Kosin Med J.
2015 Jun;30(1):29-39. 10.7180/kmj.2015.30.1.29.
Therapeutic comparison of Surgery combined with chemotherapy and chemotherapy alone for Primary Gastrointestinal Lymphoma: A single center study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Kosin University, Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea. hs3667@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2308535
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2015.30.1.29
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
There is still no consensus on the optimal treatment for primary gastrointestinal lymphoma (PGIL). The aim of this study was to compare surgery combined with chemotherapy and chemotherapy alone in PGIL.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed and analyzed the treatment outcomes of 107 patients with primary gastrointestinal lymphoma diagnosed between March 1999 and December 2009 at Kosin University Gospel Hospital. Patients were divided into two groups: 35 patients who underwent surgery combined with chemotherapy (group A) and 72 patients who were treated with chemotherapy alone (group B). And we analyzed prognostic factors associated with short survival.
RESULTS
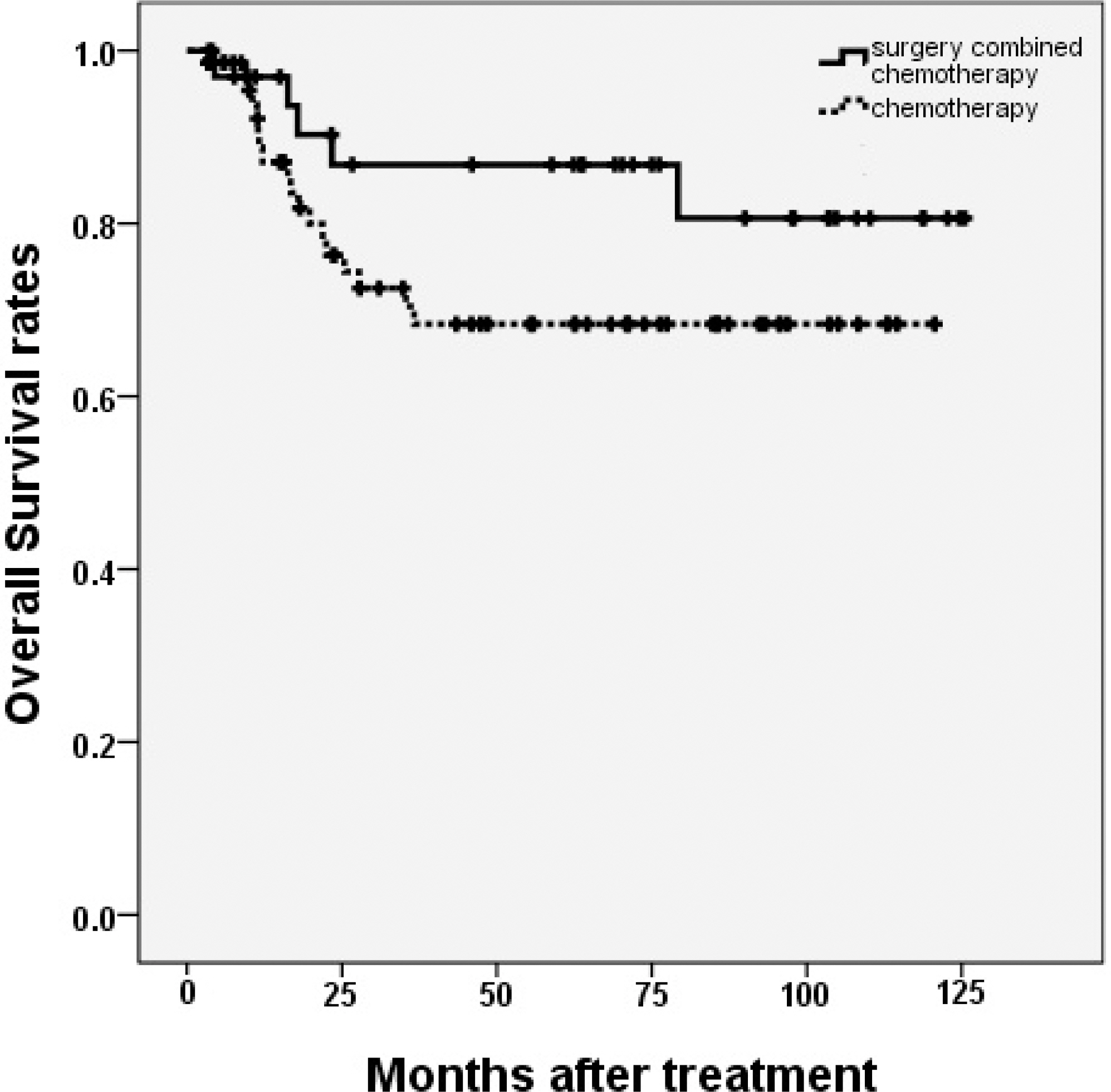
The 5-year progression free survival rates (PFS) of group A and B were 86.7% and 66.1%, respectively (P = 0.037), while the 5-year overall survival rates (OS) were 86.8% and 68.4%, respectively (P = 0.129). In multivariate analysis, Both PFS and OS were not changed by treatment strategies (surgery combined with chemotherapy or chemotherapy only). The international prognostic index (IPI) was the only independent predictive factor for PFS.
CONCLUSIONS
In our study, surgery combined with chemotherapy and chemotherapy only make no difference of survival rate. And further randomized prospective studies are needed to confirm a treatment strategies at improving survival outcomes in PGIL patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. LEE YJ, Lee JH. Gastrointestinal lymphoma, Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 2012; 12:158–65.2. d'Amore F, Brincker H, Gr⊘nbaek K, Thorling K, Pedersen M, Jensen MK, et al. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the gastrointestinal tract: a population-based analysis of incidence, geographic distribution, clinicopathologic presentation features, and prognosis. Danish Lymphoma Study Group, J Clin Oncol. 1994; 12:1673–84.3. Koch P, del Valle F, Berdel WE, Willich NA, Reers B, Hiddemann W, et al. Primary gastrointestinal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: I. Anatomic and histologic distribution, clinical features, and survival data of 371 patients registered in the German Multicenter Study, J Clin Oncol. 2001; 19:3861–73.4. Psyrri A, Papageorgiou S, Economopoulos T. Primary extranodal lymphomas of stomach: clinical presentation, diagnostic pitfalls and management, Ann Oncol. 2008; 19:1992–9.5. Kim JM, Ko YH, Lee SS, Huh J, Kang CS, Kim CW, et al. WHO classification of malignant lymphomas in Korea: report of the third nationwide study, Korean J Pathol. 2011; 45:254–60.6. Wündisch T, Thiede C, Morgner A, Dempfle A, Günther A, Liu H, et al. Long-term follow-up of gastric MALT lymphoma after Helicobacter pylori eradication. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:8018–24.
Article7. Wündisch T, Mösch C, Neubauer A, Stolte M. Helicobacter pylori eradication in gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: Results of a 196-patient series, Leuk Lymphoma. 2006; 47:2110–4.8. Koch P, Probst A, Berdel WE, Willich NA, Reinartz G, Brockmann J, et al. Treatment Results in Localized Primary Gastric Lymphoma: Data of Patients Registered Within the German Multicenter Study(GIT NHL 02/96). J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:7050–9.9. Binn M, Ruskone-Fourmestraux A, Lepage E, Haio-un C, Delmer A. Surgical resection plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone: comparison of two strategies to treat diffuse large B-cell gastric lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2003; 14:1751–7.
Article10. Jezers ek Novakovic B, Vovk M, Juznicsetina T. A single-center study of treatment outcomes and survival in patients with primary gastric lymphomas between 1990 and 2003. Ann Hematol. 2006; 85:849–56.
Article11. Avilés A, Nambo MJ, Neri N, Talavera A, Cleto S. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma of the stomach: results of a controlled clinical trial. Med Oncol. 2005; 22:57–62.
Article12. Medina-Franco H, Germes SS, Maldonado CL. Prognostic factors in primary gastric lymphoma, Ann Surg Oncol. 2007; 14:2239–45.13. Kim SJ, Kang HJ, Kim JS, Oh SY, Choi CW, Lee SI, et al. Comparison of treatment strategies for patients with intestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: surgical resection followed by chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone. Blood. 2011; 117:1958–65.
Article14. Cirocchi R, Farinella E, Trastulli S, Cavaliere D, Covarelli P, Listorti C, et al, Surgical treatment of primary gastrointestinal lymphoma. World J Surg Oncol. 2011; 9:145.15. Lee J, Kim WS, Kim K, Ahn JS, Jung CW, Lim HY, et al. Prospective clinical study of surgical resection followed by CHOP in localized intestinal diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Leuk Res. 2007; 31:359–64.
Article16. Zinzani PL, Magagnoli M, Pagliani G, Bendandi M, Gherlinzoni F, Merla E, et al. Primary intestinal lymphoma: clinical and therapeutic features of 32 patients. Haematologica. 1997; 82:305–8.17. Cheung MC, Housri N, Ogilvie MP, Sola JE, Koniaris LG. Surgery does not adversely affect survival in primary gastrointestinal lymphoma. J Surg Oncol. 2009; 100:59–64.
Article18. Beaton C, Davies M, Beynon J. The management of primary small bowel and colon lymphoma―a review. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2012; 27:555–63.
Article19. Lee J, Kim WS, Kim K, Ko YH, Kim JJ, Kim YH, et al. Intestinal lymphoma: exploration of the prognostic factors and the optimal treatment. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004; 45:339–44.
Article20. Daum S, Ullrich R, Heise W, Dederke B, Foss HD, Stein H, et al. Intestinal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a multicenter prospective clinical study from the German Study Group on Intestinal non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:2740–6.
Article21. Azab MB, Henry-Amar M, Rougier P, Bognel C, Theodore C, Carde P, et al. Prognostic factors in primary gastrointestinal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. A multivariate analysis, report of 106 cases, and review of the literature. Cancer. 1989; 64:1208–17.
Article22. Gou HF, Zang J, Jiang M, Yang Y, Cao D, Chen XC. Clinical prognostic analysis of 116 patients with primary intestinal non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Med Oncol. 2012; 29:227–34.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment Results and Prognostic Factors in Localized Gastrointestinal Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
- Intestinal Perforation in a Case of Peripheral T Cell Lymphoma after Initiation of Chemotherapy
- Comparison study of interferon-a combined chemotherapy versus chemotherapy only in patients with invasive uterine cervical cancer
- Therapeutic Comparison of Chemotherapy and Surgery for Early Stage Diffuse Large B-cell Gastric Lymphoma
- Discrepant Bowel Perforation from a Primary Lesion after Chemotherapy of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma