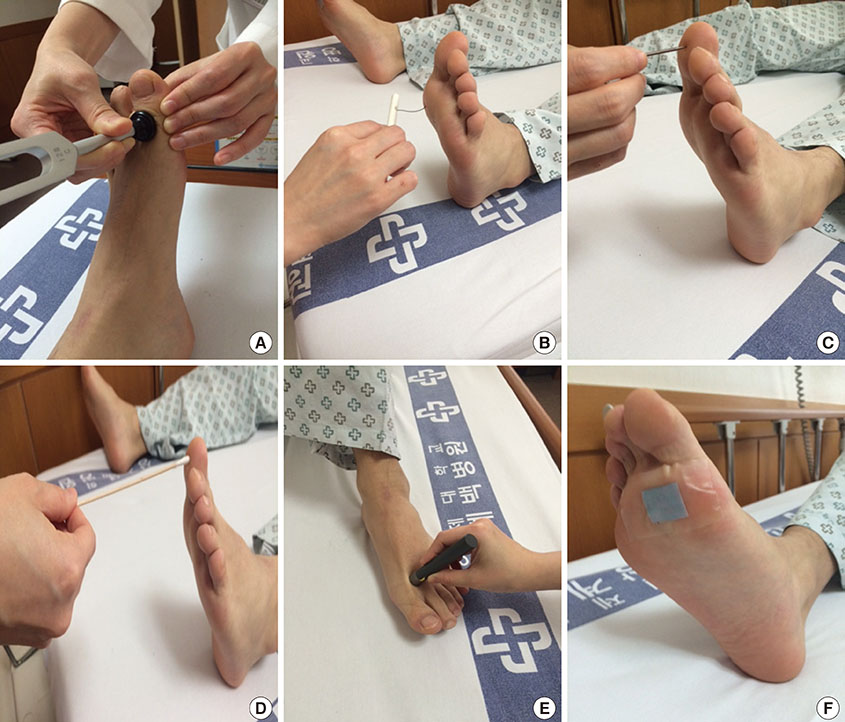
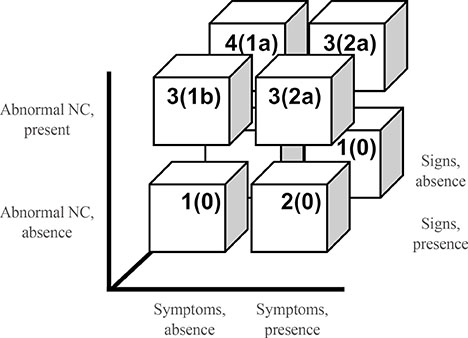
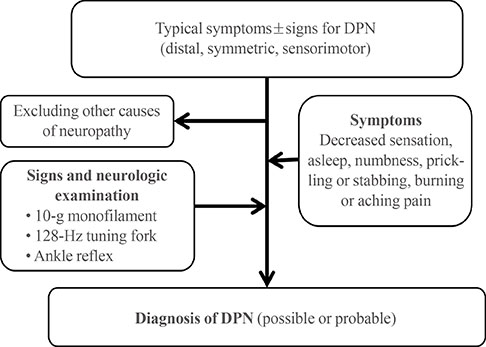
Recent Advances in Diagnostic Strategies for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Center, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drwonjc@gmail.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2308852
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.2.230
Abstract
- Diabetes is an increasing epidemic in Korea, and associated diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is its most common and disabling complication. DPN has an insidious onset and heterogeneous clinical manifestations, making it difficult to detect high-risk patients of DPN. Early diagnosis is recommended and is the key factor for a better prognosis and preventing diabetic foot ulcers, amputation, or disability. However, diagnostic tests for DPN are not clearly established because of the various pathophysiology developing from the nerve injury to clinical manifestations, differences in mechanisms according to the type of diabetes, comorbidities, and the unclear natural history of DPN. Therefore, DPN remains a challenge for physicians to screen, diagnose, follow up, and evaluate for treatment response. In this review, diagnosing DPN using various methods to assess clinical symptoms and/or signs, sensorineural impairment, and nerve conduction studies will be discussed. Clinicians should rely on established modalities and utilize current available testing as complementary to specific clinical situations.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Seong-Su Moon
J Korean Diabetes. 2018;19(3):153-159. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2018.19.3.153.Neurogenic Pain Disorder in the Foot and Ankle: Peripheral Neuropathy
Hak Jun Kim, Young Hwan Park, Soo Hyun Kim
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2017;52(4):305-309. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.4.305.SUDOSCAN in Combination with the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument Is an Effective Tool for Screening Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Tae Jung Oh, Yoojung Song, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):319-326. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0014.The Presence of Clonal Hematopoiesis Is Negatively Associated with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes
Tae Jung Oh, Han Song, Youngil Koh, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):243-248. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.1337.
Reference
-
1. Ha KH, Kim DJ. Trends in the diabetes epidemic in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2015; 30:142–146.2. Won JC, Kwon HS, Kim CH, Lee JH, Park TS, Ko KS, et al. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in hospital patients with type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabet Med. 2012; 29:e290–e296.3. Kim SS, Won JC, Kwon HS, Kim CH, Lee JH, Park TS, et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: results from a nationwide hospital-based study of diabetic neuropathy in Korea. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014; 103:522–529.4. Boulton AJ, Malik RA, Arezzo JC, Sosenko JM. Diabetic somatic neuropathies. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:1458–1486.5. Dyck PJ, Albers JW, Andersen H, Arezzo JC, Biessels GJ, Bril V, et al. Diabetic polyneuropathies: update on research definition, diagnostic criteria and estimation of severity. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2011; 27:620–628.6. Tesfaye S, Boulton AJ, Dyck PJ, Freeman R, Horowitz M, Kempler P, et al. Diabetic neuropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:2285–2293.7. Korean Diabetes Association. Treatment guideline for diabetes. J Korean Diabetes. 2015; 12:S109–S112.8. Gasser HS. The classification of nerve fibers. Ohio J Sci. 1941; 41:145–159.9. Vinik AI, Mehrabyan A. Diabetic neuropathies. Med Clin North Am. 2004; 88:947–999.10. Malik RA, Tesfaye S, Newrick PG, Walker D, Rajbhandari SM, Siddique I, et al. Sural nerve pathology in diabetic patients with minimal but progressive neuropathy. Diabetologia. 2005; 48:578–585.11. Ziegler D, Mayer P, Muhlen H, Gries FA. The natural history of somatosensory and autonomic nerve dysfunction in relation to glycaemic control during the first 5 years after diagnosis of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1991; 34:822–829.12. Selvarajah D, Wilkinson ID, Maxwell M, Davies J, Sankar A, Boland E, et al. Magnetic resonance neuroimaging study of brain structural differences in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:1681–1688.13. Partanen J, Niskanen L, Lehtinen J, Mervaala E, Siitonen O, Uusitupa M. Natural history of peripheral neuropathy in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:89–94.14. Myers MI, Peltier AC. Uses of skin biopsy for sensory and autonomic nerve assessment. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2013; 13:323.15. Callaghan BC, Little AA, Feldman EL, Hughes RA. Enhanced glucose control for preventing and treating diabetic neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 6:CD007543.16. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:977–986.17. Ismail-Beigi F, Craven T, Banerji MA, Basile J, Calles J, Cohen RM, et al. Effect of intensive treatment of hyperglycaemia on microvascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an analysis of the ACCORD randomised trial. Lancet. 2010; 376:419–430.18. Franklin GM, Shetterly SM, Cohen JA, Baxter J, Hamman RF. Risk factors for distal symmetric neuropathy in NIDDM: the San Luis Valley Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care. 1994; 17:1172–1177.19. Maser RE, Steenkiste AR, Dorman JS, Nielsen VK, Bass EB, Manjoo Q, et al. Epidemiological correlates of diabetic neuropathy. Report from Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study. Diabetes. 1989; 38:1456–1461.20. Dyck PJ, Sherman WR, Hallcher LM, Service FJ, O'Brien PC, Grina LA, et al. Human diabetic endoneurial sorbitol, fructose, and myo-inositol related to sural nerve morphometry. Ann Neurol. 1980; 8:590–596.21. Dyck PJ, Karnes J, O'Brien PC, Swanson CJ. Neuropathy symptom profile in health, motor neuron disease, diabetic neuropathy, and amyloidosis. Neurology. 1986; 36:1300–1308.22. Meijer JW, Smit AJ, Sonderen EV, Groothoff JW, Eisma WH, Links TP. Symptom scoring systems to diagnose distal polyneuropathy in diabetes: the Diabetic Neuropathy Symptom score. Diabet Med. 2002; 19:962–965.23. Abbott CA, Vileikyte L, Williamson S, Carrington AL, Boulton AJ. Multicenter study of the incidence of and predictive risk factors for diabetic neuropathic foot ulceration. Diabetes Care. 1998; 21:1071–1075.24. Dyck PJ, Litchy WJ, Lehman KA, Hokanson JL, Low PA, O'Brien PC. Variables influencing neuropathic endpoints: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study of Healthy Subjects. Neurology. 1995; 45:1115–1121.25. Singleton JR, Bixby B, Russell JW, Feldman EL, Peltier A, Goldstein J, et al. The Utah Early Neuropathy Scale: a sensitive clinical scale for early sensory predominant neuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2008; 13:218–227.26. Meijer JW, van Sonderen E, Blaauwwiekel EE, Smit AJ, Groothoff JW, Eisma WH, et al. Diabetic neuropathy examination: a hierarchical scoring system to diagnose distal polyneuropathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000; 23:750–753.27. Davies M, Brophy S, Williams R, Taylor A. The prevalence, severity, and impact of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:1518–1522.28. Feldman EL, Stevens MJ, Thomas PK, Brown MB, Canal N, Greene DA. A practical two-step quantitative clinical and electrophysiological assessment for the diagnosis and staging of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 1994; 17:1281–1289.29. Dyck PJ, Dyck PJ, Larson TS, O'Brien PC, Velosa JA. Patterns of quantitative sensation testing of hypoesthesia and hyperalgesia are predictive of diabetic polyneuropathy: a study of three cohorts. Nerve growth factor study group. Diabetes Care. 2000; 23:510–517.30. Cheng WY, Jiang YD, Chuang LM, Huang CN, Heng LT, Wu HP, et al. Quantitative sensory testing and risk factors of diabetic sensory neuropathy. J Neurol. 1999; 246:394–398.31. Ziegler D, Siekierka-Kleiser E, Meyer B, Schweers M. Validation of a novel screening device (NeuroQuick) for quantitative assessment of small nerve fiber dysfunction as an early feature of diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:1169–1174.32. Viswanathan V, Snehalatha C, Seena R, Ramachandran A. Early recognition of diabetic neuropathy: evaluation of a simple outpatient procedure using thermal perception. Postgrad Med J. 2002; 78:541–542.33. Neuropathy Study group of the Korean Diabetes Association. Management of diabetic neuropathy. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;2011. p. 16–34.34. Papanas N, Papatheodorou K, Papazoglou D, Monastiriotis C, Christakidis D, Maltezos E. A comparison of the new indicator test for sudomotor function (Neuropad) with the vibration perception threshold and the clinical examination in the diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2008; 116:135–138.35. Loeser JD, Treede RD. The Kyoto protocol of IASP Basic Pain Terminology. Pain. 2008; 137:473–477.36. Casellini CM, Parson HK, Richardson MS, Nevoret ML, Vinik AI. Sudoscan, a noninvasive tool for detecting diabetic small fiber neuropathy and autonomic dysfunction. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013; 15:948–953.37. Masson EA, Veves A, Fernando D, Boulton AJ. Current perception thresholds: a new, quick, and reproducible method for the assessment of peripheral neuropathy in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1989; 32:724–728.38. Dyck PJ, Thomas PK. Chapter 35, Nerve conduction and needle electromyography. Peripheral neuropathy. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;2005. p. 899–969.39. Dyck PJ, Davies JL, Litchy WJ, O'Brien PC. Longitudinal assessment of diabetic polyneuropathy using a composite score in the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study cohort. Neurology. 1997; 49:229–239.40. England JD, Gronseth GS, Franklin G, Miller RG, Asbury AK, Carter GT, et al. Distal symmetric polyneuropathy: a definition for clinical research: report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2005; 64:199–207.41. Dyck PJ, Lais A, Karnes JL, O'Brien P, Rizza R. Fiber loss is primary and multifocal in sural nerves in diabetic polyneuropathy. Ann Neurol. 1986; 19:425–439.42. Behse F, Buchthal F, Carlsen F. Nerve biopsy and conduction studies in diabetic neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977; 40:1072–1082.43. Dyck PJ, Carter RE, Litchy WJ. Modeling nerve conduction criteria for diagnosis of diabetic polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2011; 44:340–345.44. Breiner A, Lovblom LE, Perkins BA, Bril V. Does the prevailing hypothesis that small-fiber dysfunction precedes large-fiber dysfunction apply to type 1 diabetic patients? Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:1418–1424.45. Sumner CJ, Sheth S, Griffin JW, Cornblath DR, Polydefkis M. The spectrum of neuropathy in diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Neurology. 2003; 60:108–111.46. Hertz P, Bril V, Orszag A, Ahmed A, Ng E, Nwe P, et al. Reproducibility of in vivo corneal confocal microscopy as a novel screening test for early diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy. Diabet Med. 2011; 28:1253–1260.47. Brines M, Dunne AN, van Velzen M, Proto PL, Ostenson CG, Kirk RI, et al. ARA 290, a nonerythropoietic peptide engineered from erythropoietin, improves metabolic control and neuropathic symptoms in patients with type 2 diabetes. Mol Med. 2015; 20:658–666.48. Lauria G, Hsieh ST, Johansson O, Kennedy WR, Leger JM, Mellgren SI, et al. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on the use of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy. Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society. Eur J Neurol. 2010; 17:903–912. e44–e49.49. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2006. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:Suppl 1. S4–S42.