Kosin Med J.
2012 Dec;27(2):167-171. 10.7180/kmj.2012.27.2.167.
A Case of Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis Associated with Transient Thyrotoxicosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Kosin University, Busan, Korea. yschoi@ns.kosinmed.or.kr
- KMID: 2308526
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2012.27.2.167
Abstract
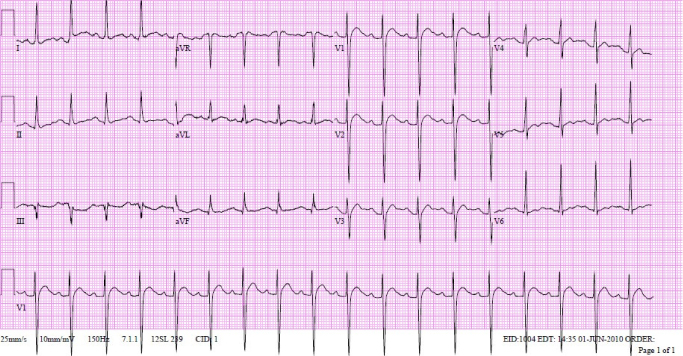
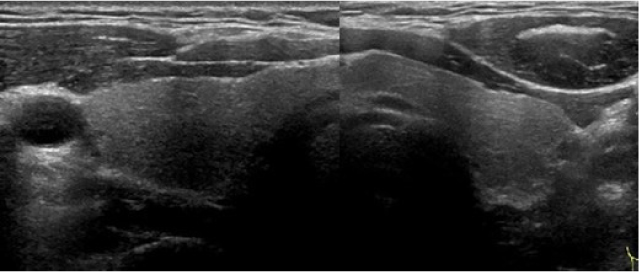
- Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis is an acute muscle weakness of the limbs associated with hypokalemia. It can occur with any form of thyrotoxicosis. Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis associated with transient thyrotoxicosis due to thyroiditis is very rare. We experienced a case of thyrotoxic periodic paralysis associated with transient thyrotoxicosis. A 39-yr-old man was referred to our hospital because of paralysis of upper and lower extremity. The laboratory results were hypokalemia and mild thyrotoxicosis. A thyroid scan with Tc-99m revealed decreased uptake in the thyroid area compatible with destructive thyroiditis. The paralytic attack did not recur after the patient recovered to euthyroid state.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kung AW. Clinical review: Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis: a diagnostic challenge. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006. 91:2490–2495.2. Hsu FS, Tsai WS, Chau T, Chen HH, Chen YC, Lin SH. Thyrotropin-secreting pituitary adenoma presenting as hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Am J Med Sci. 2003. 325:48–50.
Article3. Lee JI, Sohn TS, Son HS, Oh SJ, Kwon HS, Chang SA, et al. Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis presenting as polymorphic ventricular tachycardia induced by painless thyroiditis. Thyroid. 2009. 19:1433–1434.
Article4. Chan A, Shinde R, Chow CC, Cockram CS, Swaminathan R. In vivo and in vitro sodium pump activity in subjects with thyrotoxic periodic paralysis. BMJ. 1991. 303:1096–1099.
Article5. Layzer RB. Periodic paralysis and the sodium-potassium pump. Ann Neurol. 1982. 11:547–552.
Article6. Shishiba Y, Shimizu T, Saito T, Shizuma K. Elevated immunoreactive insulin concentration during spontaneous attacks in thyrotoxic periodic paralysis. Metabolism. 1972. 21:285–290.
Article7. Loh KC, Pinheiro L, Ng KS. Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis complicated by near-fatal ventricular arrhythmias. Singapore Med J. 2005. 46:88–89.8. Manoukian MA, Foote JA, Crapo LM. Clinical and metabolic features of thyrotoxic periodic paralysis in 24 episodes. Arch Intern Med. 1999. 159:601–606.
Article9. Ryan DP, da Silva MR, Soong TW, Fontaine B, Donaldson MR, Kung AW, et al. Mutations in potassium channel Kir2.6 cause susceptibility to thyrotoxic hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Cell. 2010. 140:88–98.
Article10. Hsu YJ, Lin YF, Chau T, Liou JT, Kuo SW, Lin SH. Electrocardiographic manifestations in patients with thyrotoxic periodic paralysis. Am J Med Sci. 2003. 326:128–132.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Thyrotoxic Hypokalemic Periodic Paralysis Presenting as Cardiac Arrest
- A Case Report of Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis; Serial Nerve Conduction Studies before and after Recovery
- A Case of Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis in 17-Year-Old Adolescent
- Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis Associated with Transient Thyrotoxicosis Due to Painless Thyroiditis
- A Case of Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis in a 16-Year-Old Adolescent