Kosin Med J.
2012 Dec;27(2):181-184. 10.7180/kmj.2012.27.2.181.
A Case of Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis Misdiagnosed as Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Gyeonggi, Korea. panic1216@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2308529
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2012.27.2.181
Abstract
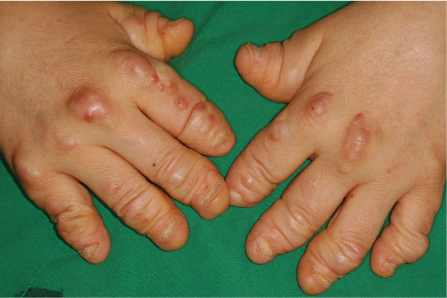
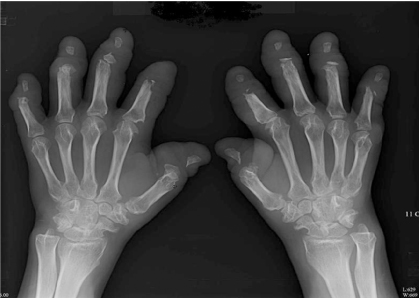
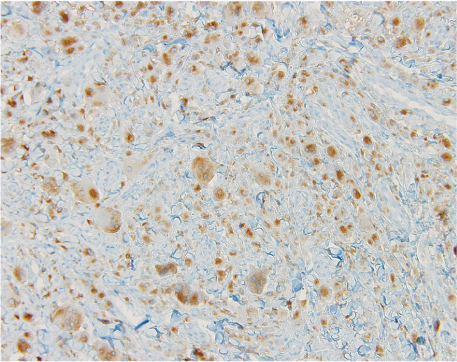
- Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (MRH) is a rare disease characterized by nodular skin lesions and severe erosive polyarthritis which is associated with malignancy in some cases. The diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of oncocytic histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells on histopathology of the cutaneous nodules and the synovial membrane. It usually remits spontaneously after 5-8 years but it can provoke destructive arthritis. We report a case of a 49-year-old female who presented with numerous nodules on the both hands, face and abdomen and progressive destructive polyarthritis of 3 years duration and has been diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. The lesion showed large histiocytes with ground-glass eosinophilic cytoplasm, typical of MRH. Clinical manifestation and radiological pattern of MRH may be misdiagnosed as other disease like rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis, but histopathologic findings of our case can differentiate MRH from any other conditions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goltz RW, Laymon CW. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis of the skin and synovia; reticulohistiocytoma or ganglioneuroma. AMA Arch Derm Syphilol. 1954. 69:717–731.
Article2. Nunnink JC, Krusinski PA, Yates JW. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis and cancer: a case report and review of the literature. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1985. 13:273–279.
Article3. Takahashi M, Mizutani H, nakamura Y, Shimizu M. A case of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis, systemic sclerosis, and Sjögren's syndrome. J Dermatol. 1997. 24:530–534.
Article4. Gelmetti C, Caputo R, Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 2008. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;1424–1432.5. Chnn YW, Kim BS, Koh WS, Park JN, Choi HC, Kim BO, Choe HJ. A Case of Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis. Korean J Dermatol. 1999. 37:912–916.6. Kang JH, Lee CW, Sung YK, Bae SC. A case of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. Korean J Dermatol. 2005. 43:672–674.7. Kwon OE, Song KH, Kim HS, Kim DC, Kim KH. A case of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis misdiagnosed as rheumatoid arthritis. Korean J Dermatol. 2005. 43:81–85.8. Lever WF. Reticulohistiocytosis in Histopathology of the skin. 2008. 9th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott;690–691.9. Lambert CM, Nuki G. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis with arthritis and cardiac infiltration: regression following treatment for underlying malignancy. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992. 51:815–817.
Article10. Barrow MV, Holubar K. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: A review of 33 patients. Medicine. 1969. 48:287–305.11. Coupe MO, Whittaker SJ, Thatcher N. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. Br J Dermatol. 1987. 116:245–247.
Article12. Cash JM, Tyree J, Recht M. Severe multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: Disease stabilization achieved with methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine. J Rheumatol. 1997. 24:2250–2253.13. Matejicka C, Morgan GJ, Schlegelmilch JG. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis treated successfully with an anti-tumor necrosis factor agent: comment on the article by Gorman et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:864–866.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Muticentric Reticulohistiocytosis Misdiagnosed As Rheumatoid Arthritis
- A Case of Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis
- A Case of Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis Mistaken as Rheumatoid Arthritis
- A Case of Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis
- Acute Phase of Sero-negative Rheumatoid Arthritis Misdiagnosed as Pyogenic Arthritis: A Case Report