Lab Med Online.
2012 Oct;2(4):183-187.
Should I Repeat My 1:2s QC Rejection?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Bio-Rad Laboratories, Quality Systems Division, Plano, TX, USA.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Repeating a QC that is outside 2SD from the mean (1:2s rule) appears to be a common practice. Although this form of repeat-sampling is frowned on by many, the comparative power of the approach has not been formally evaluated.
METHODS
We computed power functions mathematically and by computer simulation for 4 different 1:2s repeat-sampling strategies, as well as the 1:2s rule, the 1:3s rule, and 2 common QC multirules.
RESULTS
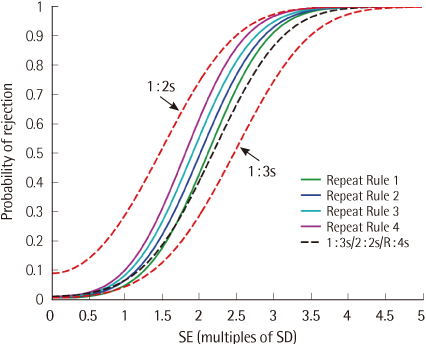
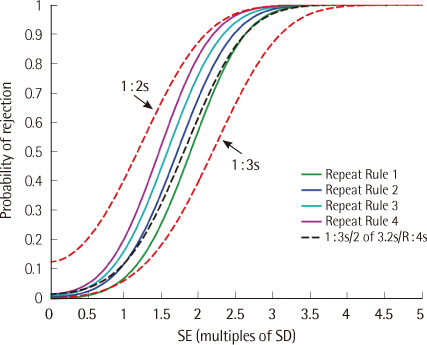
The false-rejection rates for the repeat-sampling strategies were similarly low to those of the 1:3s QC rule. The error detection rates for the repeat-sampling strategies approached those of the 1:2s QC rule for moderate to large out-of-control error conditions. In most cases, the power of the repeat-sampling strategies was superior to the power of the QC multirules we evaluated. The increase in QC utilization rate ranged from 4% to 13% for the repeat-sampling strategies investigated.
CONCLUSIONS
The repeat-sampling strategies provide an effective tactic to take advantage of the desirable properties of both the 1:2s and 1:3s QC rules. Additionally, the power of the repeat-sampling strategies compares favorably with the power of 2 common QC multirules. These improvements come with a modest increase in the average number of controls tested.
Figure
Reference
-
1. International Organization for Standardization (ISO). ISO 15189. Medical laboratories: particular requirements for quality and competence. 2007. Geneva: ISO.2. Housley D, Kearney E, English E, Smith N, Teal T. Audit of internal quality control practice and processes in the south-east of England and suggested regional standards. Ann Clin Biochem. 2008. 45:135–139.
Article3. Westgard JO. Assuring the right quality right. 2007. Madison (WI): Westgard QC.4. Cembrowski GS, Carey RN. Laboratory quality management: QC & QA. 1989. Chicago: ASCP Press.5. Daudin JJ. Double sampling X_charts. J Qual Technol. 1992. 24:78–87.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Survey and Solutions for the Current Status of Quality Control in Small Hospital Laboratories
- Moving Rate of Positive Patient Results as a Quality Control Tool for High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin T Assays
- Sensitivity and Scoring of AutoPap 300 QC System for Abnormal Cervicovaginal Cytology
- Erratum: Figure Correction: Probiotics as Complementary Treatment for Metabolic Disorders
- Internal Quality Assurance Status of Stool Examination as Assessed by a Questionnaire in Korean Clinical Laboratories