Association, European Association for the Study of Diabetes, International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, and the International Diabetes Federation: response to the Consensus Committee. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:e141.5. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33(S1):S62–S69.6. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Evaluation of precision performance of quantitative measurement methods; approved guideline. EP05-A2. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;2004.7. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures: a statistical approach; approved guideline. EP06-A. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;2003.8. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute . Method comparison and bias estimation using patient samples; approved guideline. EP09-A2-IR. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;2010.9. Lamb E, Dawnay A. Glycated haemoglobin measurement in uraemic patients. Ann Clin Biochem. 1992; 29:118–120.
Article10. Weykamp CW, Penders TJ, Siebelder CW, Muskiet FA, van der Slik W. Interference of carbamylated and acetylated hemoglobins in assays of glycohemoglobin by HPLC, electrophoresis, affinity chromatography and enzyme immunoassay. Clin Chem. 1993; 39:138–142.
Article11. Weykamp CW, Miedema K, de Haan T, Doelman CJ. Carbamylated hemoglobin interference in glycohemoglobin assays. Clin Chem. 1999; 45:438–440.
Article12. John WG, Mosca A, Weykamp C, Goodall I. HbA1c standardisation: history, science and politics. Clin Biochem Rev. 2007; 28:163–168.13. Hoelzel W, Weykamp C, Jeppsson JO, Miedema K, Barr JR, Goodall I, et al. IFCC reference system for measurement of hemoglobin A1c in human blood and the national standardization schemes in the United States, Japan, and Sweden: a method-comparison study. Clin Chem. 2004; 50:166–174.
Article14. Weykamp C, John WG, Mosca A, Hoshino T, Little R, Jeppsson JO, et al. The IFCC reference measurement system for HbA1c: a 6-year progress report. Clin Chem. 2008; 54:240–248.
Article15. Mosca A, Goodall I, Hoshino T, Jeppsson JO, John WG, Little RR, et al. International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, IFCC Scientific Division. Global standardization of glycated hemoglobin measurement: the position of the IFCC Working Group. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2007; 45:1077–1080.
Article16. Kaiser P, Akerboom T, Ohlendorf R, Reinauer H. Liquid chromatography-isotope dilution-mass spectrometry as a new basis for the reference measurement procedure for hemoglobin A1c determination. Clin Chem. 2010; 56:750–754.
Article17. Sacks DB, Arnold M, editors. Laboratory medicine practice guidelines: Guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus. Washington, DC: National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry;2011. p. 25–30.18. Park HD, Kim HJ, Kim MS, Lee SY, Kim JW. Evaluation of hemoglobin A1c on the Cobas Integra 800 immunoassay and Tosoh HLC-723 G8 HPLC analyzer. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2009; 31:239–246.19. Kim T, Kim S, Chang HE, Song SH, Park KU, Song J, et al. Performance evaluation of HbA1c test on the Toshiba 200FR NEO using autolab HbA1c reagent. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2010; 32:217–223.20. Choi Q, Han M, Chang HE, Song SH, Park KU, Song J. Performance evaluation of the ADAMS A1c HA-8180 analyzer for HbA1c. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2012; 34:25–30.21. Paisooksantivatana K, Kongsomgan A, Khupulsup K. NGSP and IFCC-derived NGSP HbA1c can be used interchangeably. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009; 85:e22–e25.
Article22. Summary of NGSP criteria. National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program. Accessed May 28, 2012. http://www.ngsp.org/critsumm.asp.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Analytical Performance of an Automated Glycated Hemoglobin Analyzer, HLC-723 G11
- Performance Evaluation of the ABL90 FLEX PLUS Point-of-Care Analyzer in Measuring Creatinine Levels
- Evaluation of the Performance of ARKRAY ADAMS HA-8180 HbA1c Analyzer
- Analytical Performance of Bio-Rad D-100 on a Hemoglobin A1c Assay
- Performance Evaluation of TOSOH Automated Glycohemoglobin Analyzer HLC-723GHb V A1c 2.2TM